
The early Solar System was like a debris field where objects smashed into each other in cascades of collisions.
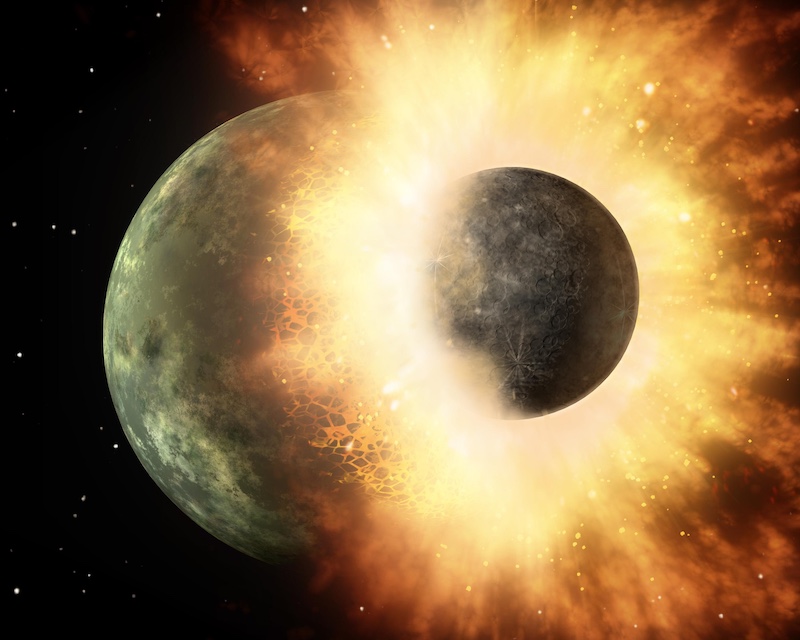

A grazing giant collision between two similar-sized rocky bodies likely created Mercury a few billion years ago.

Around 1,645 light-years from Earth sits a binary star system, containing a white dwarf and a red dwarf on such a close orbit that each revolution smacks their magnetic fields together, producing a burst of radio waves.

A strange star has revealed to astronomers a mysterious past - one that involves the merger of two ancient suns.
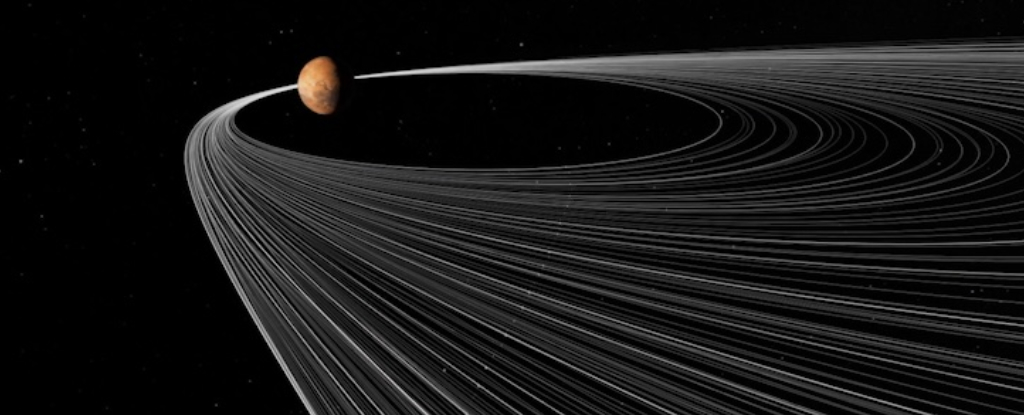

