
As our evolution slows and industrialization and technology accelerates, a growing body of research suggests that human biology is struggling to keep pace.
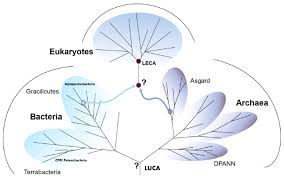
An international collaboration has published groundbreaking research, shedding light on the most significant increase in complexity in the history of life's evolution on Earth: the origin of the eukaryotic cell.

The fact that this bacteria so closely resembles that transition point, from two single cells with different genetics to one inseparable cluster, is fascinating: embryo comparisons have provided many clues about our evolutionary history.
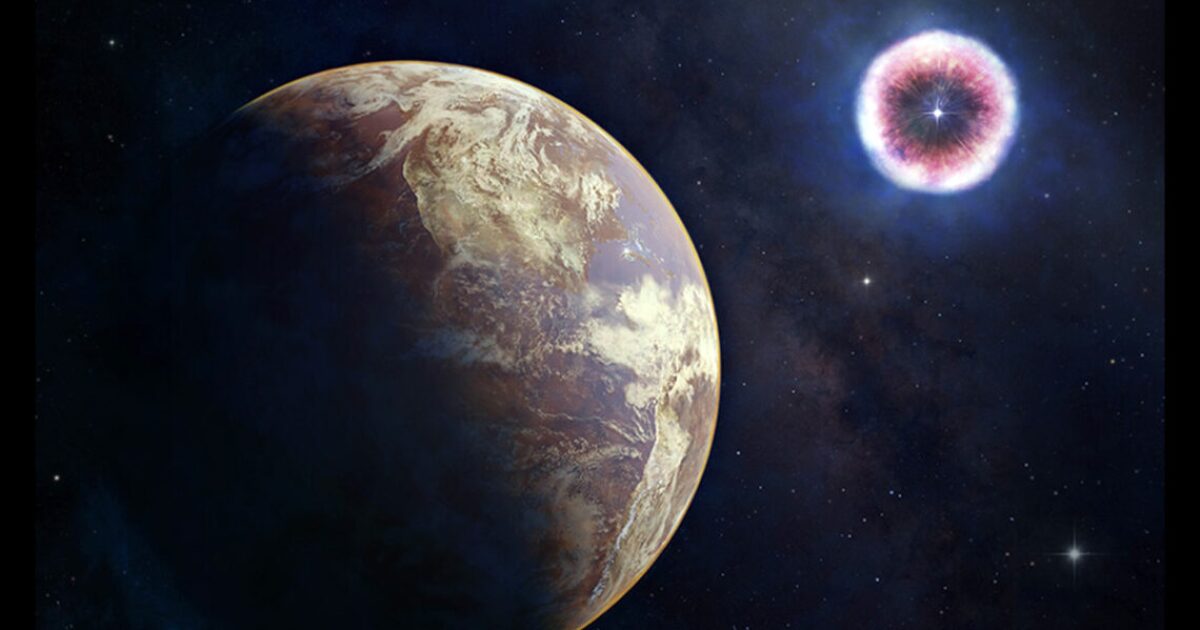

