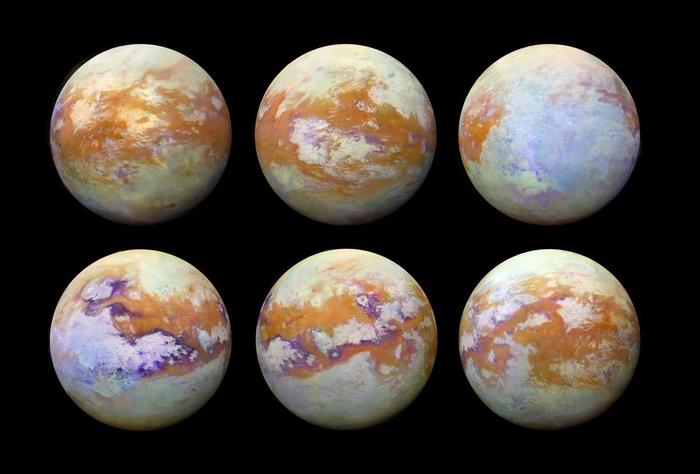

Careful reanalysis of data from more than a decade ago indicates that Saturn’s biggest moon, Titan, does not have a vast ocean beneath its icy surface, as suggested previously.
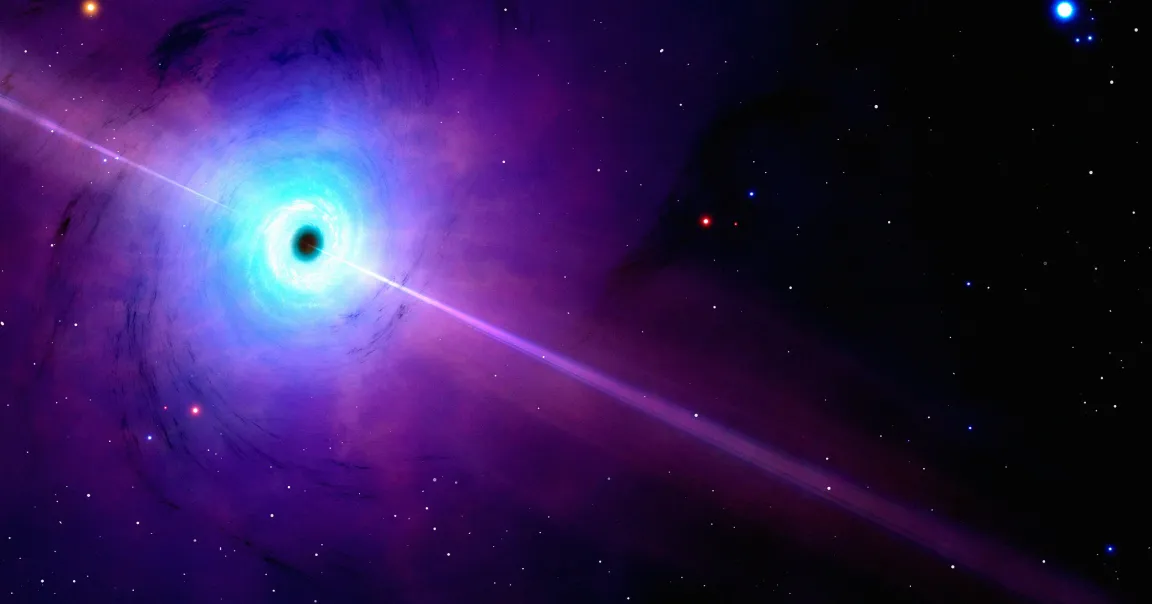

An international team of astronomers claim to have made a baffling discovery with the help of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope: the first runaway supermassive black hole that’s rocketing away from its home at a staggering speed.

Astronomers from the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA) and elsewhere report the discovery of a new brown dwarf about 60 times more massive than Jupiter.

