Once maligned for their psychedelic properties, magic mushrooms are increasingly attracting attention for their same mind-altering potential as a therapy for a wide variety of mental health issues.
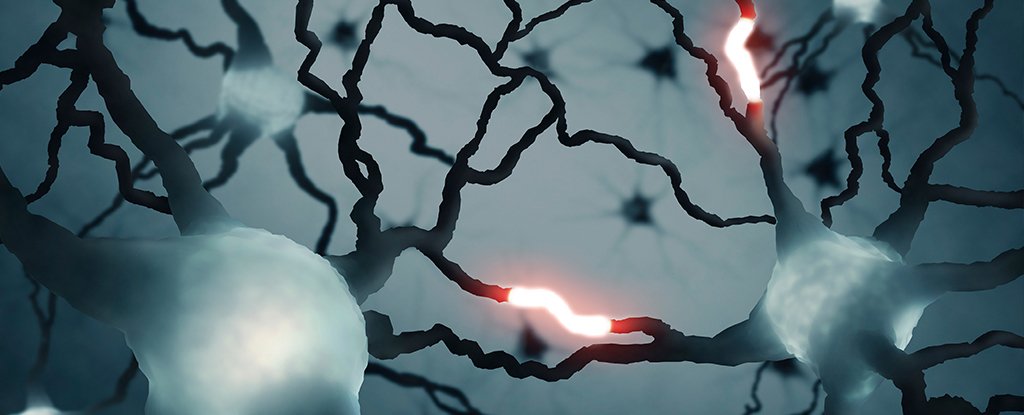

Scientists have identified a unique form of cell messaging occurring in the human brain, revealing just how much we still have to learn about its mysterious inner workings.
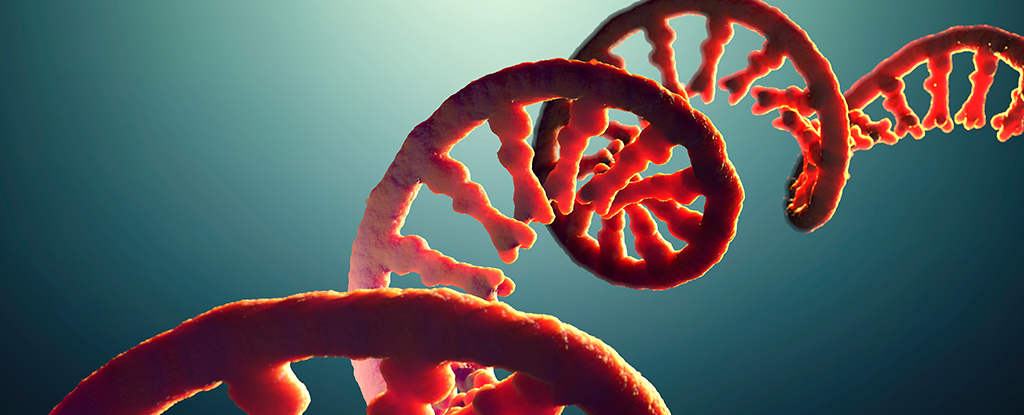

A comparison of post-mortem brain tissue and samples taken from living patients has revealed for the first time significant differences in the way strands of RNA are modified.

