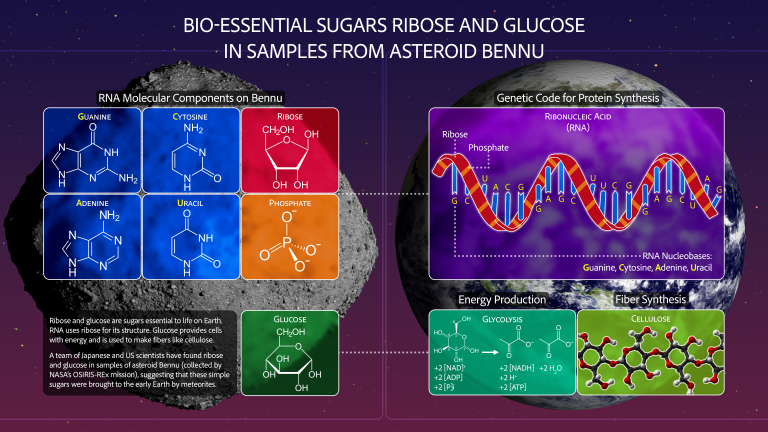
The asteroid Bennu continues to provide new clues to scientists’ biggest questions about the formation of the early solar system and the origins of life.
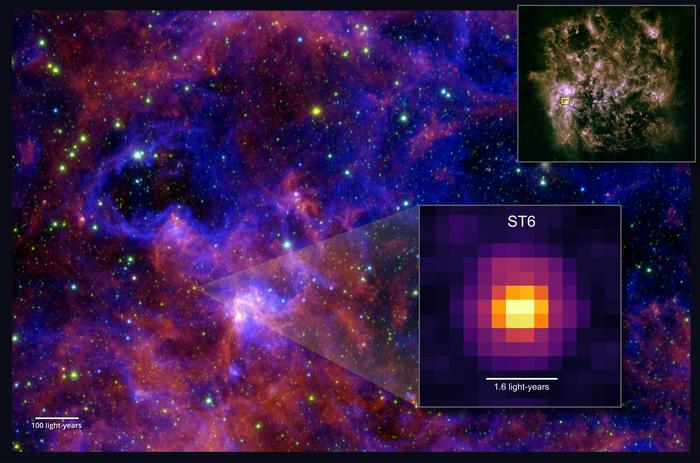
A team led by a University of Maryland astronomer detected large complex organic molecules in ices outside of the Milky Way for the first time, offering a glimpse into the chemistry of the early universe.

78 million years ago, a 1.6 km asteroid slammed into what is now Finland, creating a crater 23 km (14 mi) wide and 750 m deep. The catastrophic impact created a fractured hydrothermal system in the shattered bedrock under the crater.

Astronomers studying the young star V883 Orionis reported spotting complex organic molecules floating in its dusty disk that’s in the process of forming planets.

Researchers from Germany have simulated ancient environment in a vial, and found that archaic life forms that live in the deep sea today can thrive under these primordial conditions.
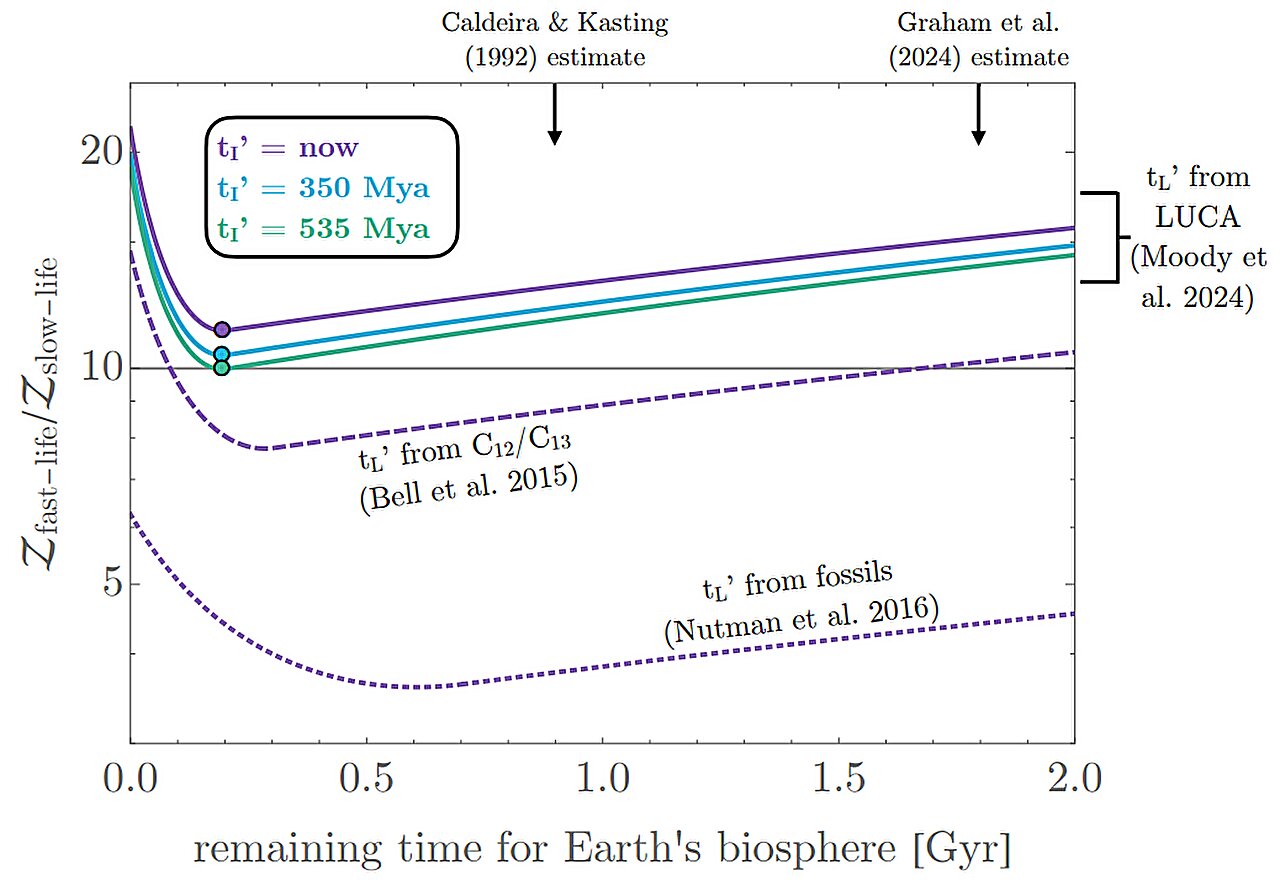
An astronomer at Columbia University is suggesting that because life emerged so soon on Earth after its formation, it may emerge rapidly on Earth-like planets after the right conditions arise in general.