Researchers using the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope have confirmed an actively growing supermassive black hole within a galaxy just 570 million years after the Big Bang.
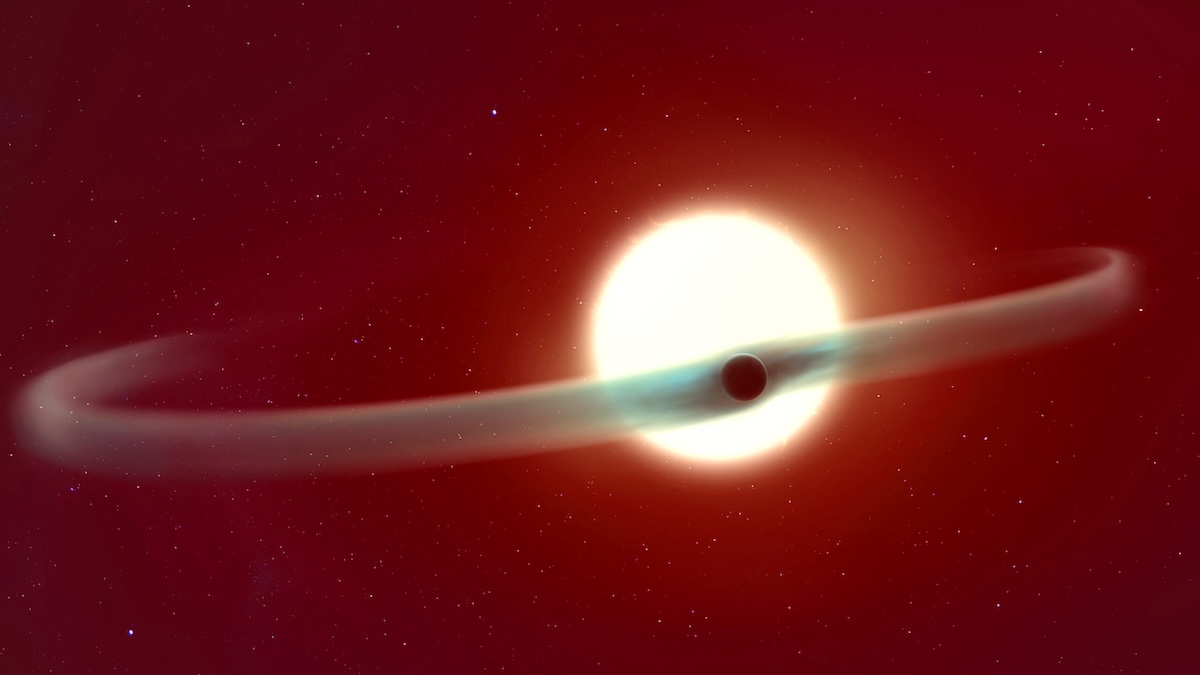

About 880 light-years from Earth, a hot mess of an exoplanet is slowly spilling its atmosphere into space, creating two enormous tails of helium that stretch more than halfway around its star.

A new Swiss-led study uses innovative hybrid modeling to reveal that these planets could just as easily be dominated by rock as by water-rich ices.

Astronomers using the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope have discovered chemical fingerprints of primordial stars weighing between 1,000 and 10,000 times the mass of the Sun in GS 3073,an early galaxy.
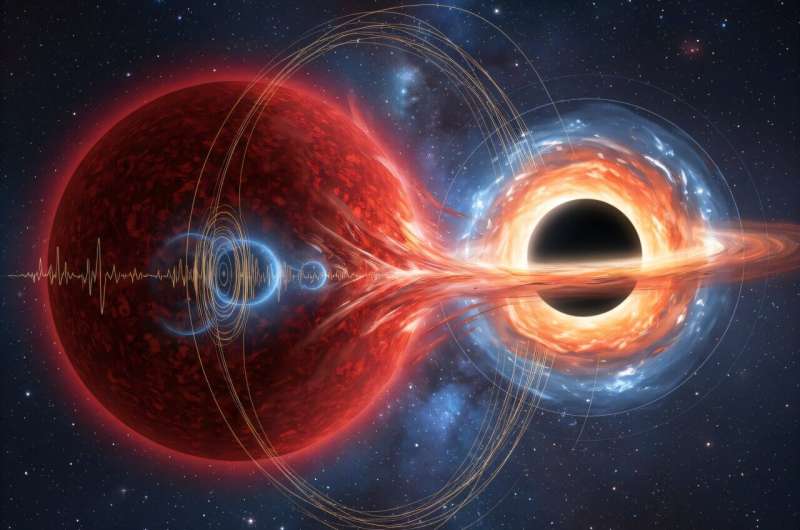
Astronomers from the University of Hawaiʻi Institute for Astronomy (IfA) have uncovered the turbulent past of a distant red giant by listening to its celestial "song."
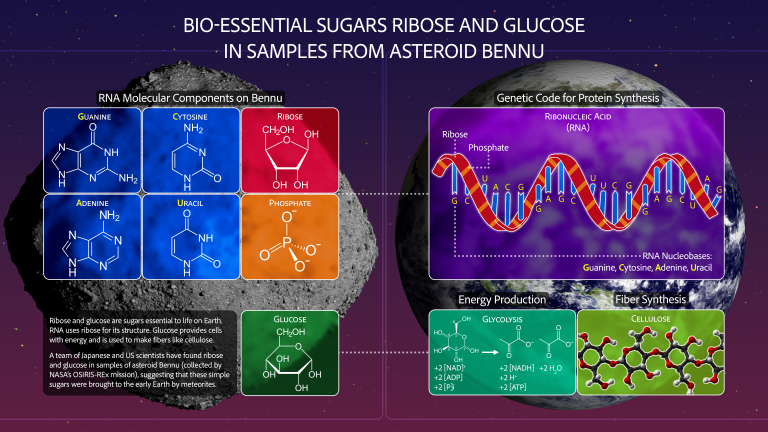
The asteroid Bennu continues to provide new clues to scientists’ biggest questions about the formation of the early solar system and the origins of life.
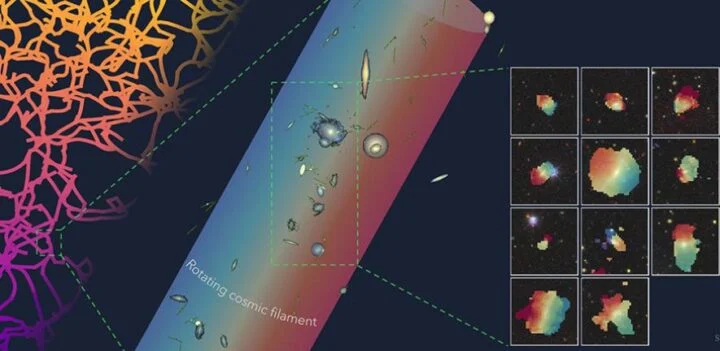
An international team led by the University of Oxford has identified one of the largest rotating structures ever reported: a “razor-thin” string of galaxies embedded in a giant spinning cosmic filament, 140 million light-years away.