Martian moons could be a result of an early collision similar to that of Earth and Theia. This new model proposes an interesting middle way. Rather than an impact or direct capture, the authors propose a near miss by a large asteroid.
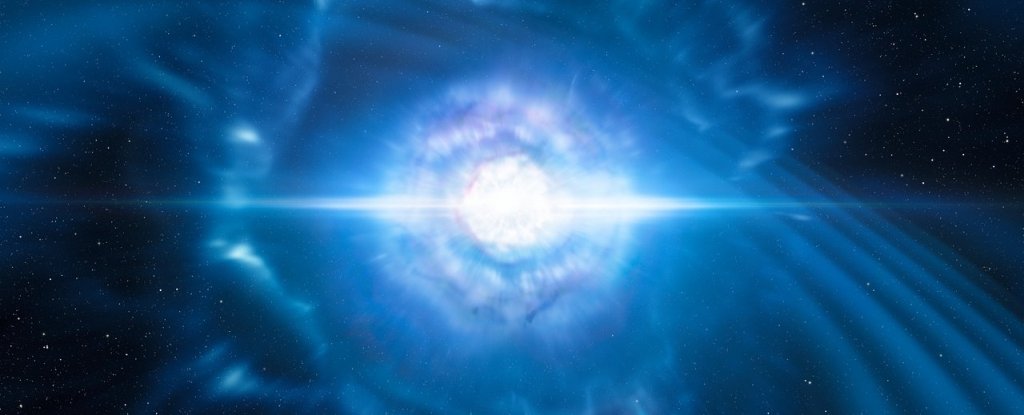

In August 2017, humanity observed a wonder. For the first time, we got to see two neutron stars colliding.

Look hard enough at the roiling mist of gas and starlight that is our galaxy, and you'll find traces of a violent upbringing.

For years, astronomers thought it was the Milky Way’s destiny to collide with its near neighbor the Andromeda galaxy a few billion years from now. But a new simulation finds a 50% chance the impending crunch will end up a near-miss.

Two giant clusters of galaxies observed in the process of colliding are going so hard that their dark matter has basically detached from normal matter and flown ahead.

Dark matter could provide supermassive black holes the brakes they need to bring them crashing together at the end of a long, spiraling journey towards their destiny.
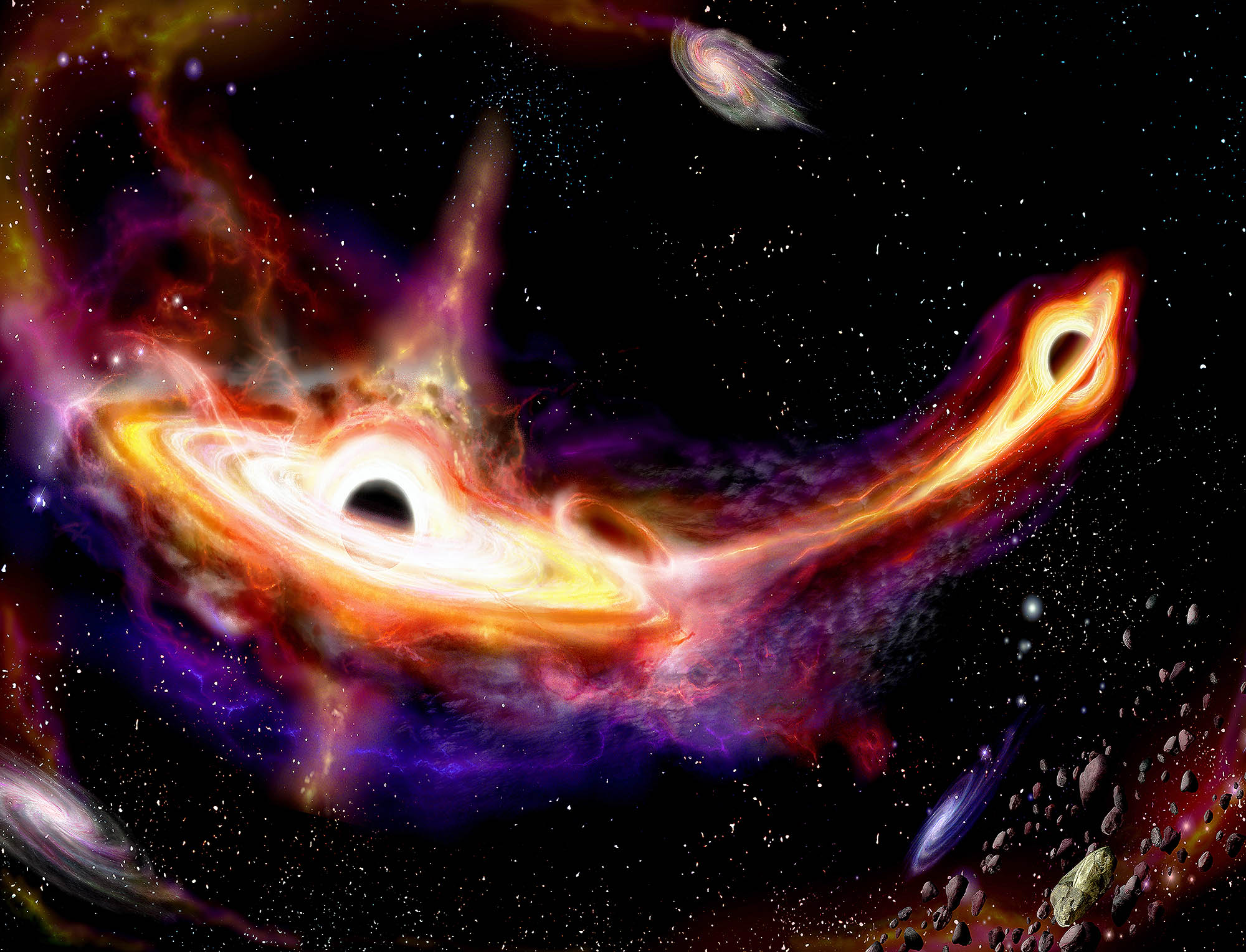

