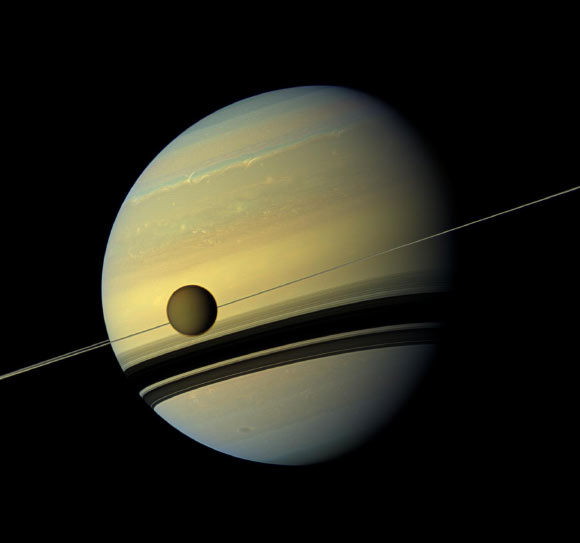

Scientists argue that two Saturnian moons, Titan and Hyperion, are not primordial worlds, but the result of a dramatic merger between two ancient moons.

The researchers found that additional studies of the data from Curiosity show that non-biological sources they had considered don’t fully explain the organics. They conclude, therefore, that a biological source is a reasonable hypothesis.

Vast amounts of hydrogen could also be locked away in our planet's core, attached to the densely packed alloyed iron that lurks therein

By firing tiny projectiles of iron-carbon alloy from a high-speed cannon, scientists have finally demonstrated that a weird part-solid, part-liquid-like state thought to exist inside Earth's inner core is indeed possible.
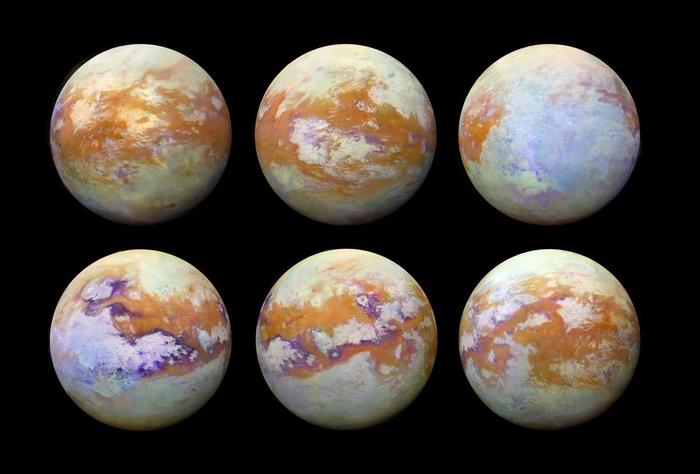

Careful reanalysis of data from more than a decade ago indicates that Saturn’s biggest moon, Titan, does not have a vast ocean beneath its icy surface, as suggested previously.