Scientists have uncovered a surprising role for calcium in shaping the building blocks of life.
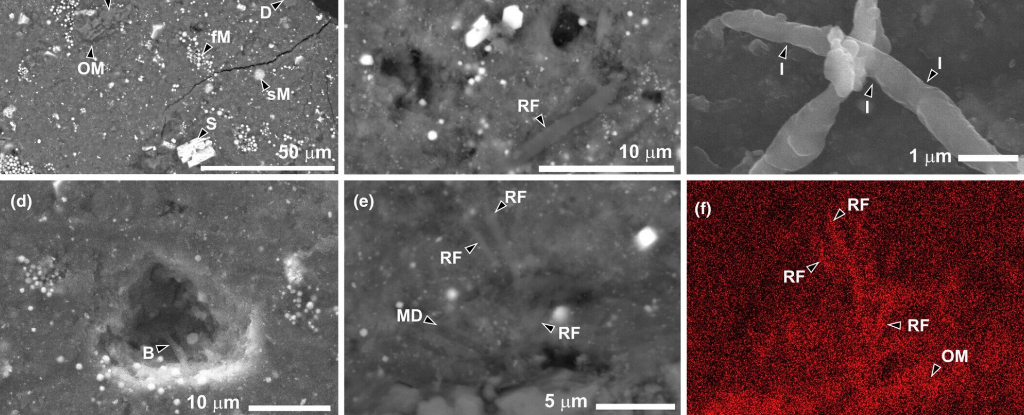

