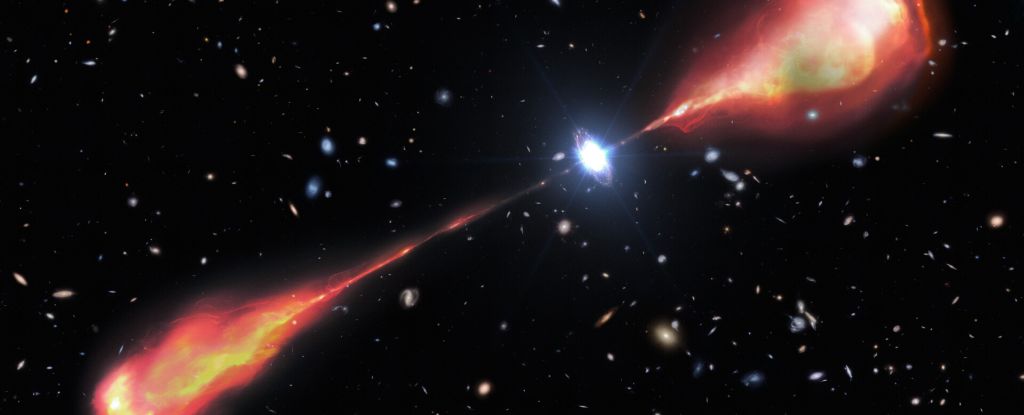

A supermassive black hole in the early Universe has been spotted blasting out powerful jets of plasma that are at least twice as long as the Milky Way is wide.

In this blog, Professor Enrique Gaztanaga from the Institute of Cosmology and Gravitation at the University of Portsmouth, puts forward a new theory about how the Universe was created.
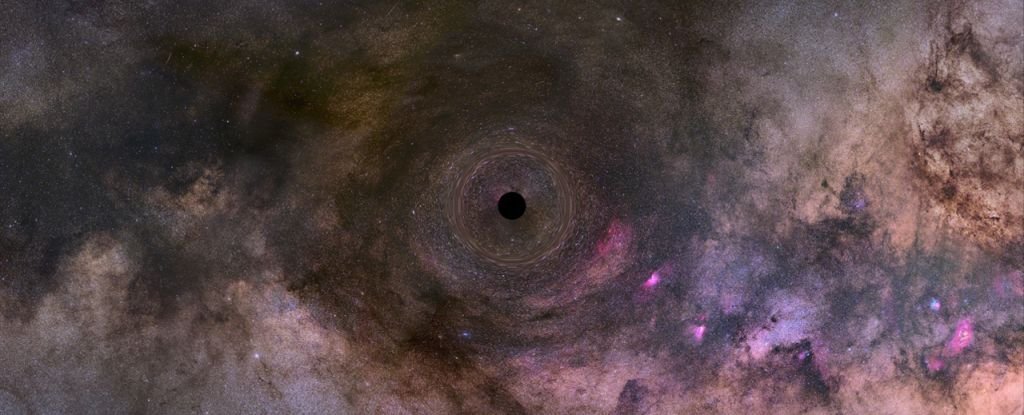

A lonely black hole roaming the cosmos in solitude has been confirmed for the first time.

A massive black hole at the heart of a galaxy in the Virgo constellation is waking up, shooting out intense X-ray flares at regular intervals that have puzzled scientists

In 2022 NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope discovered an abundance of tiny red objects scattered across the sky in the early universe. A large fraction of them are likely galaxies with supermassive black holes growing at their centers.

Traditional models of star formation suggest there may be as few as 300 black holes in the closest region of the supermassive black hole Sagittarius A*. But a new study suggests the number of stellar-mass black holes is much higher.

When you peer out into the depths of the cosmos, a mystery lies there, waiting. In a survey of the deep sky, most of the galaxies are seen rotating in the same direction.

New research suggests black holes may transition into 'white holes', ejecting matter and potentially even time back into the universe, defying our current understanding of these cosmic giants.

In 2007, astronomers discovered the Cosmic Horseshoe, a gravitationally lensed system of galaxies. New research reveals the presence of an Ultra-Massive Black Hole in the foreground galaxy with a staggering 36 billion solar masses.

Using the James Webb Space Telescope, scientists witnessed a brilliant light show at the heart of our Milky Way galaxy.
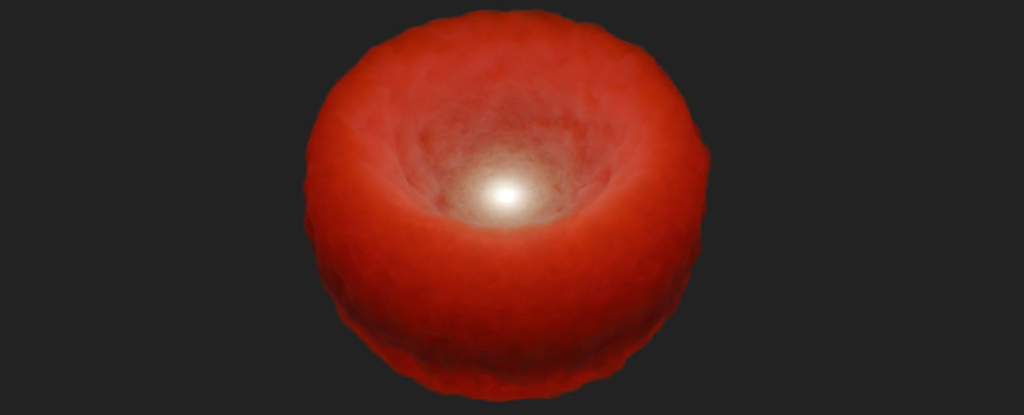

