A new study suggests a solution to the Little Red Dots mystery. Scientists think young supermassive black holes may go through a “cocoon phase,” where they grow surrounded by high-density gas they feed on.
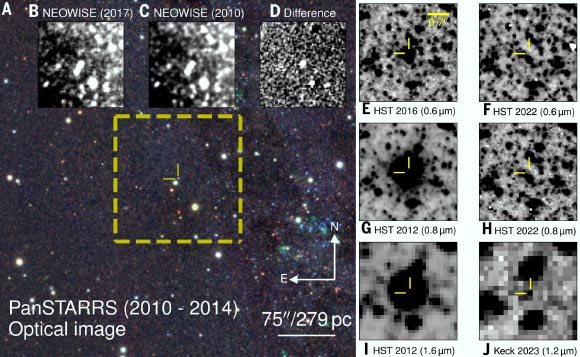
astronomers identified the clearest observational record yet of a massive star fading and vanishing into a black hole — an event once theorized but rarely seen.

A nearby active galaxy called VV 340a offers a dramatic look at how a supermassive black hole can reshape its entire host.

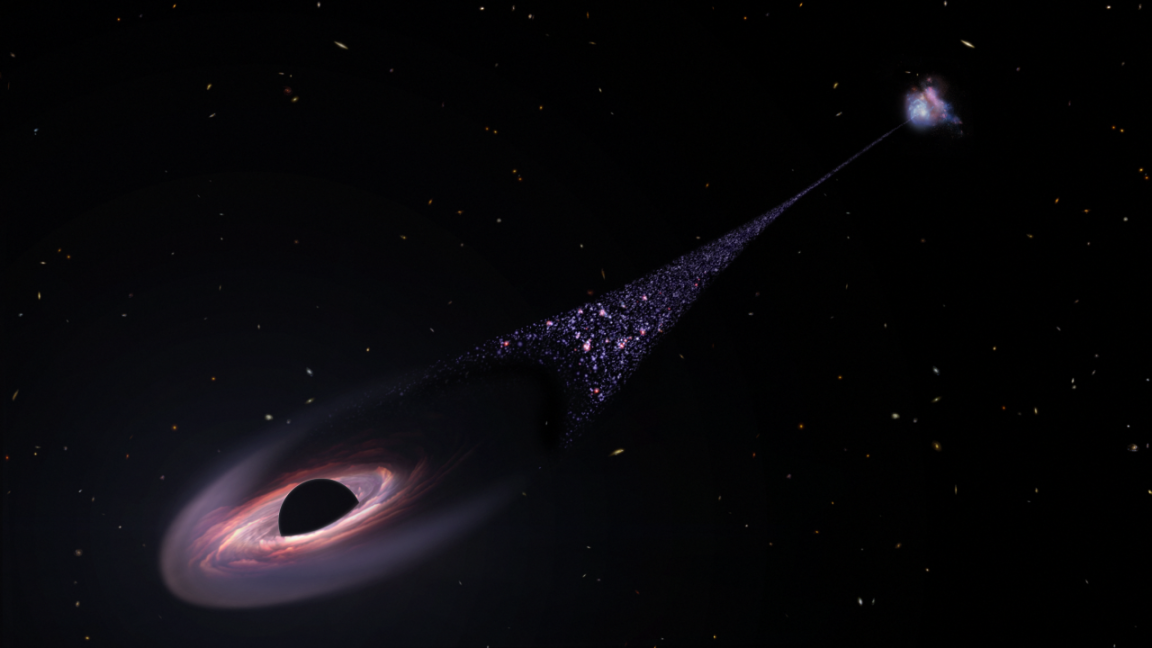
An international team of astronomers claim to have made a baffling discovery with the help of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope: the first runaway supermassive black hole that’s rocketing away from its home at a staggering speed.
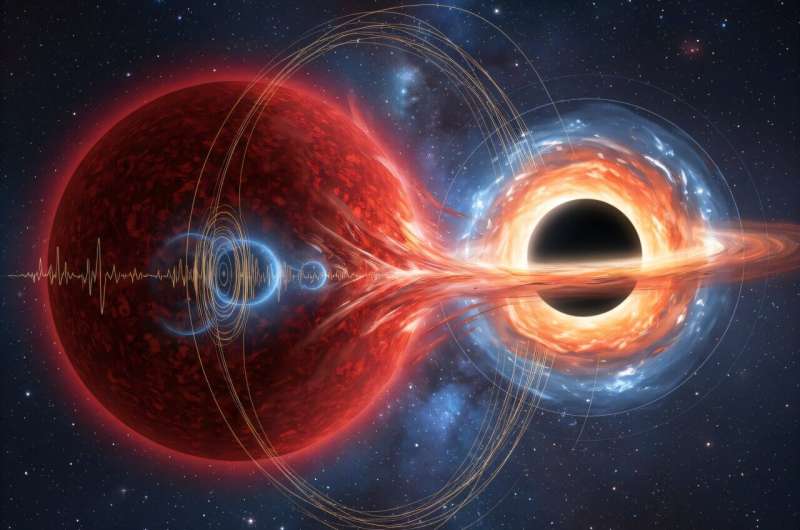
Astronomers from the University of Hawaiʻi Institute for Astronomy (IfA) have uncovered the turbulent past of a distant red giant by listening to its celestial "song."