There is a radical idea that Earth was seeded not just with the building blocks of life but life itself.
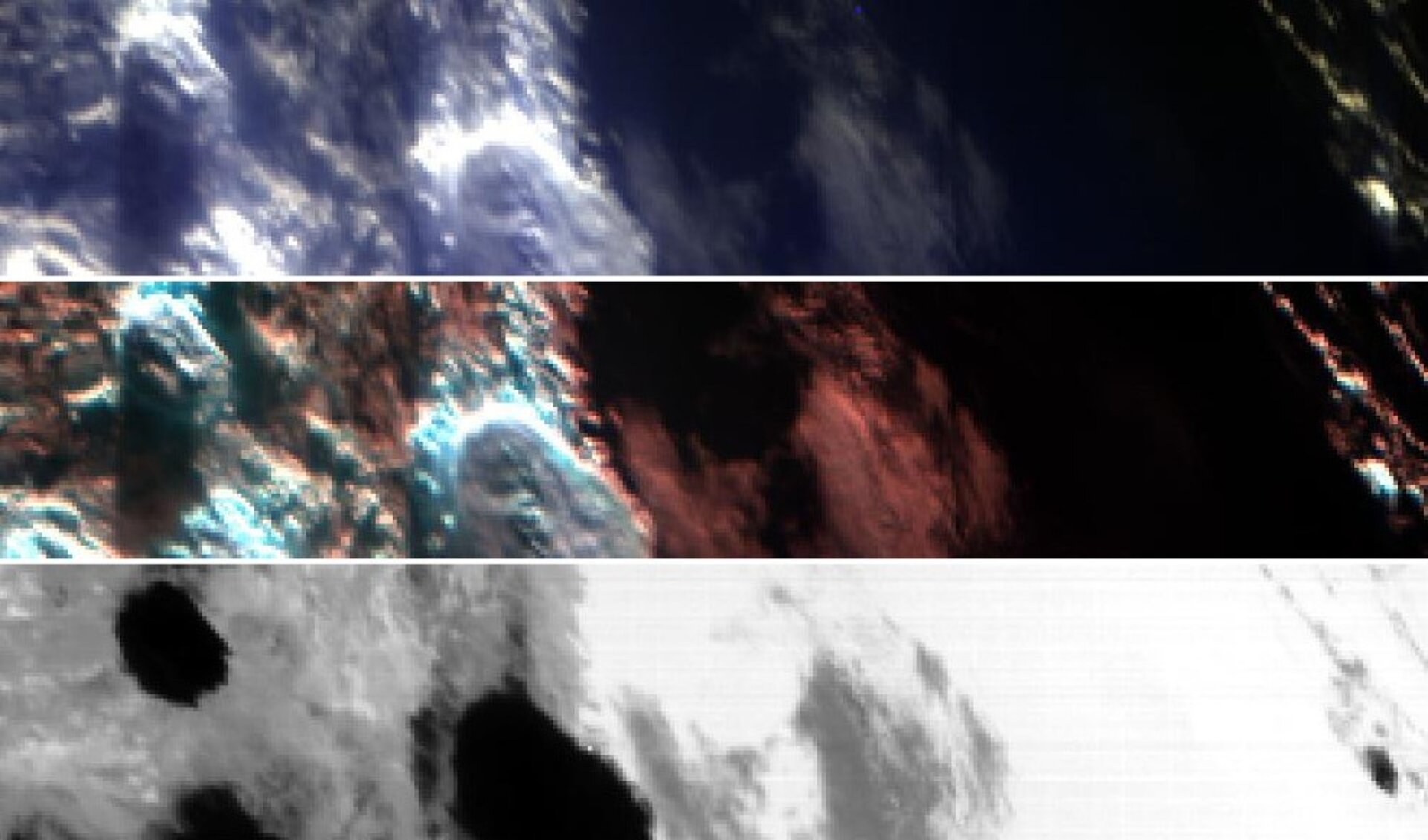
During its flyby of Earth on 20 August, ESA's Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (Juice) found ingredients for life in Earth's atmosphere - the so-called ‘CHNOPS’ elements (carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorous and sulphur).
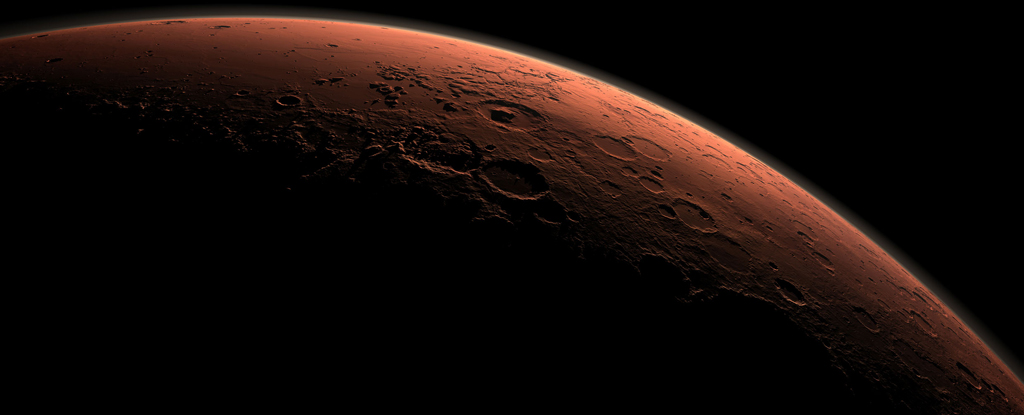
A team of researchers has uncovered evidence of its origins in the atmosphere, where carbon dioxide bathed in ultraviolet sunlight reacted to form a mist of carbon molecules that rained onto the planet's surface.

The analysis is key to confirming carbon and nitrogen-rich dusts and organic compounds essential for life. However, the sample also revealed the presence of magnesium-sodium phosphate, which had not been detected before.

A new study aimed at answering the latter question finds that some building blocks didn’t need to have formed on Earth, but could have arrived from space.

Recently scientists have discovered one plausible pathway for how protocells may have first formed and chemically progressed to allow for a diversity of functions.

The research team investigated how the emergence of the first living systems from inert geological materials happened on Earth more than 3.5 billion years ago.

The discovery of phosphorus in a molecular cloud at the edge of the Milky Way galaxy extends the presence of the element almost twice as far out as where it was known to exist.