A new study suggests a solution to the Little Red Dots mystery. Scientists think young supermassive black holes may go through a “cocoon phase,” where they grow surrounded by high-density gas they feed on.
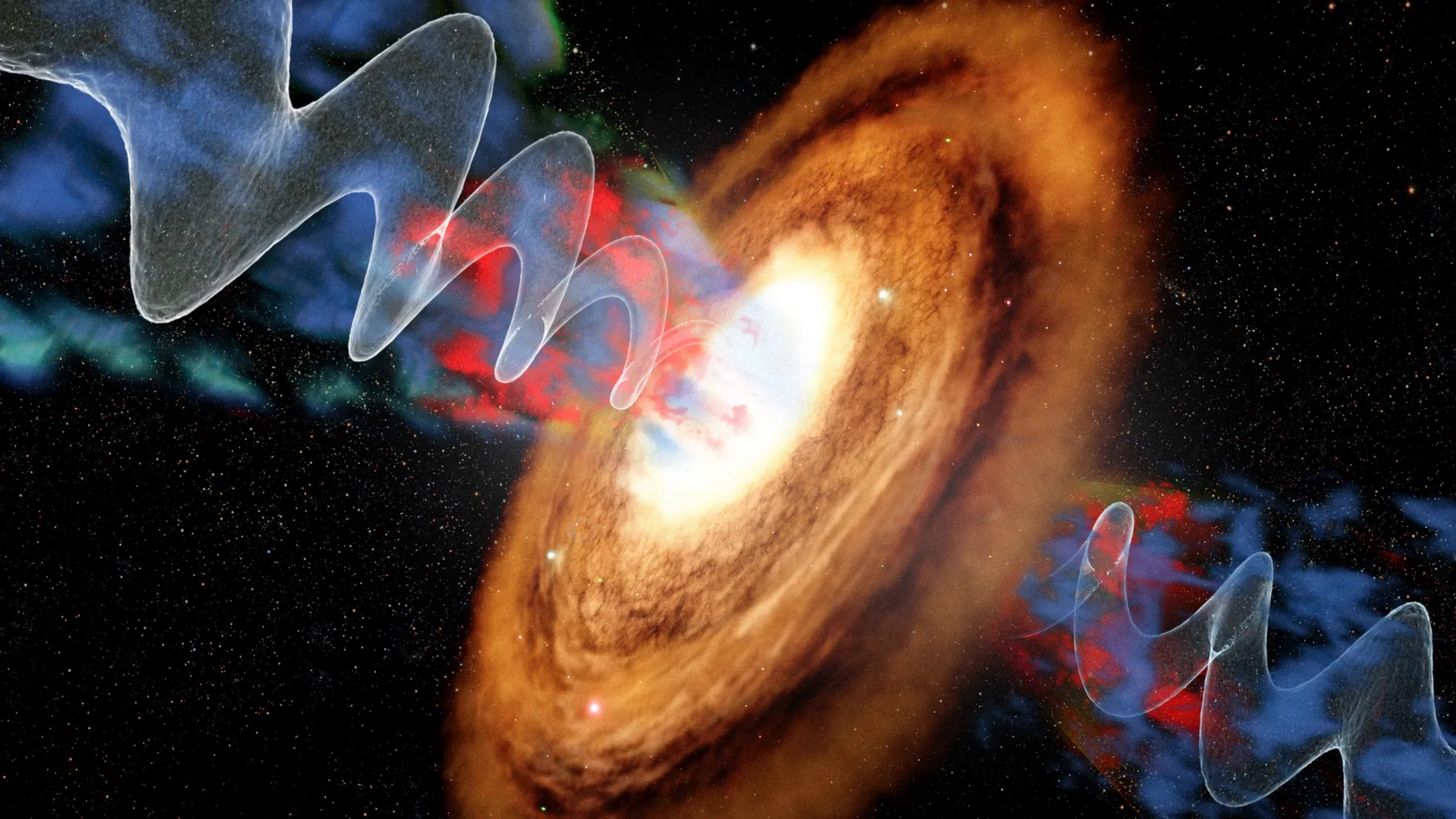