A new Swiss-led study uses innovative hybrid modeling to reveal that these planets could just as easily be dominated by rock as by water-rich ices.
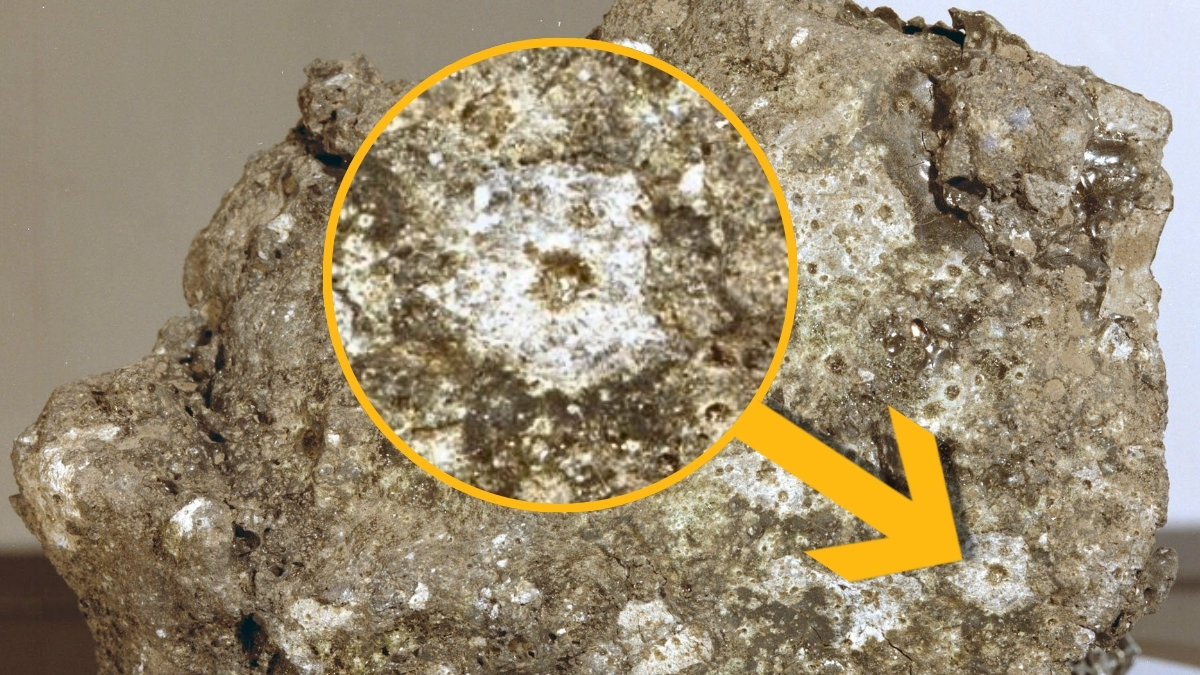

The Moon has no atmosphere, yet it faces an invisible bombardment more relentless than any terrestrial storm, a constant rain of micrometeoroids, tiny fragments of rock and metal traveling at speeds up to 70 kilometers per second.

Astronomers found evidence of three rings around Chiron, which orbits the Sun between Uranus and Saturn.
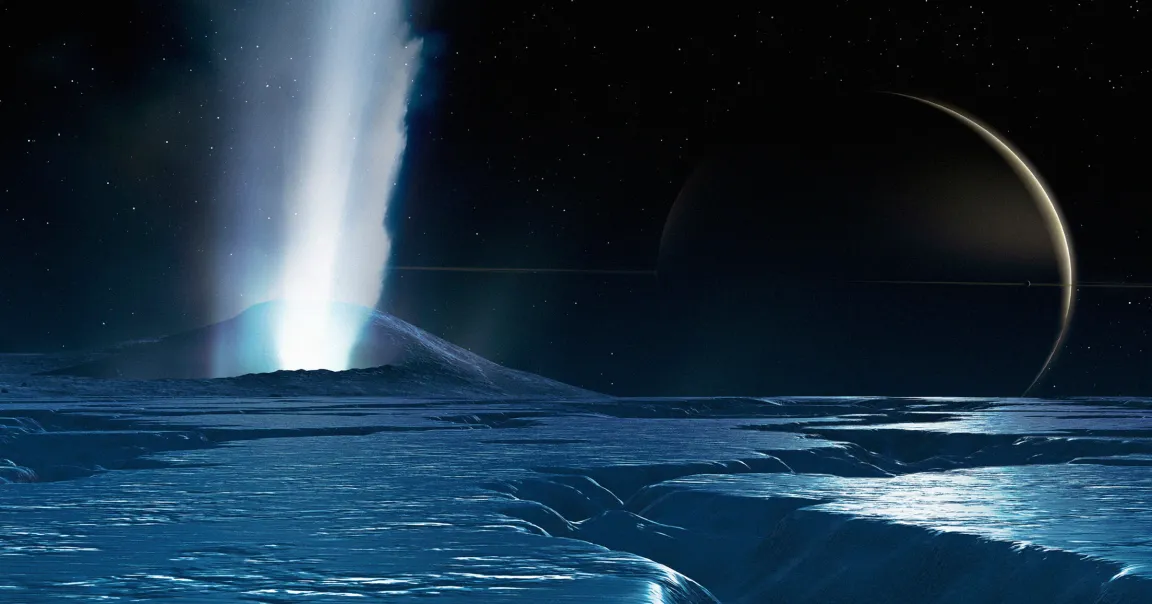

Astronomers have found that Saturn’s moon, Enceladus, is spewing out copious amounts of complex organic molecules, suggesting it’s an even more promising place to look for extraterrestrial life than previously thought.

