
Among several recent findings, the rover has found rocks made of pure sulfur — a first on the Red Planet.
A team of researchers has uncovered evidence of its origins in the atmosphere, where carbon dioxide bathed in ultraviolet sunlight reacted to form a mist of carbon molecules that rained onto the planet's surface.
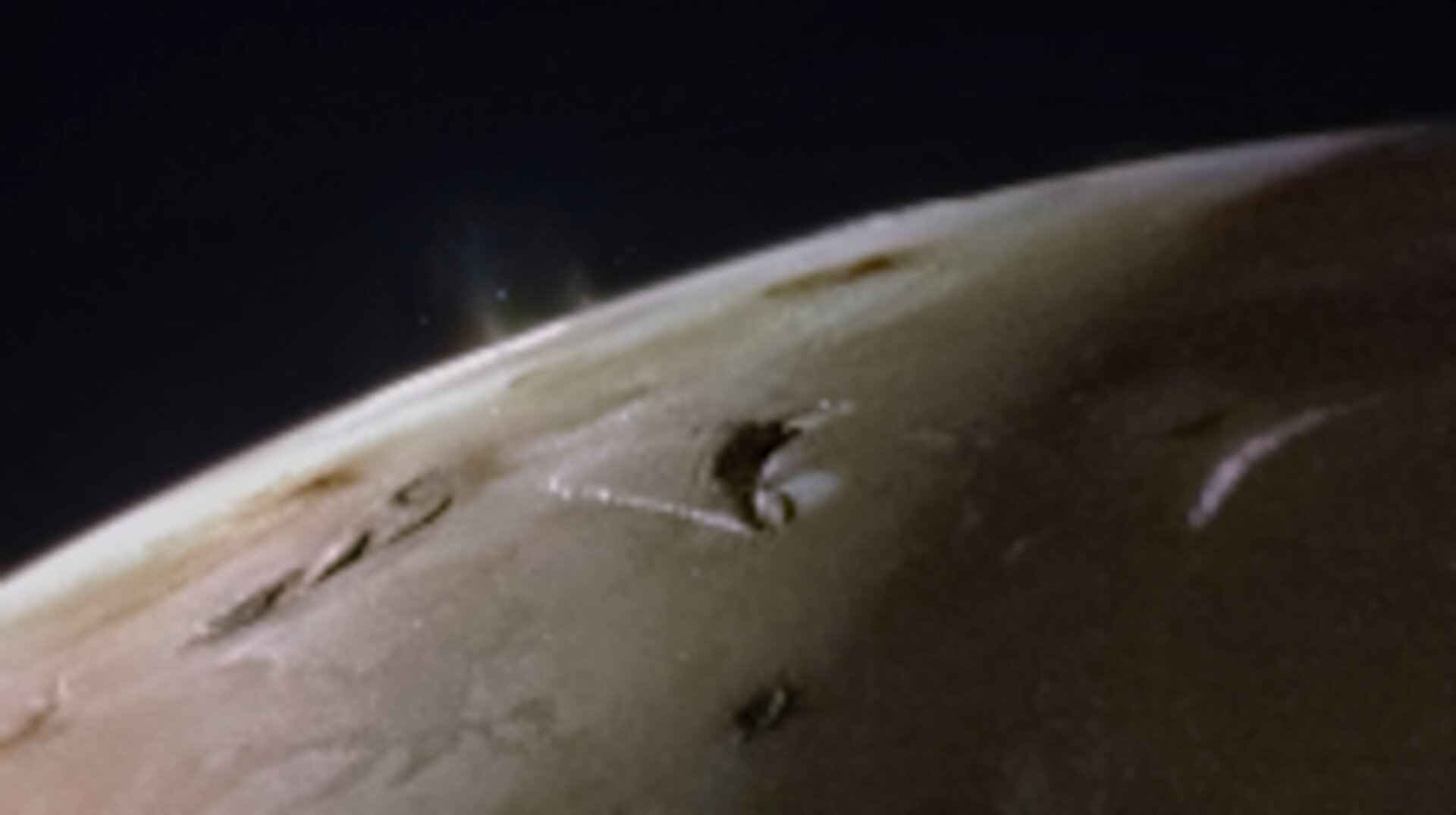

From around 2,400 miles away, the probe’s Jovian Infrared Auroral Mapper (JIRAM) instrument “revealed that the whole surface of Io is covered by lava lakes contained in caldera-like features.