Two stars, now located some 400 to 500 light-years from Earth, swung through our neighborhood on their journey through the Milky Way, coming as close as 32 light-years.
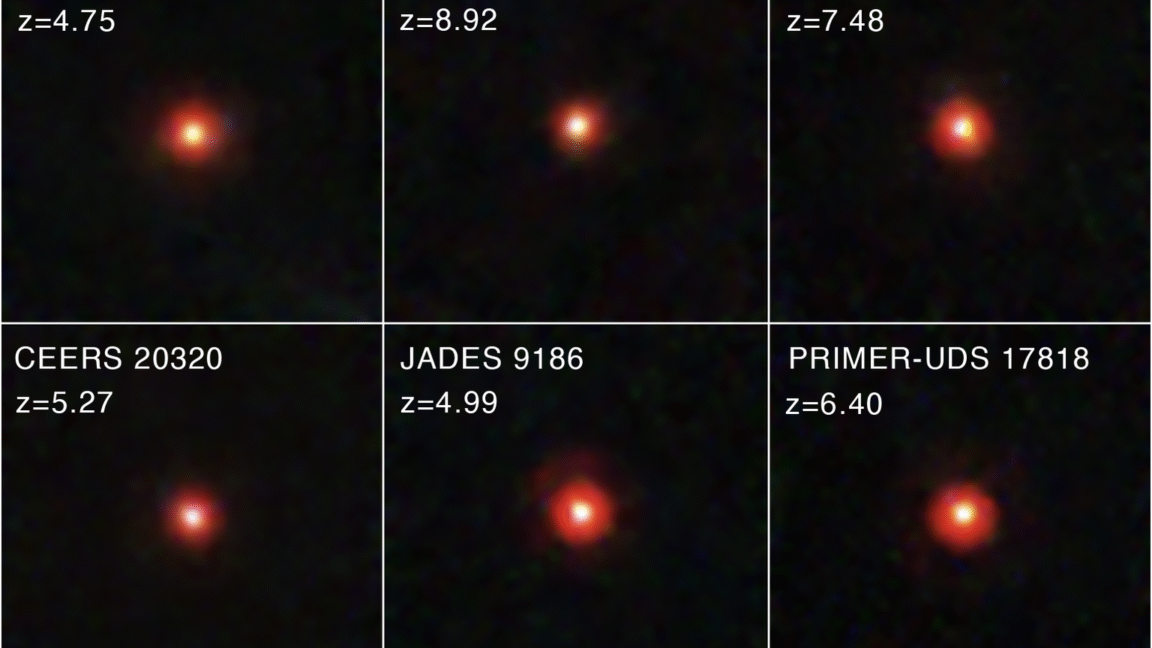

