
Our home galaxy also has a colossal wave rippling through it, pulling and pushing an ocean of stars and cosmic dust in its wake.
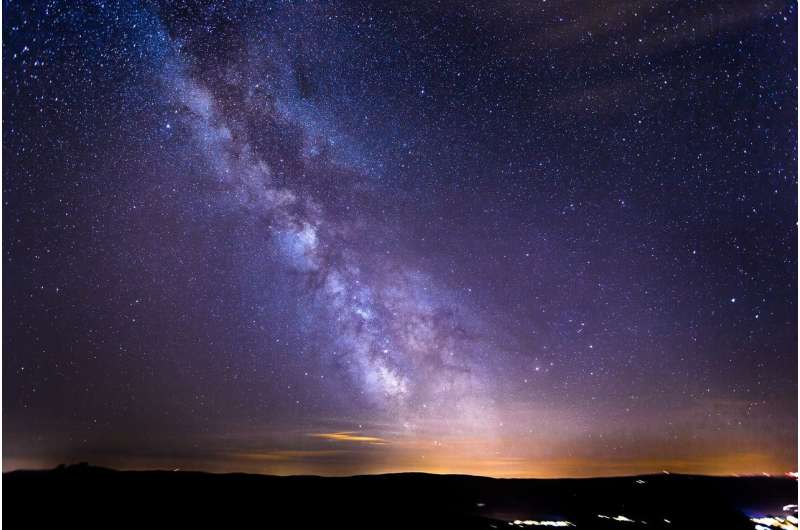

New research has uncovered a striking link between the structure of our galaxy and the evolution of Earth's crust, showing its development was shaped by the impact of meteorites during its journey through the Milky Way.

A team of astronomers has identified a giant spiral galaxy so well-formed that it already has a stable galactic bar; a long, straight structure filled with stars across the galaxy's center. It was formed just 2.6 billion years after the Big Bang.

NASA's Chandra X-Ray Observatory helped diagnose the cause behind a large kink in a huge filament near the center of the Milky Way.

A team of researchers at Nagoya University has discovered evidence that the Small Magellanic Cloud is potentially being torn apart by gravitational forces from its larger companion.

An international team of astronomers using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) discovered a surprising new filamentary structure around the Mikly Way's core.
Recent research proposes a new form of dark matter that may actually be lighter in mass than other dark matter candidates.

Millions of years ago, our Solar System traveled through a densely populated galactic region and was exposed to increased interstellar dust.

The European Space Agency's Milky Way-mapper Gaia has completed the sky-scanning phase of its mission, racking up more than three trillion observations of about two billion stars and other objects over the last decade.

The plot has just thickened in the mystery tale about the unseen mass skulking inside the largest cluster of stars in the Milky Way galaxy.
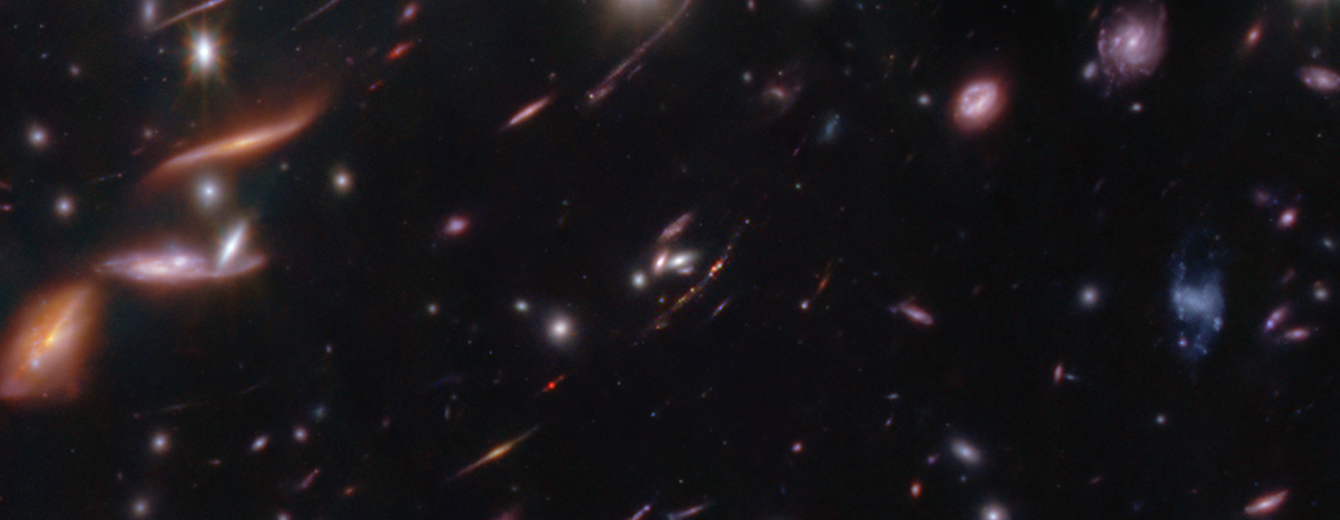