The glow above the Great Red Spot on Jupiter has recently been discovered and the researchers suspect that something else altogether is causing it - powerful gravitational interactions rarely seen on Earth.

An international team of researchers combine orbital imagery with seismological data from NASA’s Mars InSight lander to derive a new impact rate for meteorite strikes on Mars.
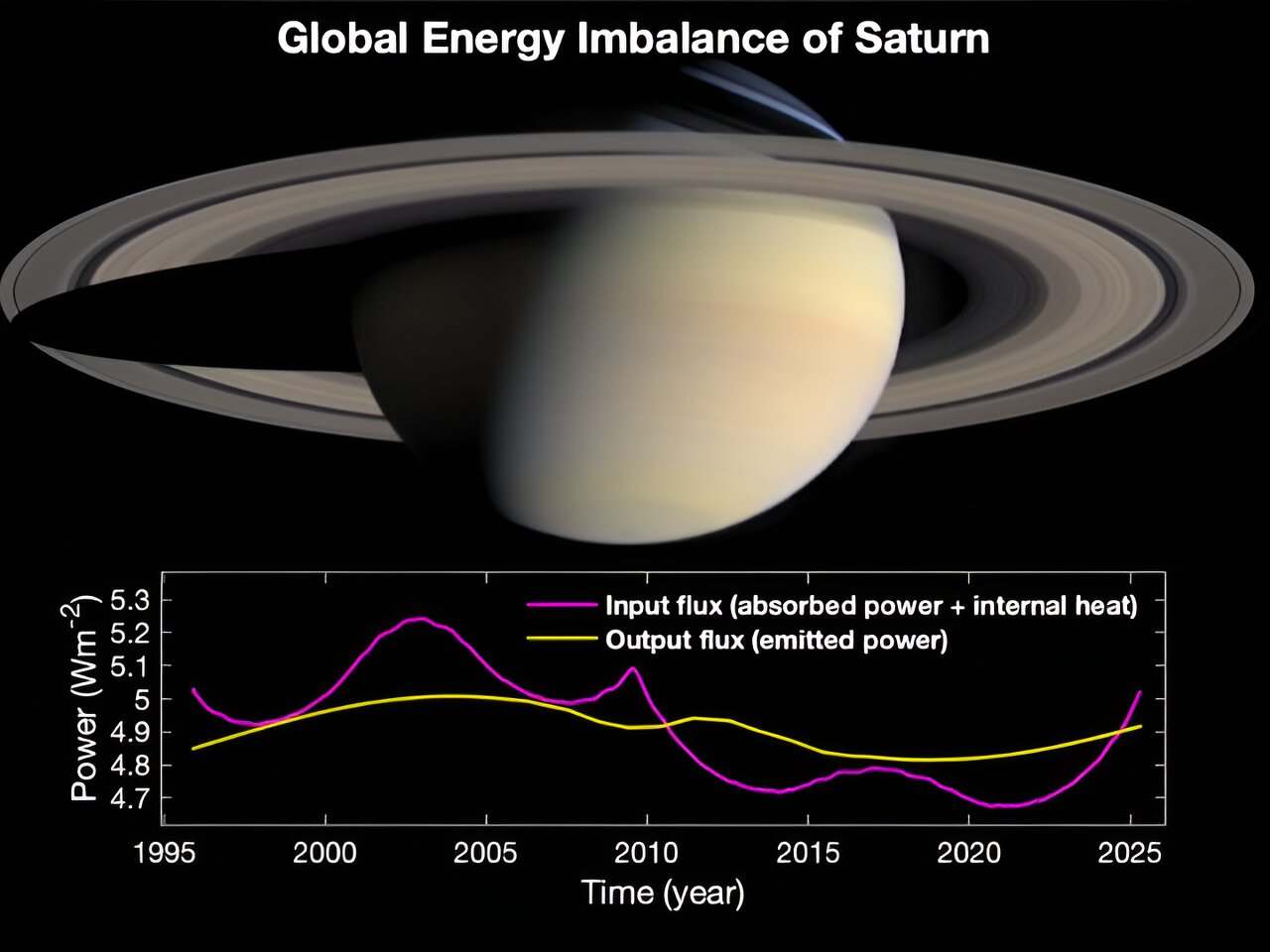
The imbalance is due to Saturn's large orbital eccentricity, resulting in huge seasonal variations in absorbed solar energy.
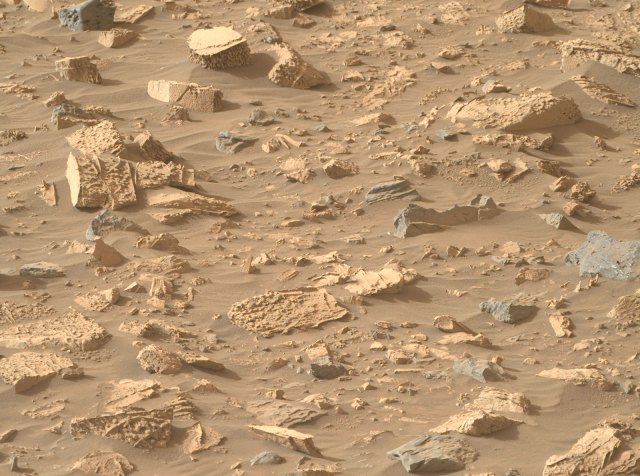

