
Deep beneath our feet, in the heart of our planet, something unexpected is happening. Scientists have discovered that Earth’s inner core, a solid iron-nickel sphere roughly the size of the moon, is slowing down.
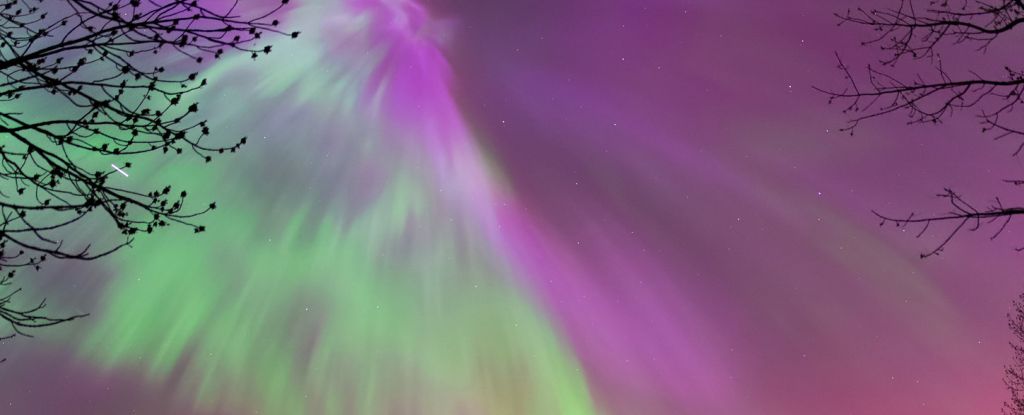

A solar storm that filled Earth's skies with shimmering curtains of light in May 2024 was so intense that its effects were felt, even at the bottom of the ocean.
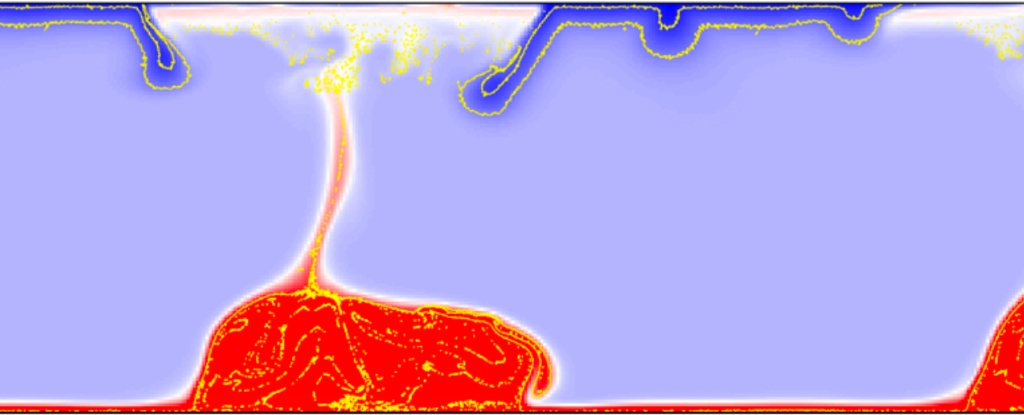
On the scale of cataclysmic events, the whomping impact of a Mars-sized object that crashed into Earth some 4.5 billion years ago ranks pretty highly: thought to have set in motion the movement of our planet's fractured, rocky crust.
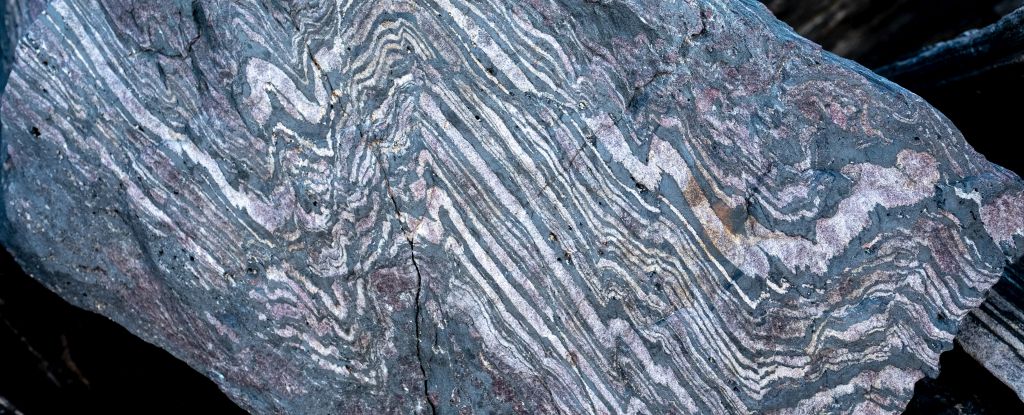

Rocks that formed some 3.7 billion years ago in the early Archean have given us the earliest glimpse yet of Earth's magnetic field.

Falling pieces of space debris could be altering the stratosphere and negatively impacting our climate, new research suggests.

Study reveals that deep-sea currents have been weakening, strengthening during 2.4m-year climate cycles

For a quiet, dusty lump of a planet we see today, Mars has had a surprisingly violent history, one that could reveal some clues about Earth.

A team led by geoscientists Yachong An and Hao Ding of Wuhan University have determined that Earth's inner core wobbles with a periodicity of 8.5 years.

The burst that originated some 2.4 billion light-years away from Earth and struck the planet on 9 October last year may have led to changes in the upper ionosphere, according to a new study.

Long ago, an alien planet crashed into Earth – causing a collision so big the debris formed the Moon and left mysterious remnants lodged deep in the Earth’s mantle.

Fine dust suspended in the atmosphere may have played a significant role in the extinction of dinosaurs after all.

Researchers note a "synchronicity" of geochemical signals suggesting that fragments of a comet struck Earth approximately 13,000 years ago.

In 250 million years, for the first time since Pangea cracked apart, the continents of Earth will crash together into a new supercontinent dubbed Pangea Ultima.

NASA has awarded a contract to TransAstra to clean up space junk. One category of debris they will target is CubeSats, small satellites the size of a Rubik’s Cube. The recycling centers would allow the collected debris to be recycled.

Scientists are seeking to confirm that a black rock discovered in Morocco in 2018 departed Earth's pull for outer space, only to return to it like a prodigal child.