Scientists have traced radioactive elements on the seafloor back to the cosmic explosions they might have come from – and potentially linked the event to evolutionary changes in viruses in a lake in Africa.
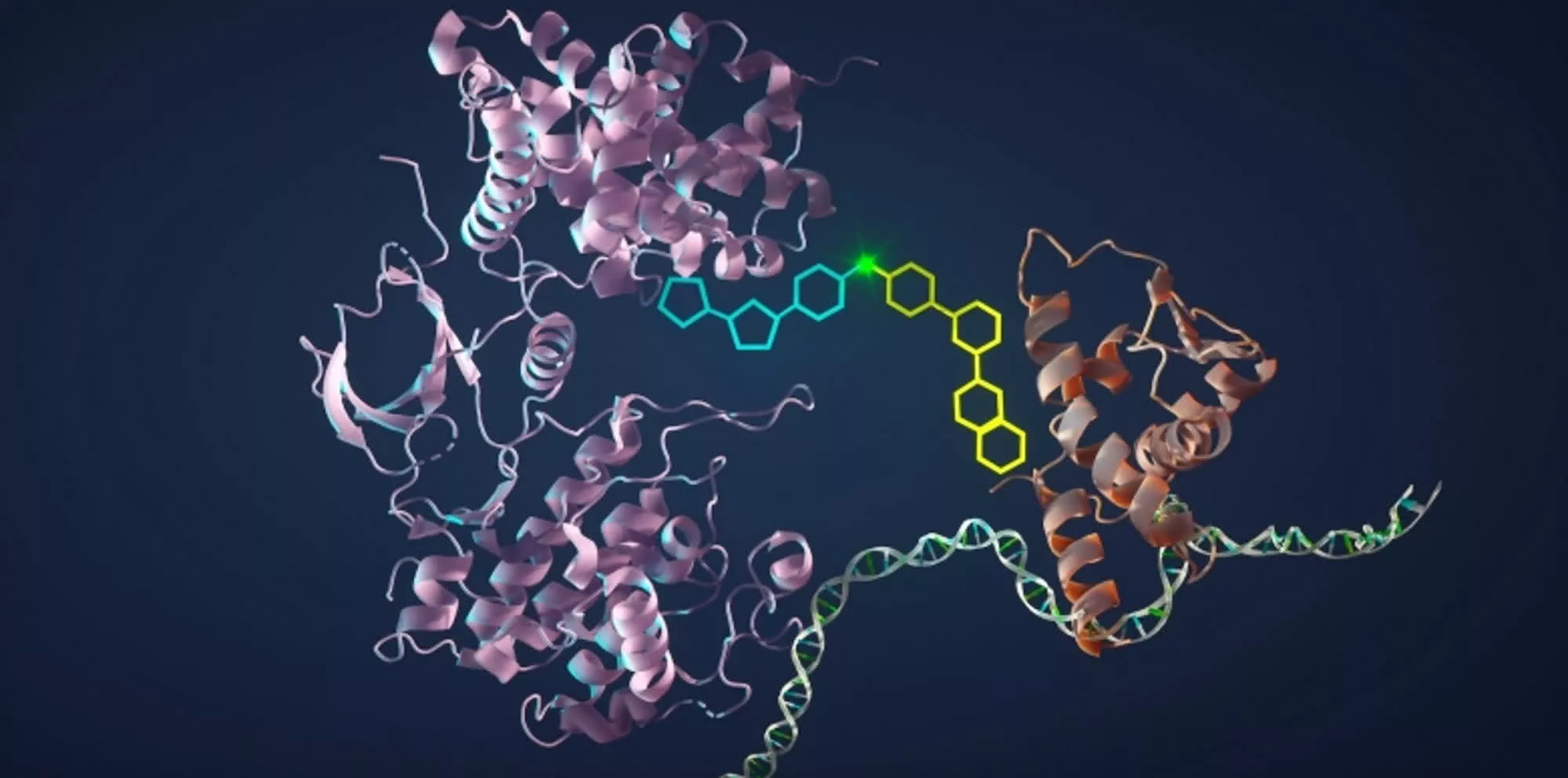
A team of AI researchers, biologists and evolutionary specialists have designed and built an AI model capable of generating the code to synthesize novel proteins.
Fossilized skeletons and shells clearly show how evolution and extinction unfolded over the past half a billion years, but a new analysis extends the chart of life to nearly 2 billion years ago.