After months of driving, Perseverance has finally arrived at "Bright Angel", discovering oddly textured rock unlike any the rover has seen before.
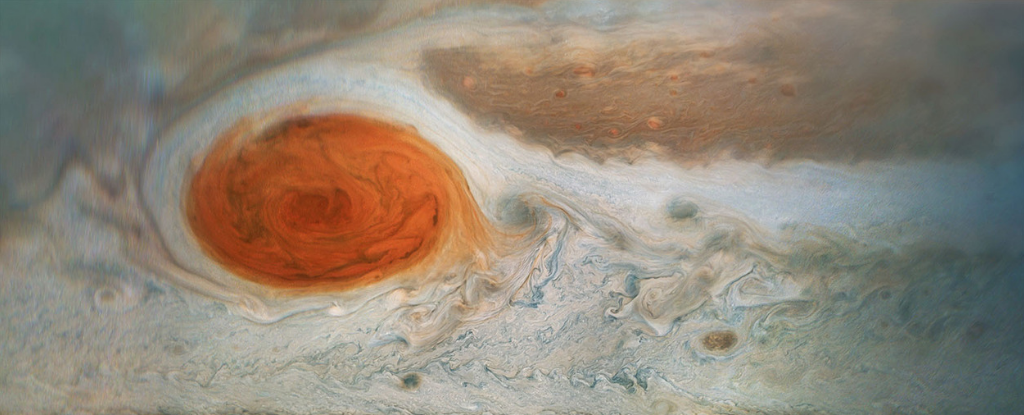

Jupiter's Great Red Spot (GRS) is one of the Solar System's defining features. It's a massive storm that astronomers have observed since the 1600s. However, its date of formation and longevity are up for debate.