Early superdense star clusters may have planted seeds for monster black holes.
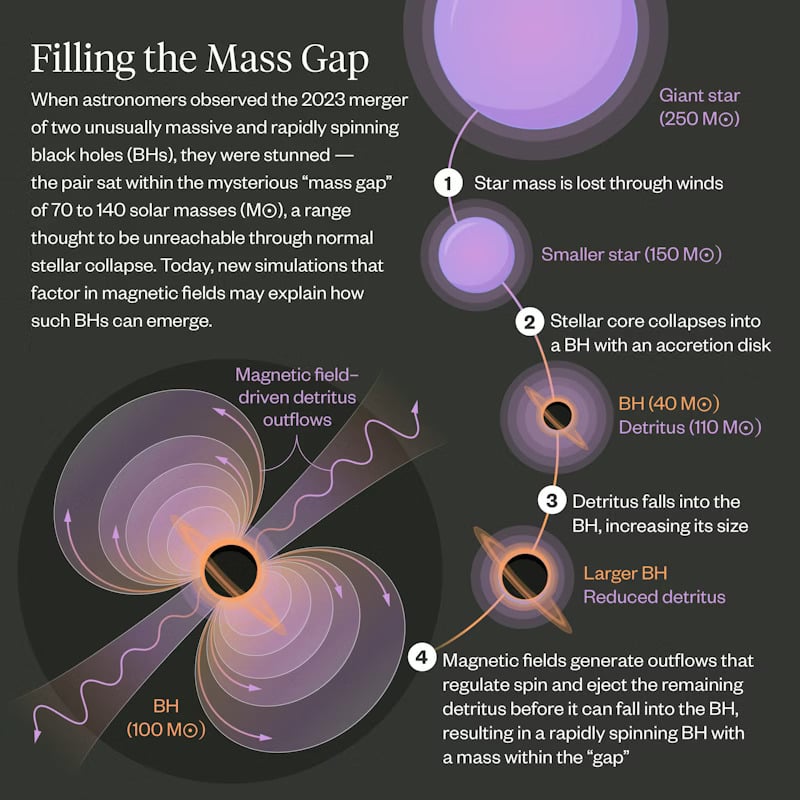
The black hole was bigger than expected, and while the answer was hiding in plain sight, it still rewrites what we thought was possible.

Gravitational waves from the birth of two newborn black holes caught the attention of scientists last year. Scientists have discovered something spectacular about the birth of one of the black holes.

If a new proposal by MIT physicists bears out, the recent detection of a record-setting neutrino could be the first evidence of elusive Hawking radiation.