A nearby active galaxy called VV 340a offers a dramatic look at how a supermassive black hole can reshape its entire host.
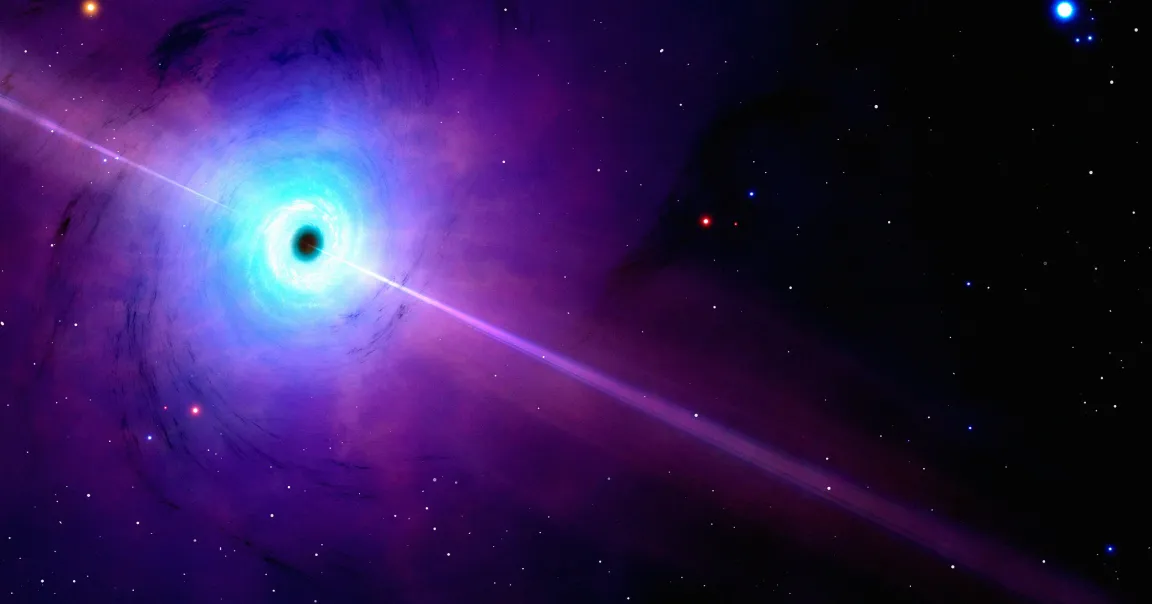

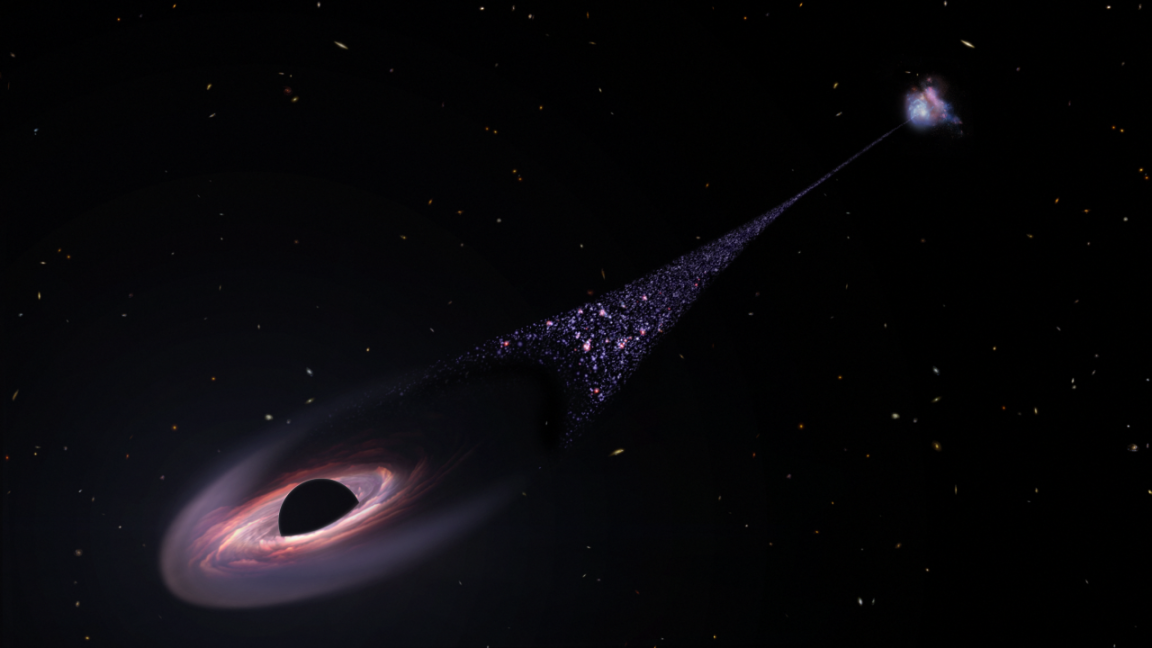
An international team of astronomers claim to have made a baffling discovery with the help of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope: the first runaway supermassive black hole that’s rocketing away from its home at a staggering speed.