In addition to producing auroras, a recent extreme storm provided more detail on how much radiation future astronauts could encounter on the Red Planet.
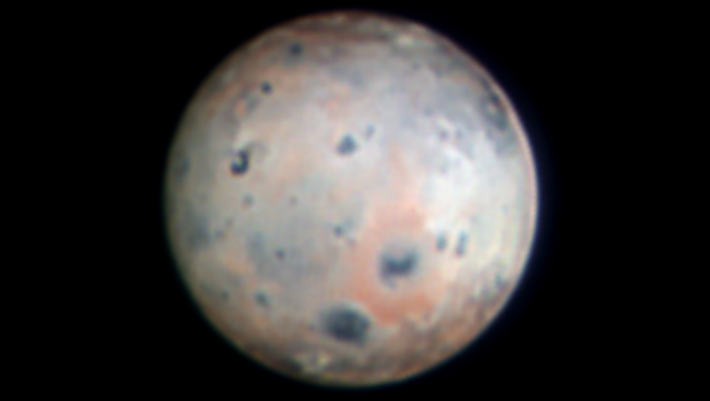

Using the SHARK-VIS instrument on the Large Binocular Telescope on Mount Graham in Arizona, the United States, astronomers have captured the highest resolution optical images of Io ever obtained from a ground-based telescope.
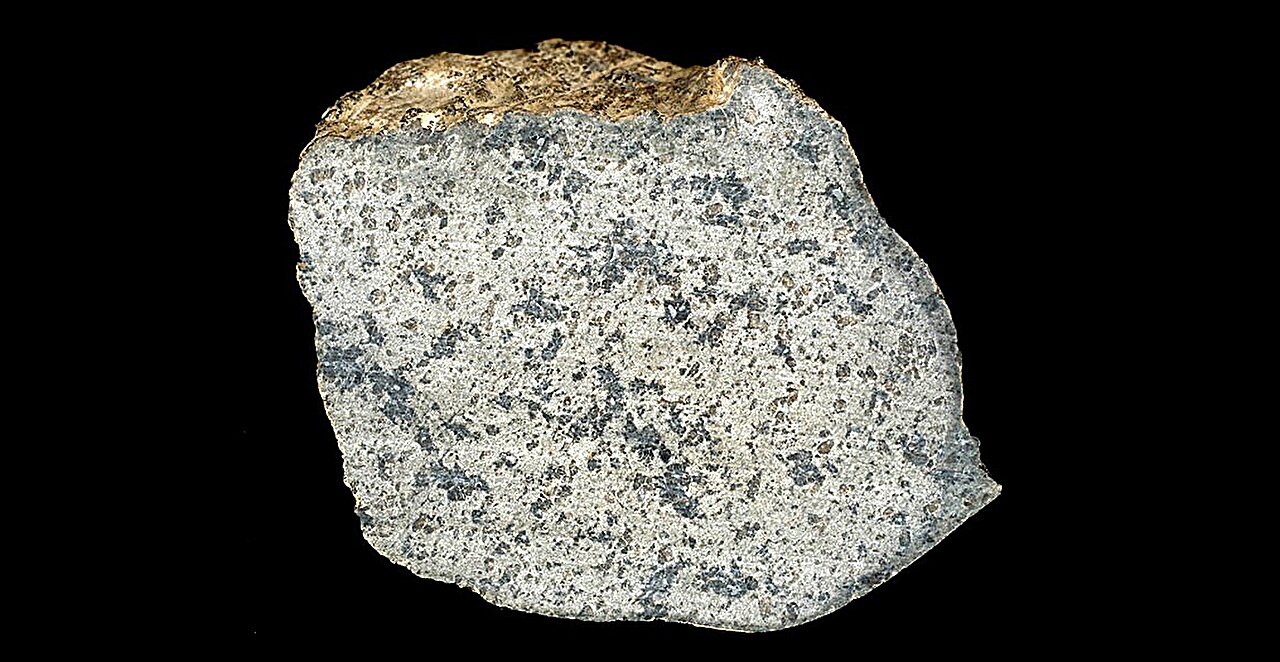