A "provocative" new piece in Nature has proposed a whole new group of ancient humans - cousins of the Denisovans and Neanderthals - that once lived alongside Homo sapiens in eastern Asia more than 100,000 years ago.
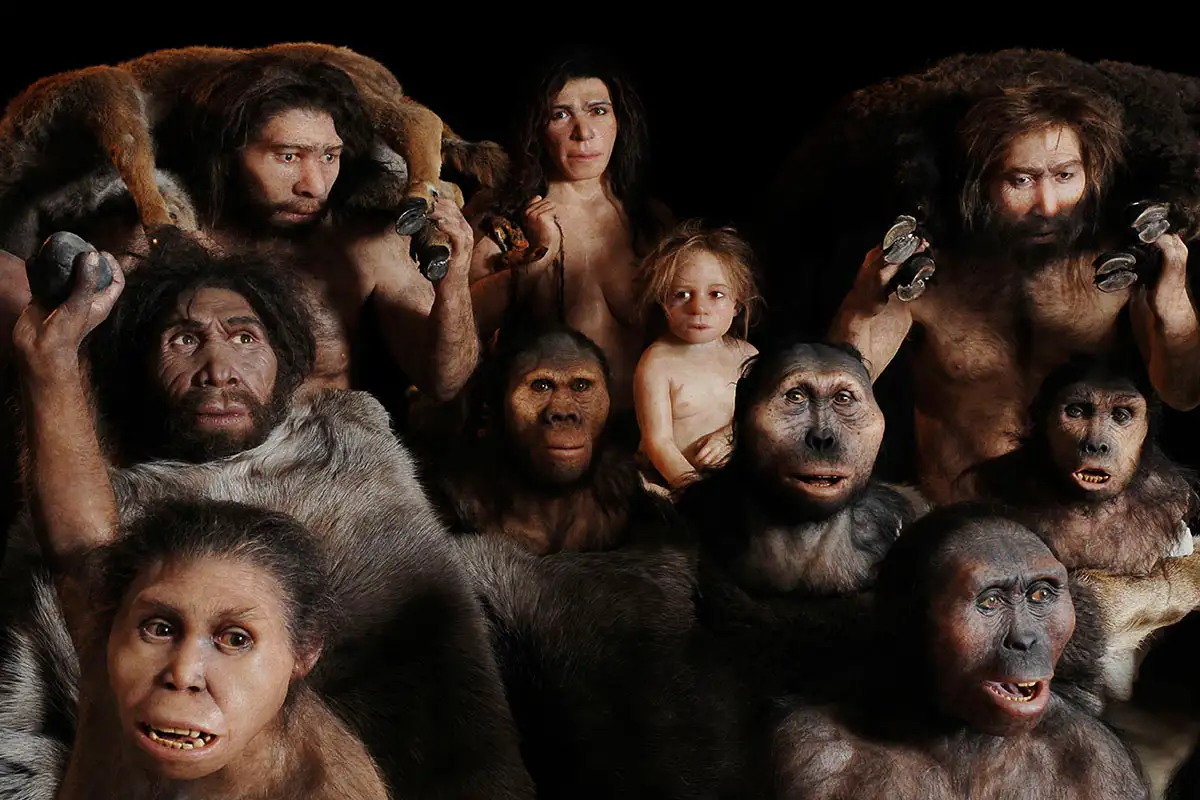

Ancient footprints in Kenya unveiled Homo erectus and Paranthropus boisei coexisting 1.5 million years ago, unlocking fascinating clues about their shared world.

Life on Earth may have developed the ability to form embryos even before it grew the very first animals.