If a new proposal by MIT physicists bears out, the recent detection of a record-setting neutrino could be the first evidence of elusive Hawking radiation.
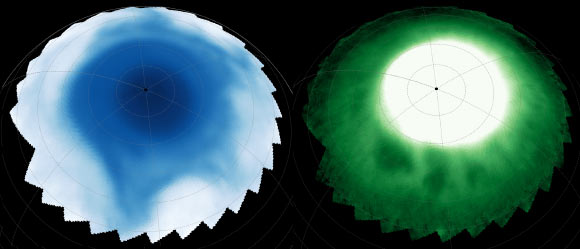
Astronomers using the NASA/ESA James Webb Space Telescope have detected a series of dark, bead-like and asymmetric star-shaped features in the ionosphere and stratosphere of Saturn.
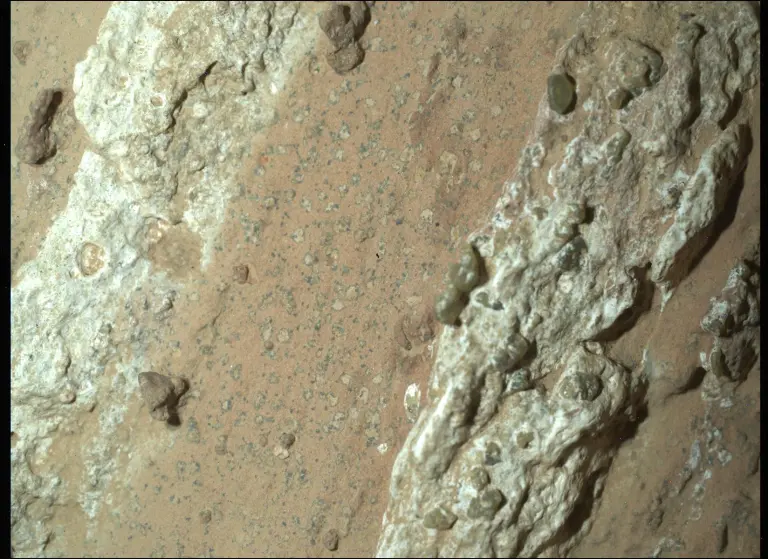

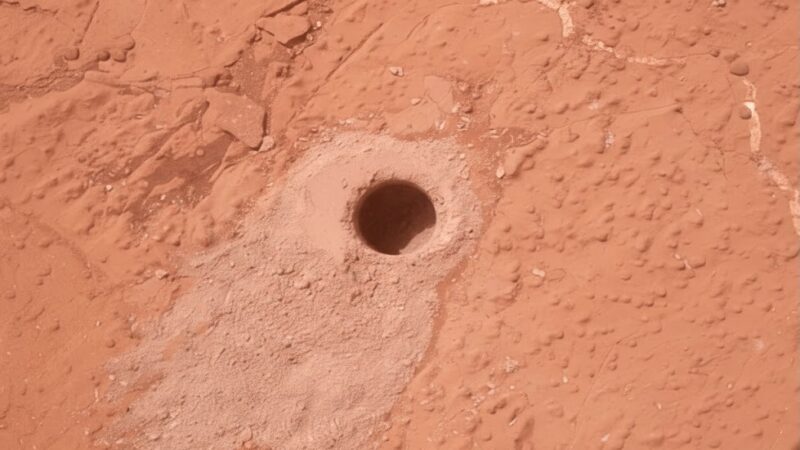
A sample collected by NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover from an ancient dry riverbed in Jezero Crater could preserve evidence of ancient microbial life.