Early superdense star clusters may have planted seeds for monster black holes.
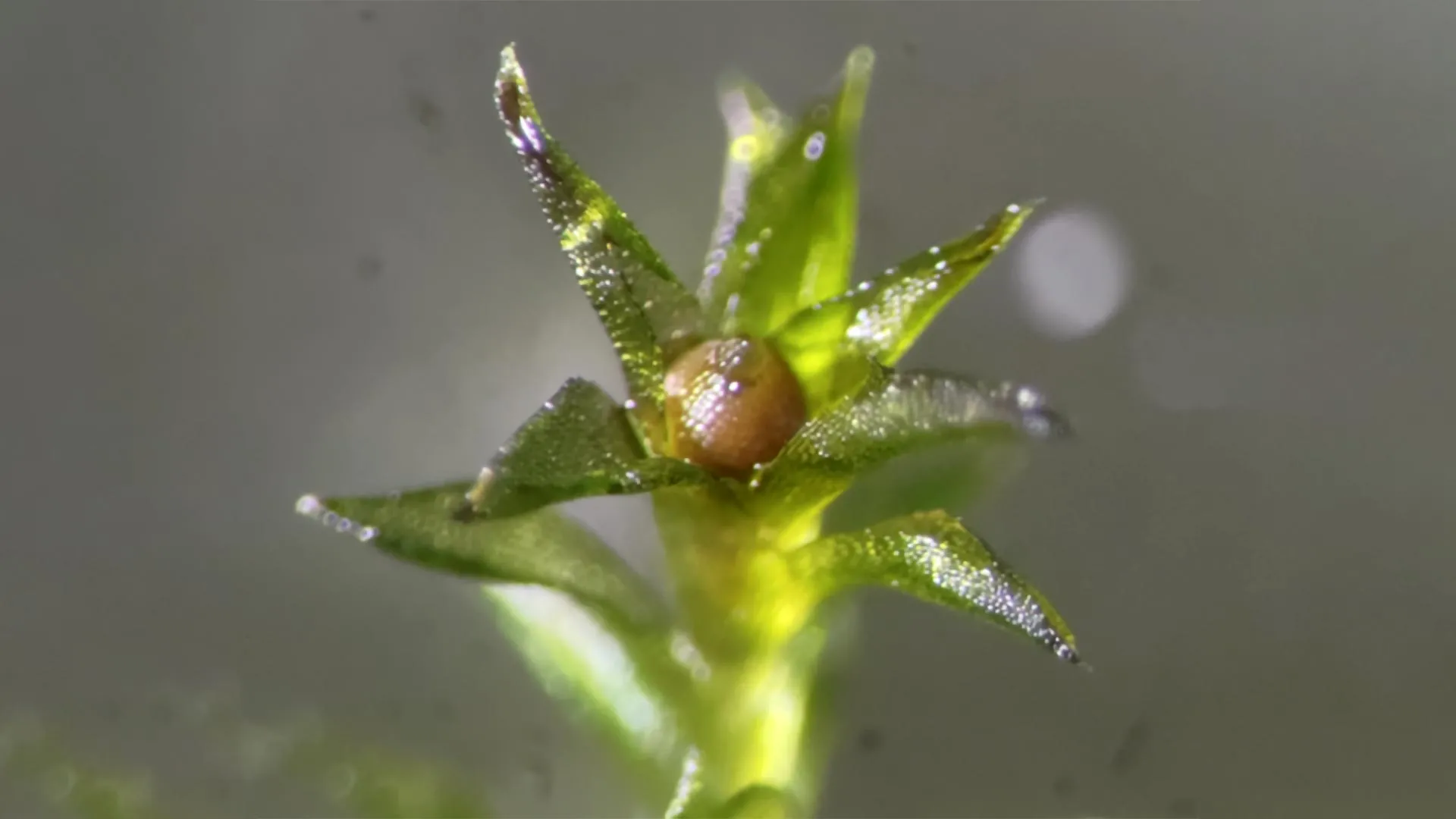

