
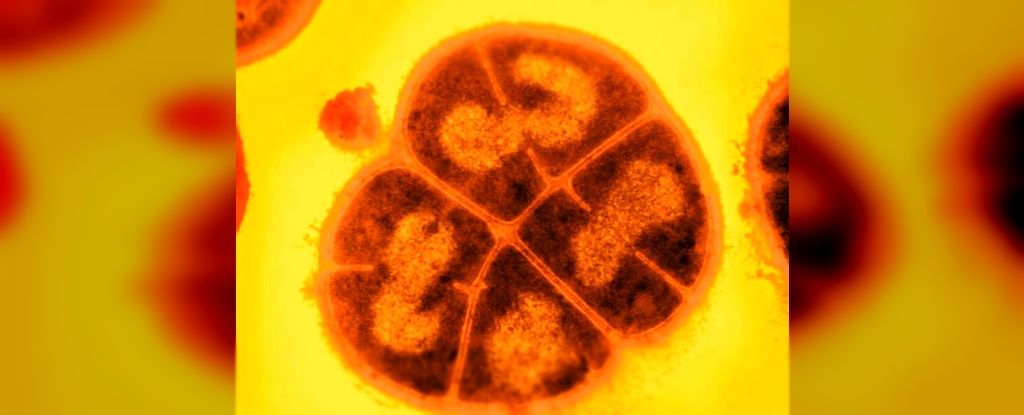
The fact that this bacteria so closely resembles that transition point, from two single cells with different genetics to one inseparable cluster, is fascinating: embryo comparisons have provided many clues about our evolutionary history.
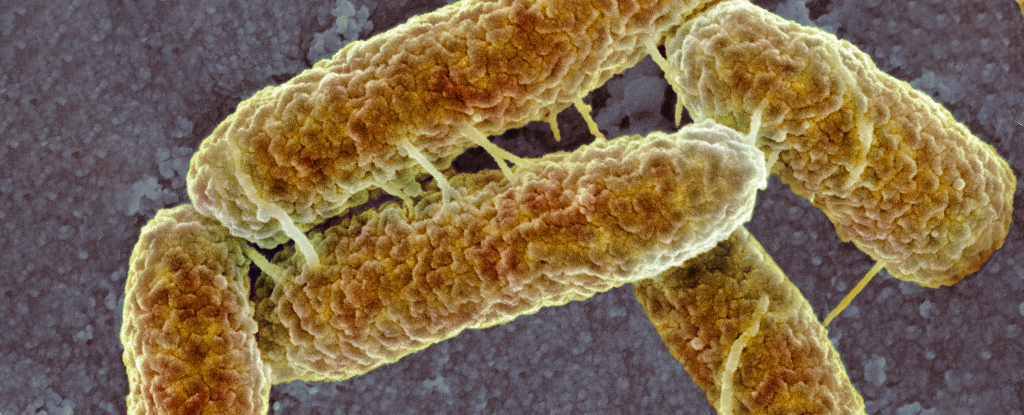
Capable of handling extreme cold, acid, and dehydration, the microbe Deinococcus radiodurans handles doses of radiation that would kill a human tens of thousands of times over.
Bacteria can develop a heightened new sensitivity to acid levels when exposed to different environmental extremes in the laboratory, a new study shows.
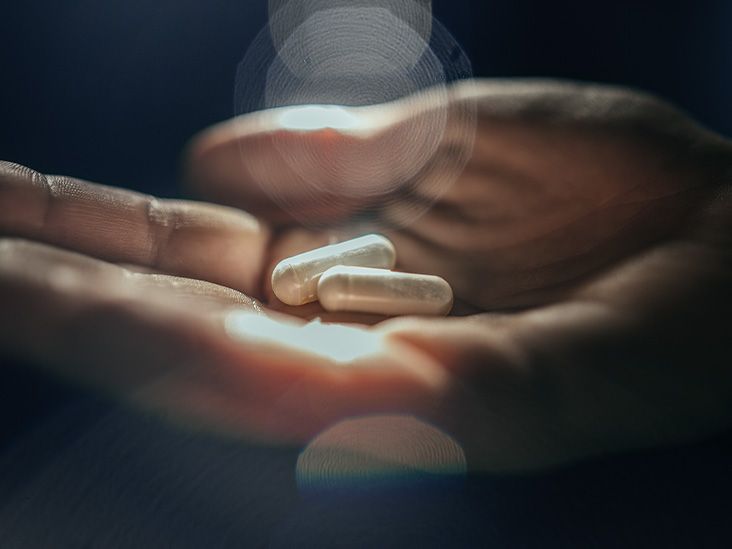

A recent study shows promise for a new antibiotic that effectively fights several bacteria while sparing the helpful bacteria that occur naturally in the gut.

In 'extreme environmental conditions' scientists have discovered 968 species featuring a hugely diverse range of microbes. Excitingly, 82 % of the genomes were novel species.

International scientists have discovered a new class of compounds that uniquely combine direct antibiotic killing of pan drug-resistant bacterial pathogens with a simultaneous rapid immune response.

Acetobacterium woodii is a new bacteria that is able to live in both hydrogen rich and hydrogen absent environments. This allow it to live in a variety of extreme environments, like the ocean floor or maybe another planet.

MIT scientists have revealed that their AI discovered an antibiotic compound, halicin, that can not only kill many forms of resistant bacteria but do so in a novel way.

Latest studies showed that bacteria-infecting viruses called bacteriophages, or simply phages, could kill different strains of the bacterium E. coli by making mutations in a viral protein that bound to host cells.

An all-Princeton research team has identified bacteria that can detect the speed of flowing fluids.

Researchers working off the coast of Mexico have discovered evidence of arsenic-breathing life in oxygen-starved waters. These resilient microbes could also be a sign of things to come under the influence of climate change.

Researchers analyzing soil from Ireland have discovered that it contains a previously unknown strain of bacteria which is effective against four of the top six superbugs that are resistant to antibiotics.

Changing the gut microbiome to beat illness really does hold great potential, but first scientists must answer what constitutes a healthy gut microbiome and in whom.

A team of US biologists has discovered thousands of four- and five-drug combinations of antibiotics that are more effective at killing harmful bacteria than the prevailing views suggested.

US researchers report that dietary iron supplements help to survive a normally lethal bacterial infection and resulted in later generations of those bacteria being less virulent.