For most of our evolutionary history, human activity has been linked to daylight. Technology has liberated us from these ancient sleep-wake cycles, but there is evidence sunlight has left and continues to leave its mark.
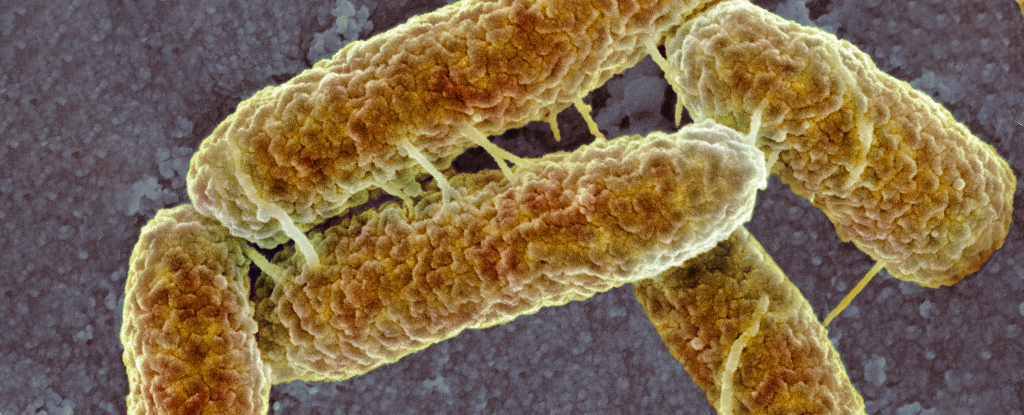
Bacteria can develop a heightened new sensitivity to acid levels when exposed to different environmental extremes in the laboratory, a new study shows.
A new study has found that life on Earth emerged surprisingly early. Scientists have determined that the last universal common ancestor (LUCA), the first organism that spawned all the life that exists today on Earth, emerged as early as 4.2 billion years ago.
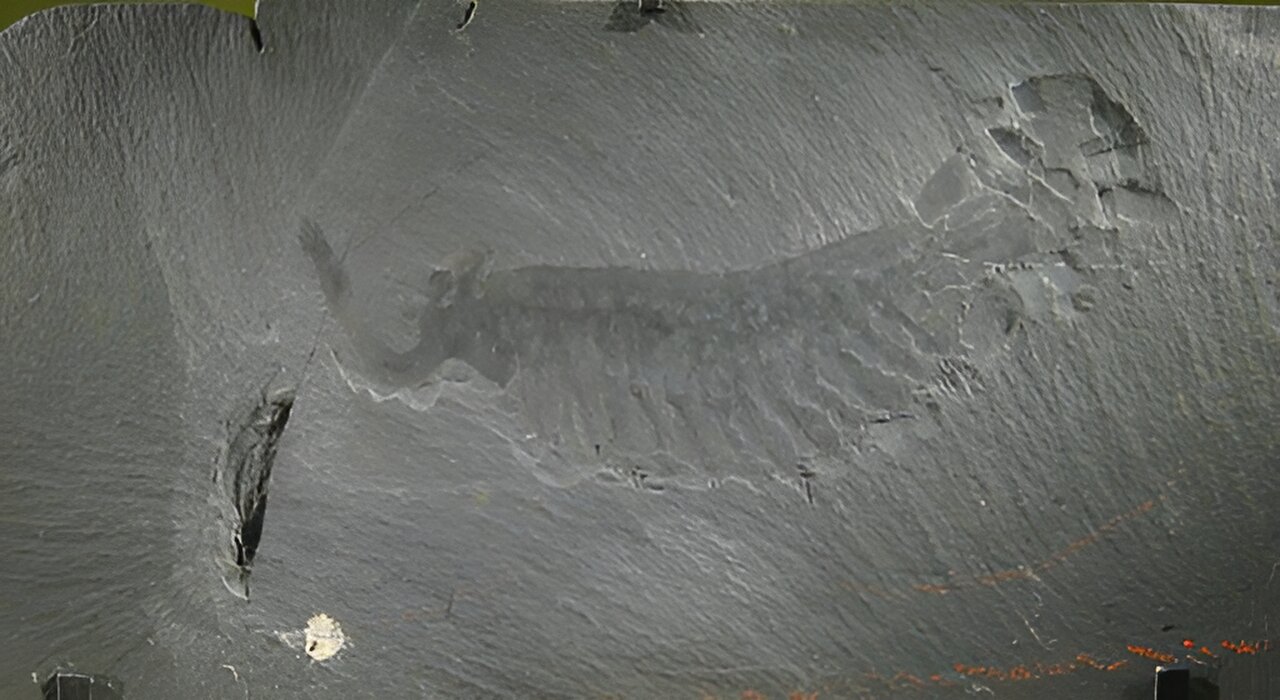

New research provides the clearest evidence yet that the Cambrian explosion - a rapid burst of evolution 540 million years ago, could have been triggered by only a small increase in oxygen levels in Earth's atmosphere and shallow ocean waters.
The Homo sapiens genome today contains a little bit of Neanderthal DNA. These genetic traces come from almost every part of the Neanderthal genome – except the Y sex chromosome, which is responsible for making males.
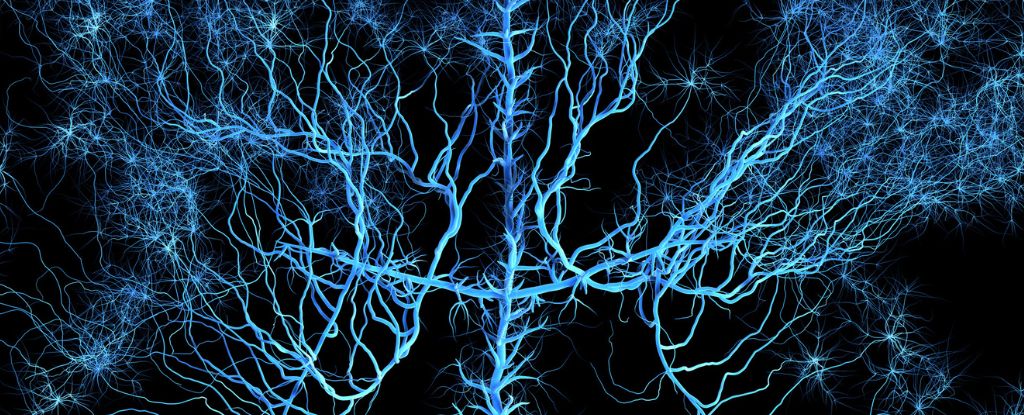
The human brain is said to be the most complex object in the known Universe. Its 89 billion neurons each have around 7,000 connections on average, and the physical structure of all those entities may be balanced precariously on a knife's edge.