Astronomers discovered the first pair of merging quasars from the Cosmic Dawn, 900 million years after the Big Bang.
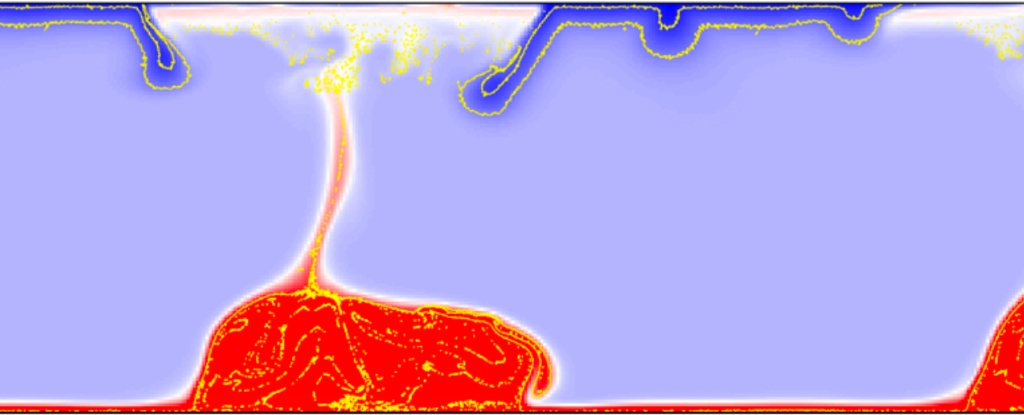
On the scale of cataclysmic events, the whomping impact of a Mars-sized object that crashed into Earth some 4.5 billion years ago ranks pretty highly: thought to have set in motion the movement of our planet's fractured, rocky crust.

The experts attribute the formation of the unique heart-shaped terrain to a colossal oblique-angle collision with a celestial body approximately 700 kilometers in diameter – roughly twice the size of Switzerland from east to west.

A gravitational wave detected in May of last year has given us a type of cosmic collision we've never seen before.

Long ago, an alien planet crashed into Earth – causing a collision so big the debris formed the Moon and left mysterious remnants lodged deep in the Earth’s mantle.