Mars has a distinct structure in its mantle and crust with discernible reservoirs, and this is known thanks to meteorites that scientists have analyzed.
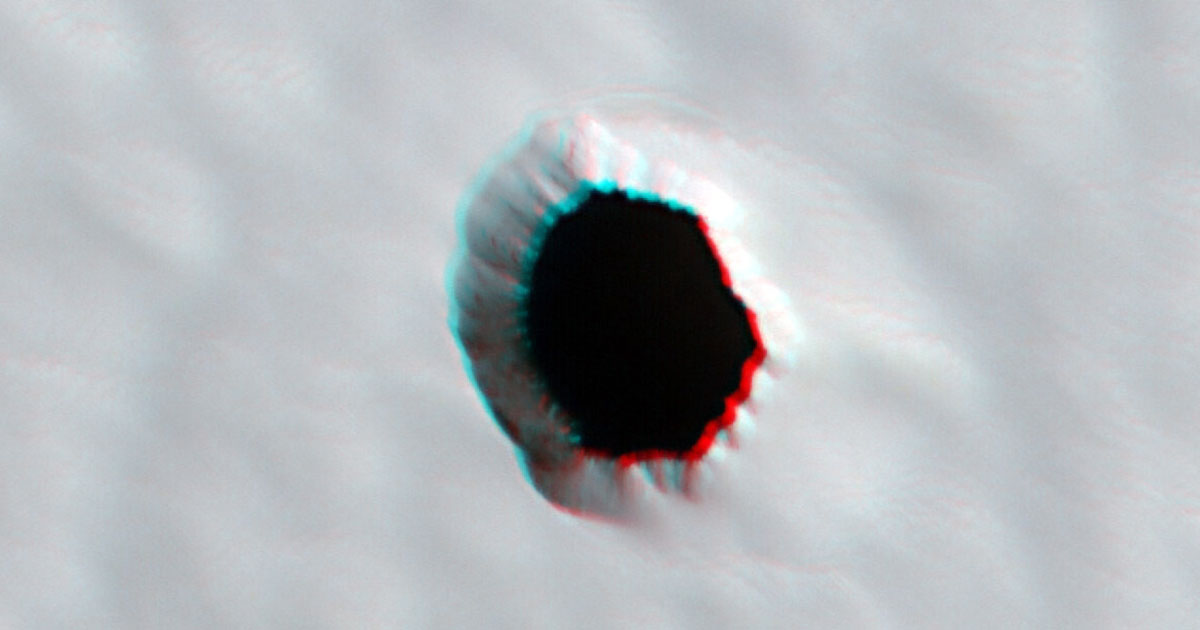

NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) has discovered another intriguing formation on the planet's barren surface. Despite their best efforts, scientists can only guess as to how exactly holes like this one were formed.
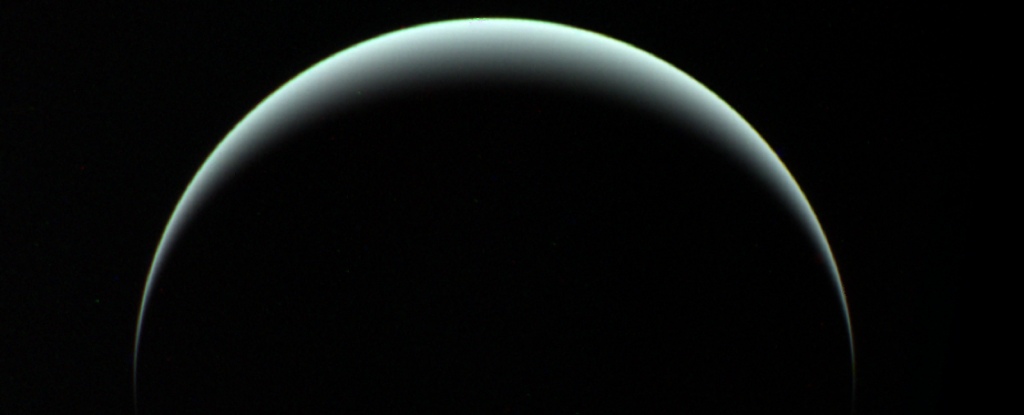

One of the most peculiar things about Uranus and Neptune is their magnetic fields.