The researchers suggest that LIGO and Virgo picked up the signals of a black hole collision in a different universe than ours.
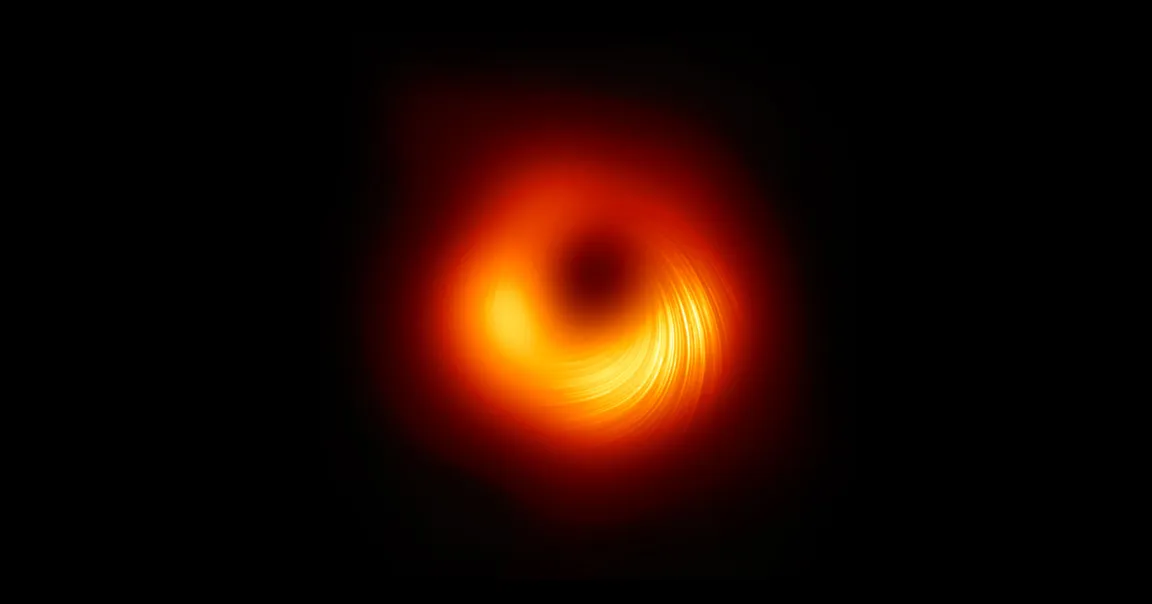

Now, by comparing observations from 2017, 2018, and 2021, scientists made a surprising discovery about how the magnetic fields near the black hole, dubbed M87*, change over time.

A supermassive black hole in the center of the radio quasar RACS J032021.44-352104.1 (RACS J0320-35 for short) is growing at one of the fastest rates ever recorded.