Researchers found that time cells in the brain are crucial for learning complex tasks, acting like a personalized time code.
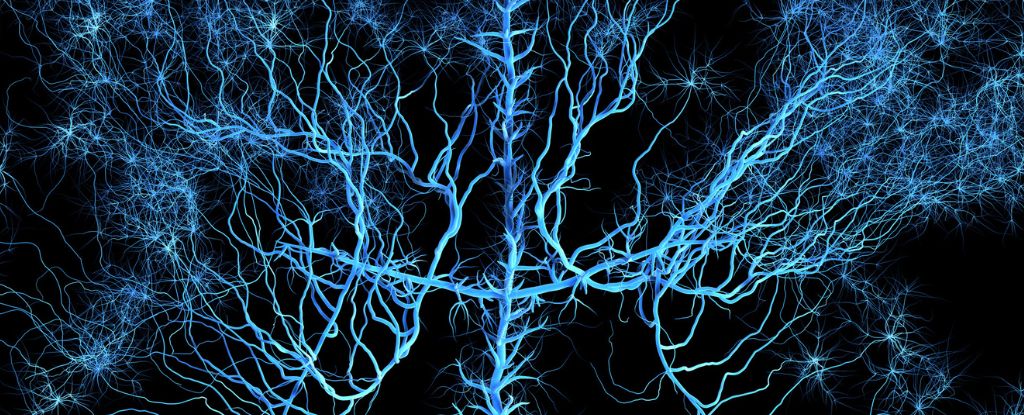
The human brain is said to be the most complex object in the known Universe. Its 89 billion neurons each have around 7,000 connections on average, and the physical structure of all those entities may be balanced precariously on a knife's edge.
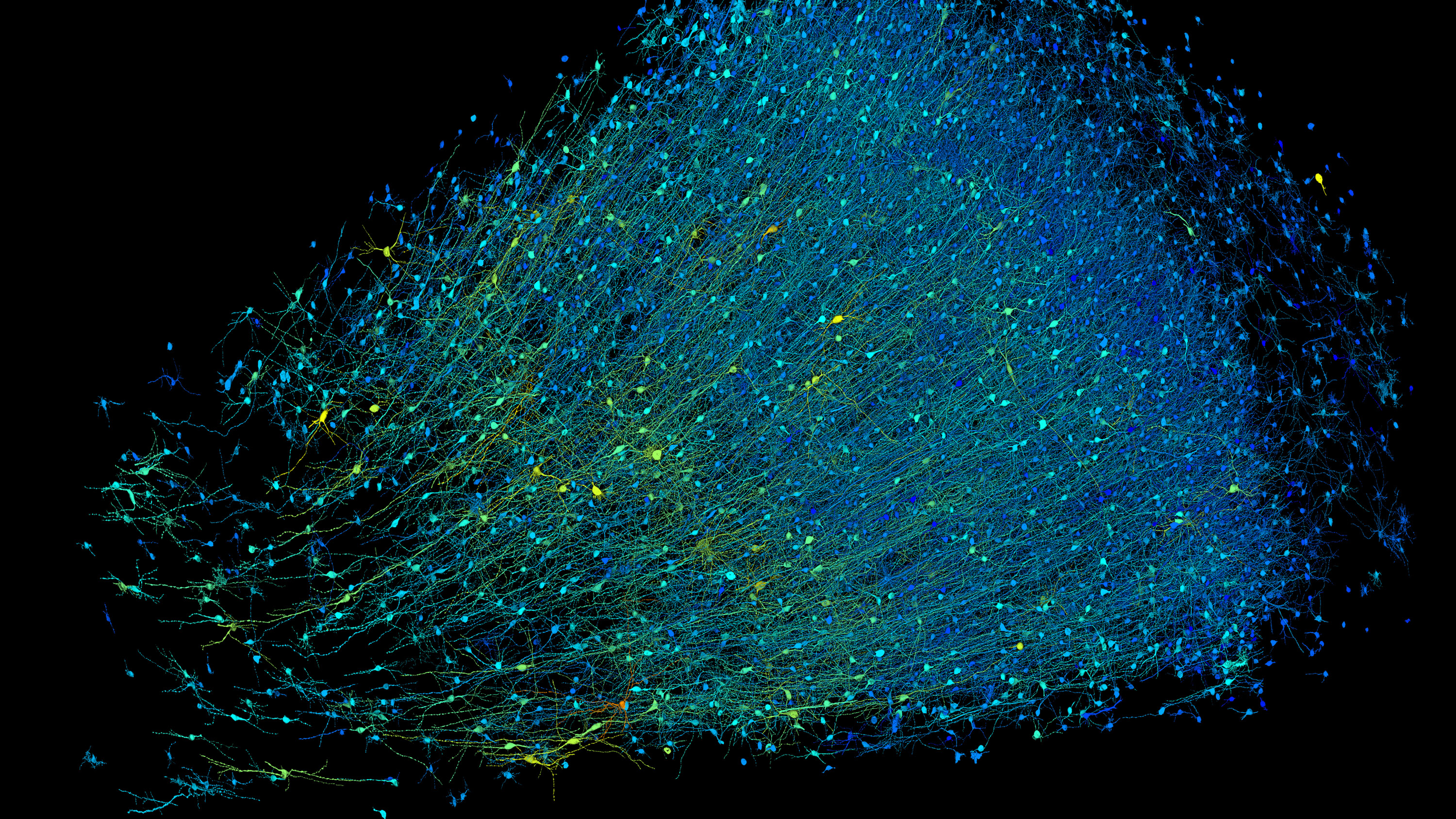
Although the map covers just a fraction of the organ—a whole brain is a million times larger—that piece contains roughly 57,000 cells, about 230 millimeters of blood vessels, and nearly 150 million synapses.

The intermittent energy restriction (IER) diet changes the human brain-gut-microbiome axis. There are highly dynamic changes in the gut microbiome and in the activity in addition-related brain regions during and after the diet.

Researchers have discovered that people born in more recent decades have larger brain volumes compared to those born in earlier decades.

By carefully monitoring neural activity of people who were recalling memories or forming new ones, the researchers managed to detect how a newly appreciated type of brainwave influences the storage and retrieval of memories.

Even small doses of LSD could have therapeutic benefits for mental health and task performance, a new study shows.

Narrowly focused soundwaves aimed at an area of the brain called the insula reduced both the perception of pain and the body’s reaction to it, according to a new study.

Millions of years ago, vertebrates were infected by a virus, which played an important role in the evolution of human beings and the development of brains and human bodies.

Research suggests that 'time cells' – neurons in the hippocampus thought to represent temporal information – could be the glue that sticks our memories together in the right sequence so that we can properly recall the correct order in which things happened.

Mini brains grown in a lab from stem cells spontaneously developed rudimentary eye structures, scientists reported in a fascinating paper in 2021.

A study by evolutionary neuroscientists suggests our minds develop thanks to fermentation. It made food easier to digest and contained more nutrients, facilitating our grey matter’s development.