One of the most peculiar things about Uranus and Neptune is their magnetic fields.
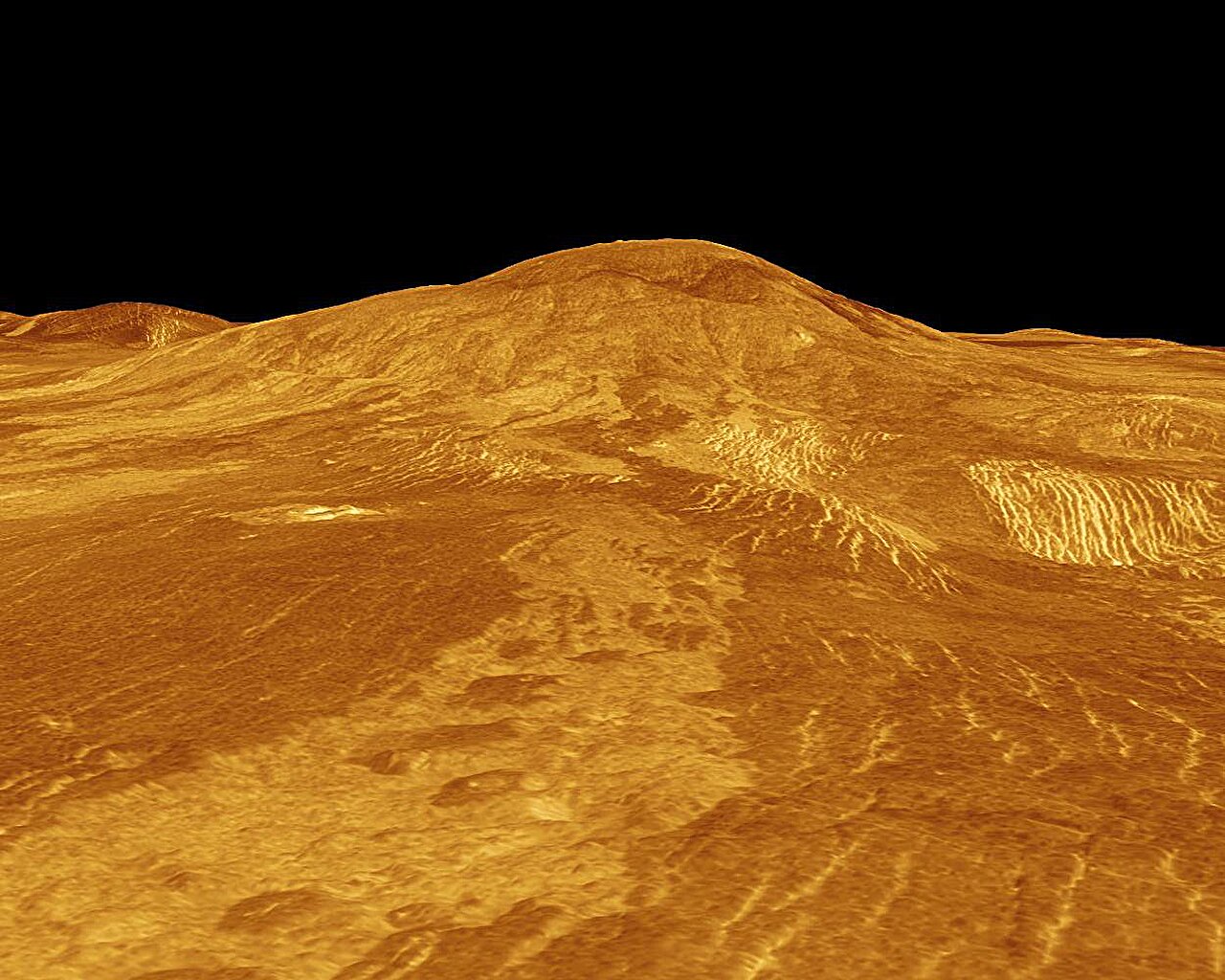
A new analysis of data collected on Venus more than 30 years ago suggests the planet may currently be volcanically active.