Mars isn’t the neatly layered world we once imagined — its mantle is filled with ancient, jagged fragments left over from colossal impacts billions of years ago.
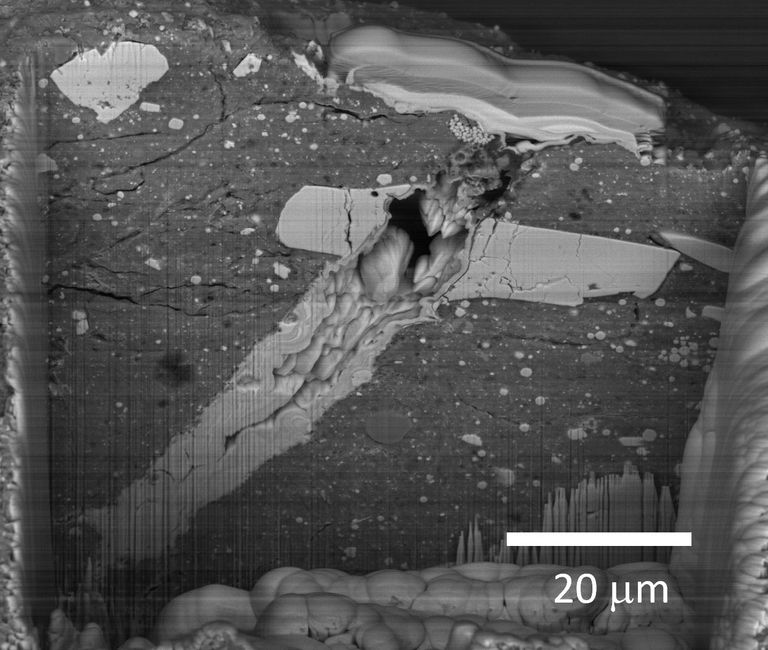
Asteroid Bennu, sampled by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission in 2020, is a mixture of dust that formed in our solar system, organic matter from interstellar space, and pre-solar system stardust.
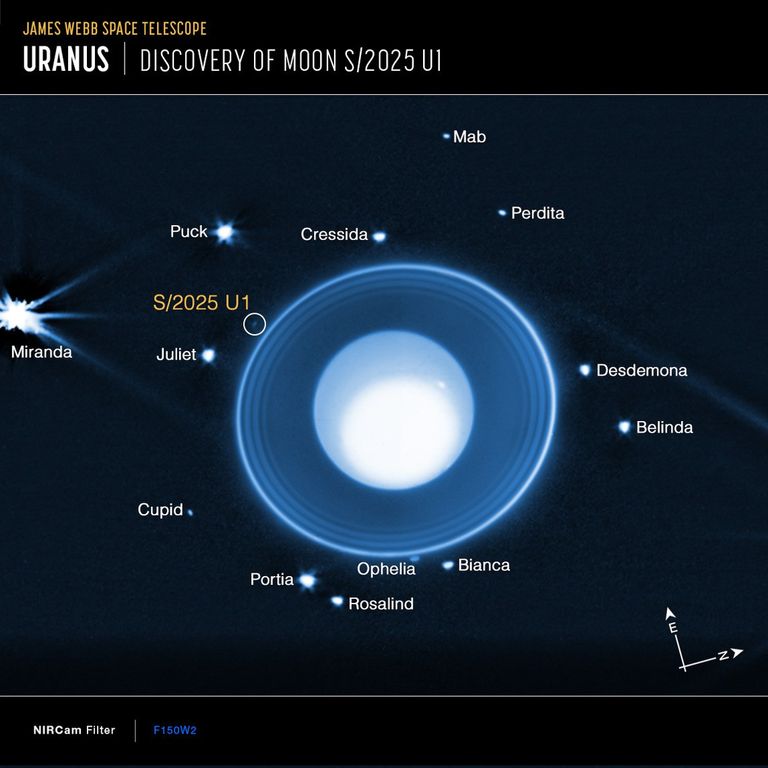
Using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, a team has identified a previously unknown moon orbiting Uranus, expanding the planet’s known satellite family to 29.