By some reckoning, as few as 15 percent of supermassive black holes are hidden behind dust clouds.
As far as supermassive black holes go, the one at the center of the Milky Way is relatively sedate. But on 6 April 2024, the black hole let out a flare observed in mid-infrared wavelengths, followed by a radio flare counterpart.
An international team of astronomers show that distinguishing features of Palomar 5 star cluster are likely the result of an oversized black hole population of more than 100 black holes in the center of the cluster.
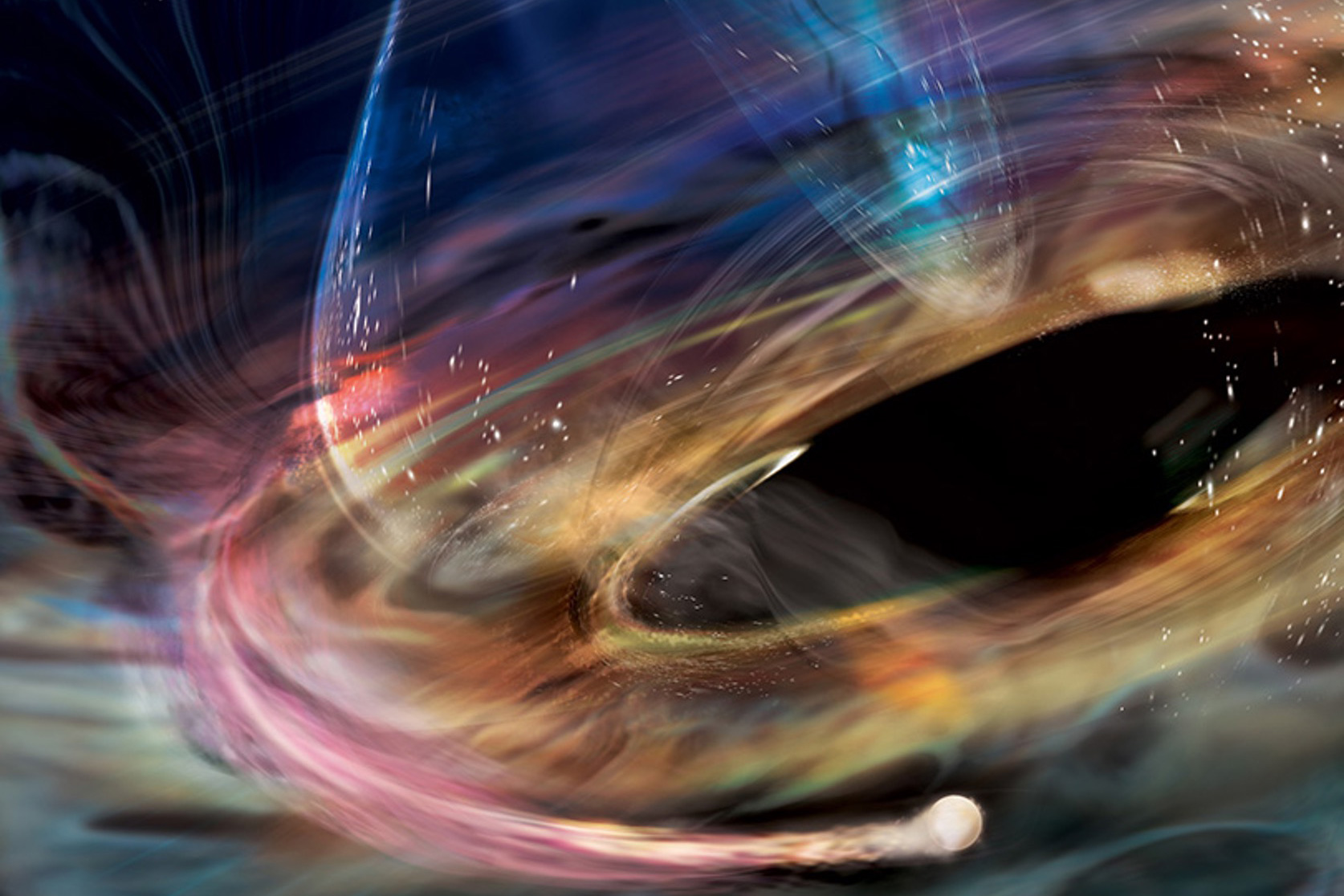

MIT astronomers observed flashes of X-rays coming from a supermassive black hole at a steadily increasing clip. The source could be the core of a dead star that's teetering at the black hole's edge.

Using the Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers homed in on a quasar called 3C 273, some 2.5 billion light-years from Earth.