Researchers using the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope have confirmed an actively growing supermassive black hole within a galaxy just 570 million years after the Big Bang.
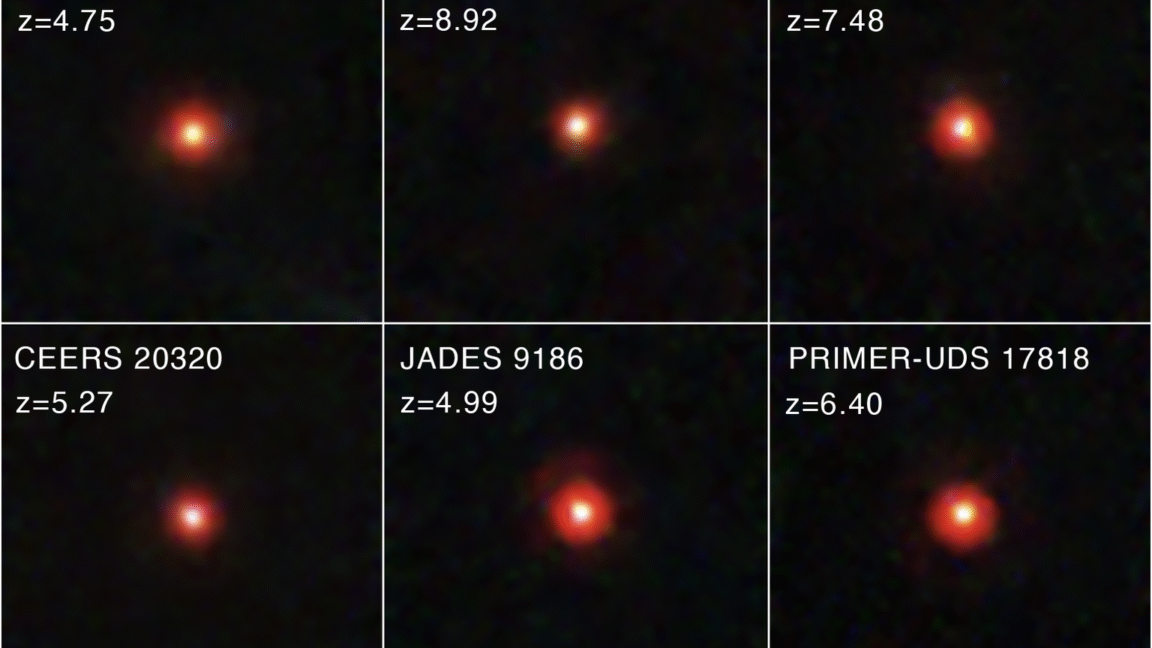

Early superdense star clusters may have planted seeds for monster black holes.
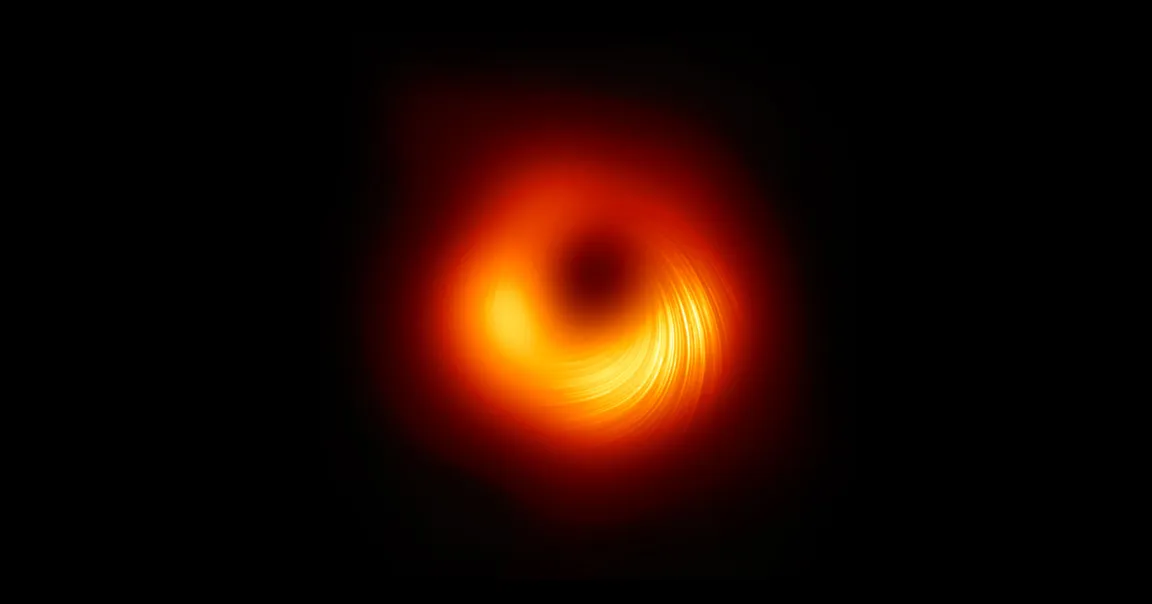

Now, by comparing observations from 2017, 2018, and 2021, scientists made a surprising discovery about how the magnetic fields near the black hole, dubbed M87*, change over time.