For the first time, NASA's James Webb Space Telescope has detected and "weighed" a galaxy that not only existed around 600 million years after the big bang, but is also similar to what our Milky Way.

The Milky Way is only one system and may not be typical of how other galaxies formed. That's why it's critical to find similar galaxies and compare them
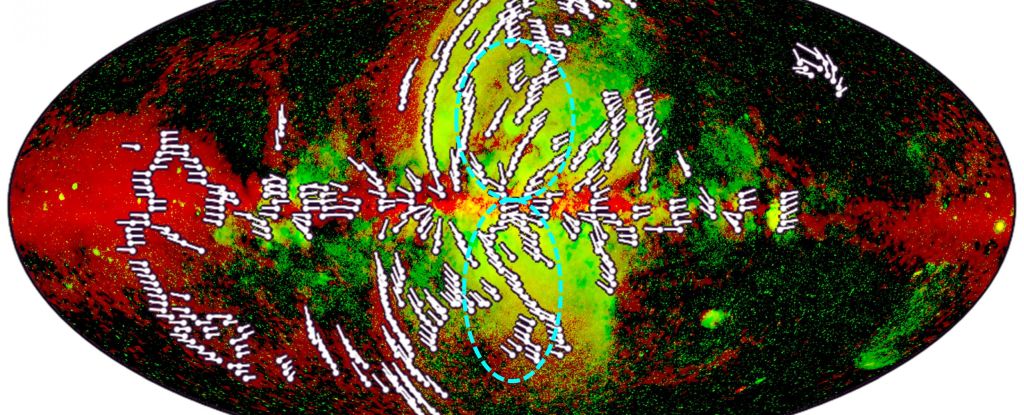
By studying hot gas glowing in circumgalactic space, astrophysicists have found evidence of enormous magnetic fields that wind through and around our galaxy's dark matter 'halo'.
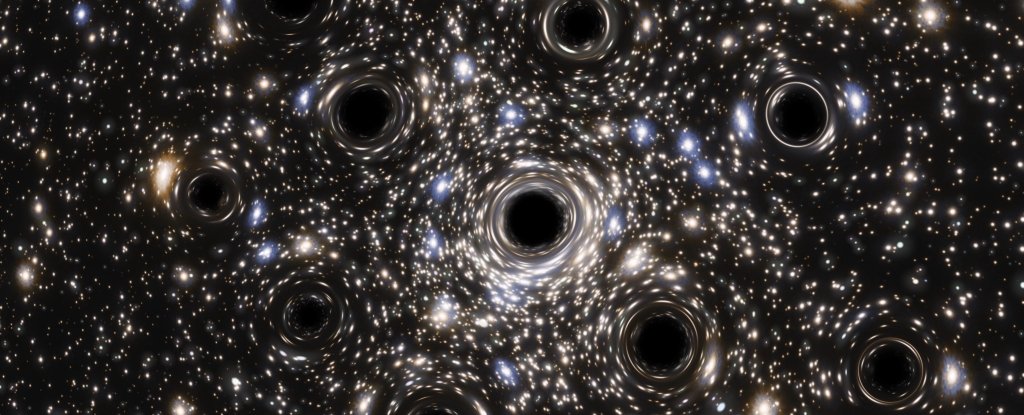

A fluffy cluster of stars spilling across the sky may have a secret hidden in its heart: a swarm of over 100 stellar-mass black holes.

The study suggests Sagittarius A* likely formed through a merger with another black hole, explaining its spin and misalignment.