Moss spores survived an extended stay on the outside of the ISS and remained capable of germinating once back on Earth.
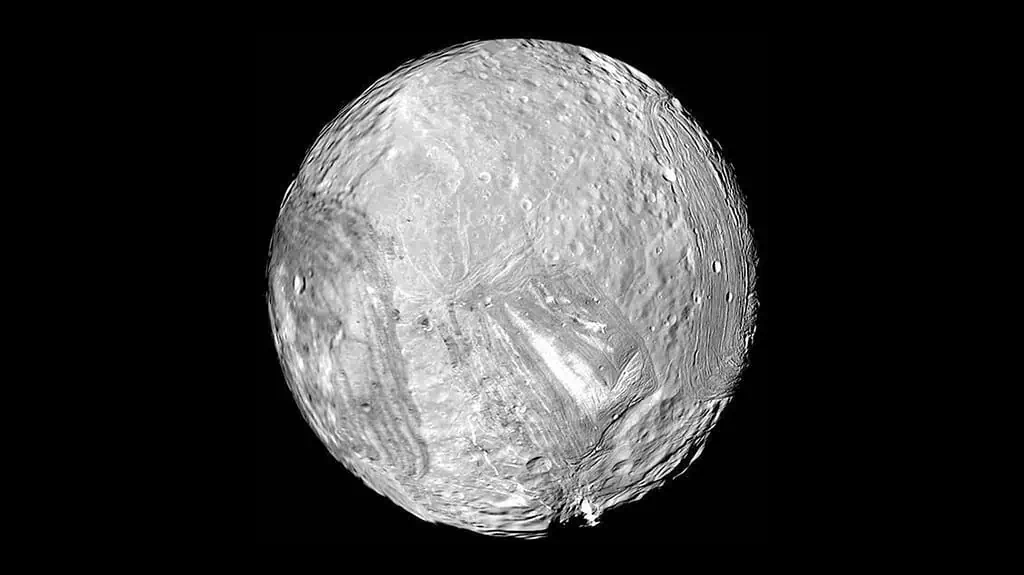
There are several frozen moons in our solar system, orbiting the gas giants. Some of them have liquid water under the surface and deep down in the dark, the ocean may be boiling.
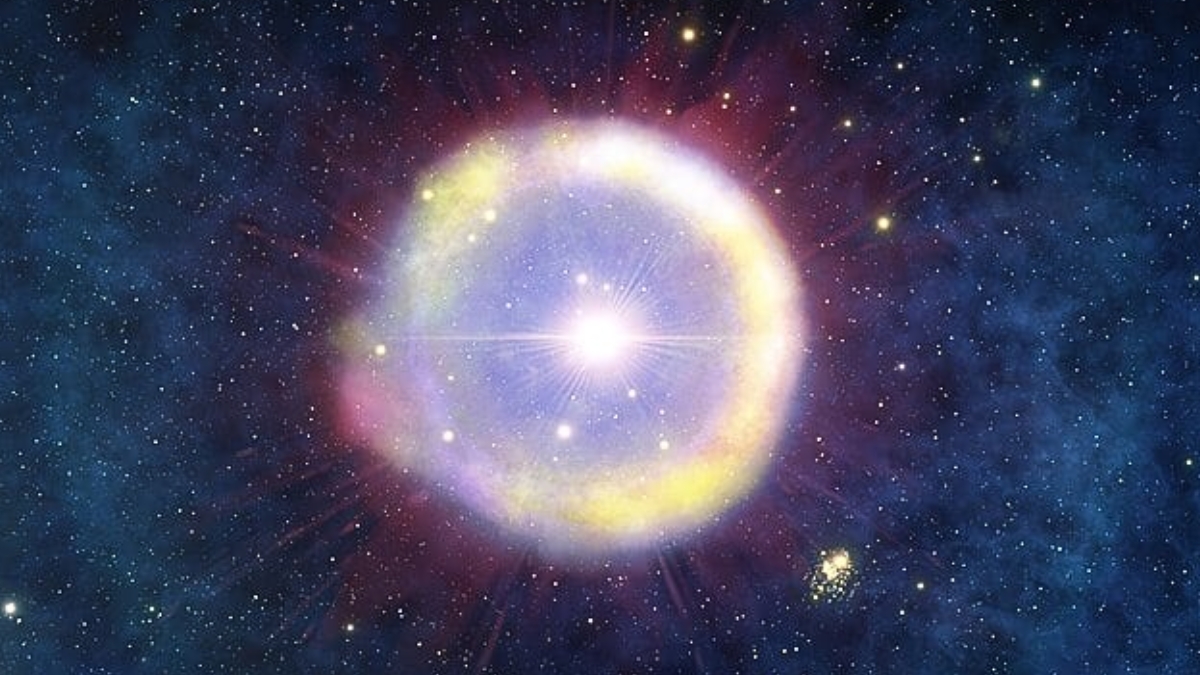

A galaxy formed around 11 billion years ago that appears to be "metal-free", indicating that it might contain a set of elusive first-generation (Pop III) stars.