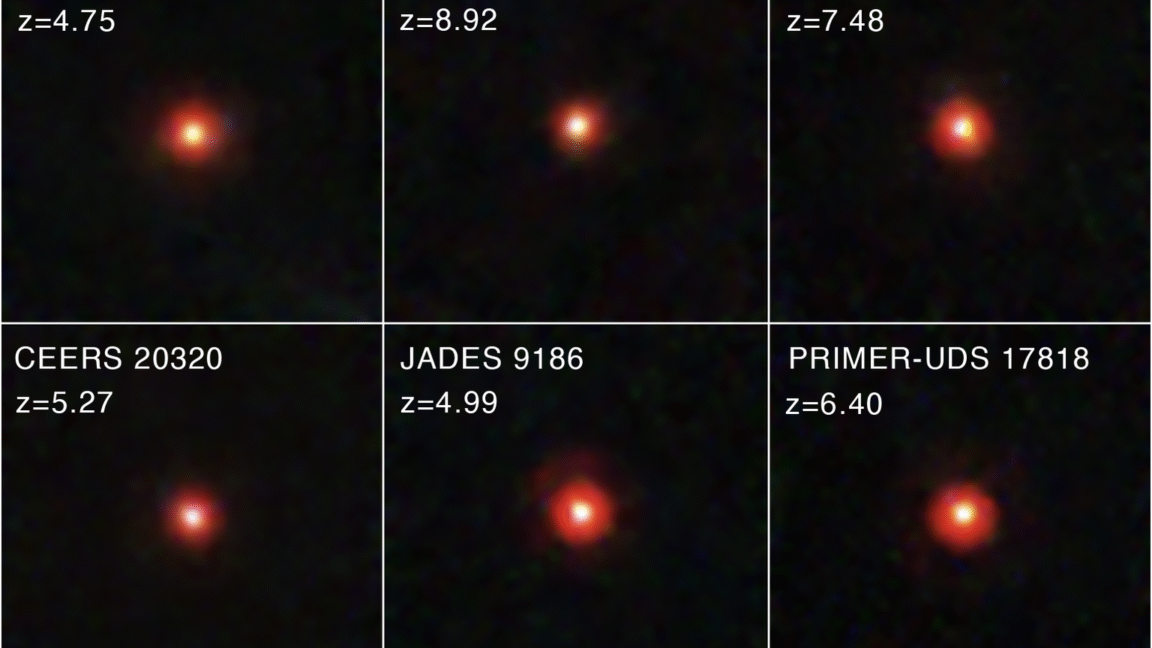
A tiny blob of red light spotted at the beginning of the Universe could represent the first direct evidence for a supermassive black hole formation pathway.
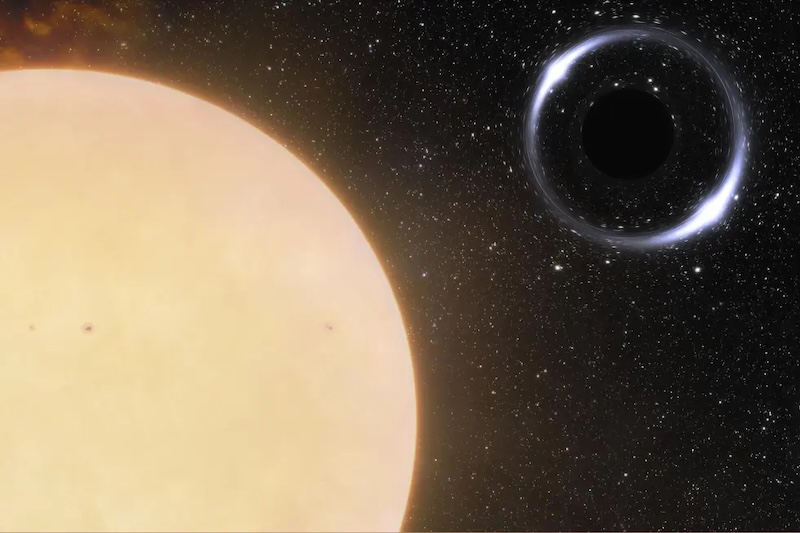

Dark matter particles could accumulate inside giant Jupiter-like exoplanets. Dense dark matter particles could eventually collapse to form a black hole inside a planet. The black hole could then ultimately consume the entire planet.
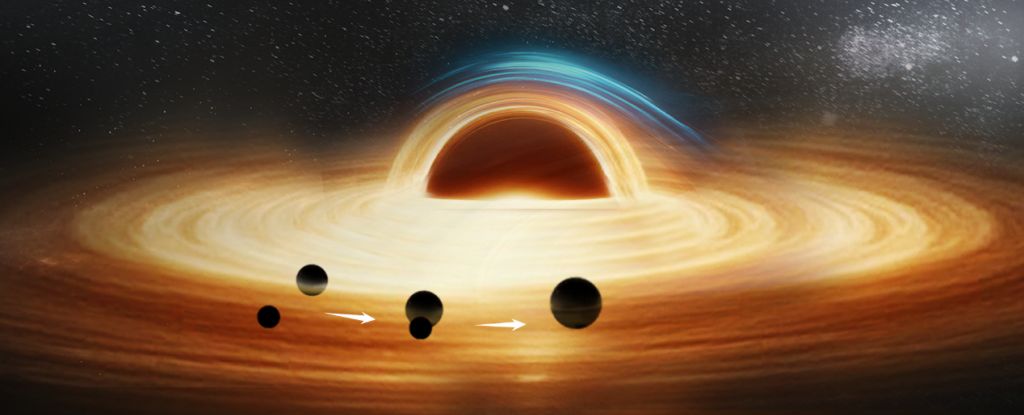

According to a new analysis of data from the LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA collaboration, data from a 2019 binary black hole collision showed signs of an anomalous acceleration that suggests the presence of a third black hole.