A supermassive black hole in the center of the radio quasar RACS J032021.44-352104.1 (RACS J0320-35 for short) is growing at one of the fastest rates ever recorded.

A new theory proposes that Population III.1 supermassive stars were progenitors of supermassive black holes in the early Universe.

Astronomers have caught a supermassive black hole in the act of awakening from a long slumber, providing an unprecedented glimpse into the earliest stages of black hole activity.
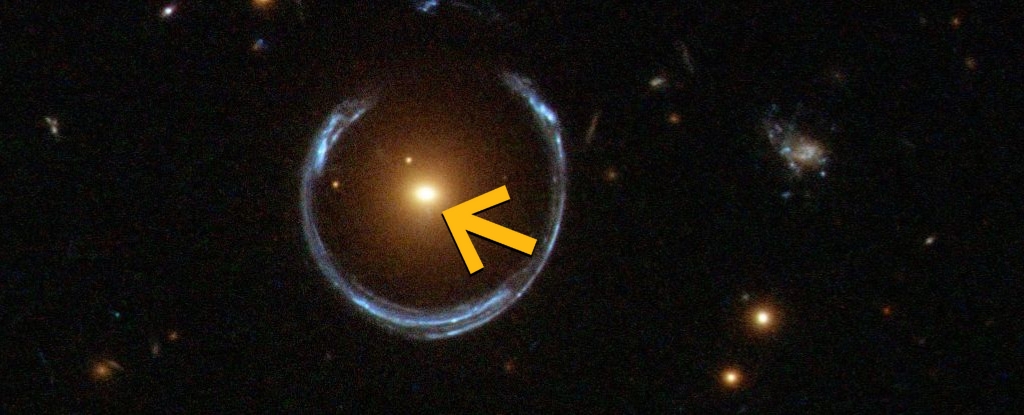
A black hole deep in the cosmos, some 5 billion light-years away, could be the most massive ever found.
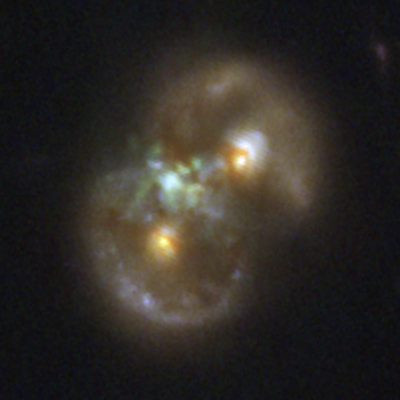

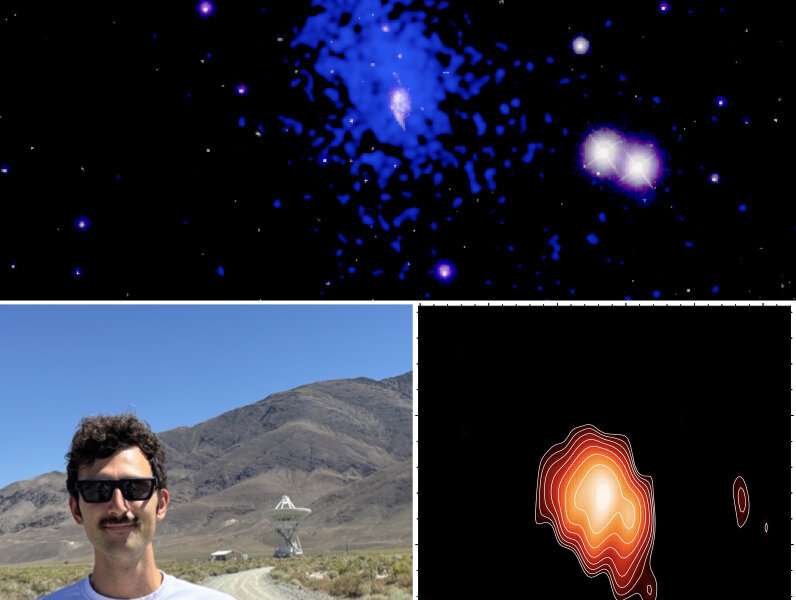
A pair of galaxies whose light has traveled for 8.3 billion years contains what astronomers believe is a supermassive black hole in the act of forming.

A team of astronomers led by Michael Janssen (Radboud University, The Netherlands) has trained a neural network with millions of synthetic black hole data sets.

A massive black hole at the heart of a galaxy in the Virgo constellation is waking up, shooting out intense X-ray flares at regular intervals that have puzzled scientists

In 2022 NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope discovered an abundance of tiny red objects scattered across the sky in the early universe. A large fraction of them are likely galaxies with supermassive black holes growing at their centers.

Using the James Webb Space Telescope, scientists witnessed a brilliant light show at the heart of our Milky Way galaxy.