
After a decade of searching, NASA's MAVEN (Mars Atmosphere Volatile Evolution) mission has, for the first time, reported a direct observation of an elusive atmospheric escape process called sputtering.

A green glow snapped from Mars marks the first time that an aurora has been observed from the surface of another planet.
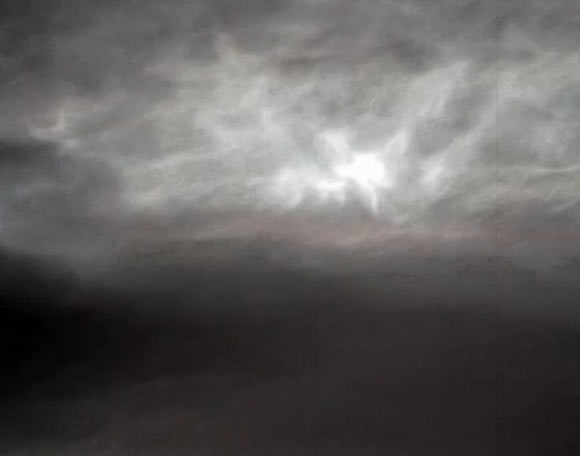

New images, taken over 16 min on January 17, 2025 by the Mastcam instrument on NASA's Curiosity rover, show noctilucent, or twilight clouds, in the atmosphere of Mars.
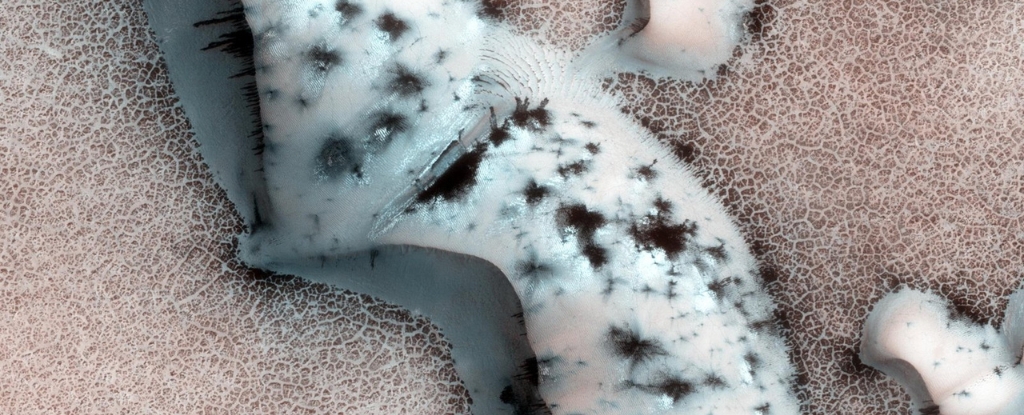
Though it's a cold, dead planet, Mars still has its own natural beauty about it. This image shows us something we'll never see on Earth - Martian CO2 geysers.
A team of researchers has uncovered evidence of its origins in the atmosphere, where carbon dioxide bathed in ultraviolet sunlight reacted to form a mist of carbon molecules that rained onto the planet's surface.

The scientists made a startling observation when they observed that the atmosphere of Mars dramatically ballooned outwards because of a void created due to a powerful gust of solar wind.

When future astronauts explore Mars's polar regions, they will see a green glow lighting up the night sky. For the first time, a visible nightglow has been detected in the martian atmosphere by ESA's ExoMars mission.

Sunlight on Mars interacts with iron-rich dust that hangs in the atmosphere. This ultimately scatters lower-frequency red light through the sky during the day. At twilight, however, the red light is filtered away and the sky glows a cool blue.