
An object spotted in deep space is the strongest candidate yet for a galaxy arrested during early development.
Something massive is lurking in the darkness of space, a mysterious object with the weight of a million Suns but no light to give it away.

Dark dwarfs are hypothetical dark matter-powered objects that formed from the cooling of brown dwarfs.

Dark matter particles could accumulate inside giant Jupiter-like exoplanets. Dense dark matter particles could eventually collapse to form a black hole inside a planet. The black hole could then ultimately consume the entire planet.

Scientists are on the trail of a mysterious five-particle structure that could challenge one of the biggest theories in physics: string theory.

Dark matter affects how stars move within galaxies, how galaxies build up over time, and how everything in the universe is held together - but no existing tool has directly detected it. While dark matter does not reflect, absorb, or emit light, it can still be indirectly observed by telescopes.

Researchers propose a new theory for the origin of dark matter. It could have formed in the early universe from the collision of massless particles that lost their energy and condensed.
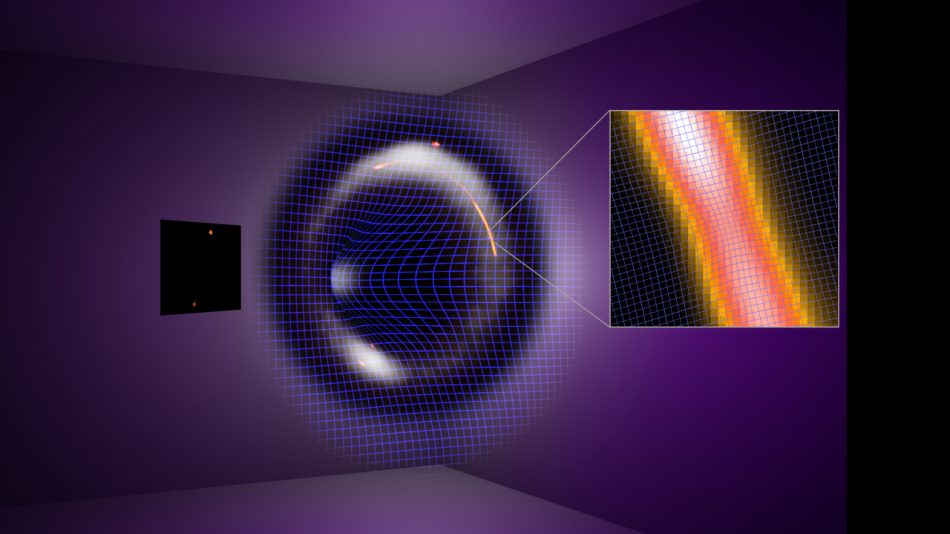
Recent research proposes a new form of dark matter that may actually be lighter in mass than other dark matter candidates.
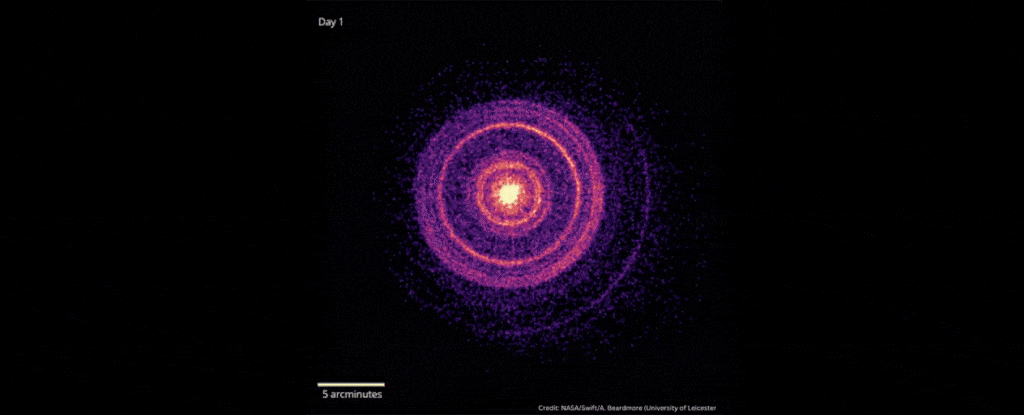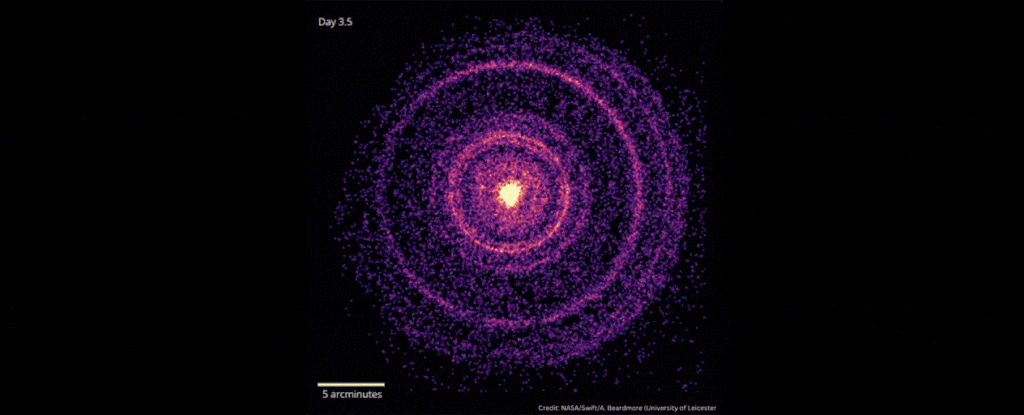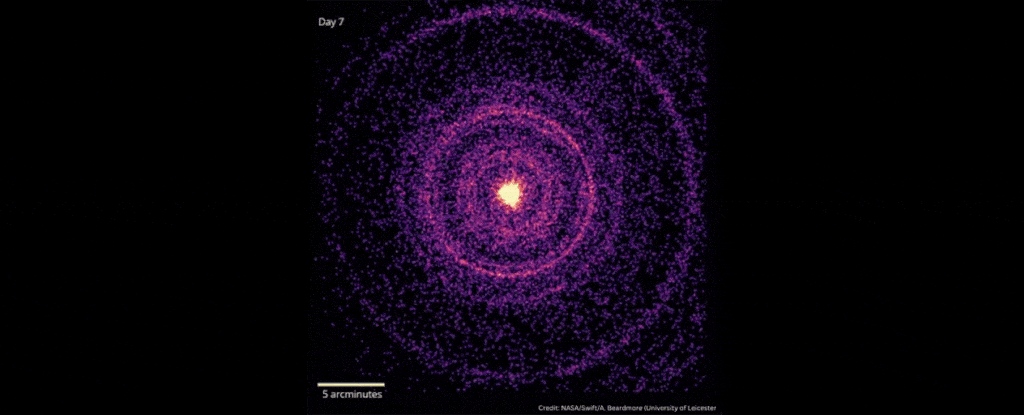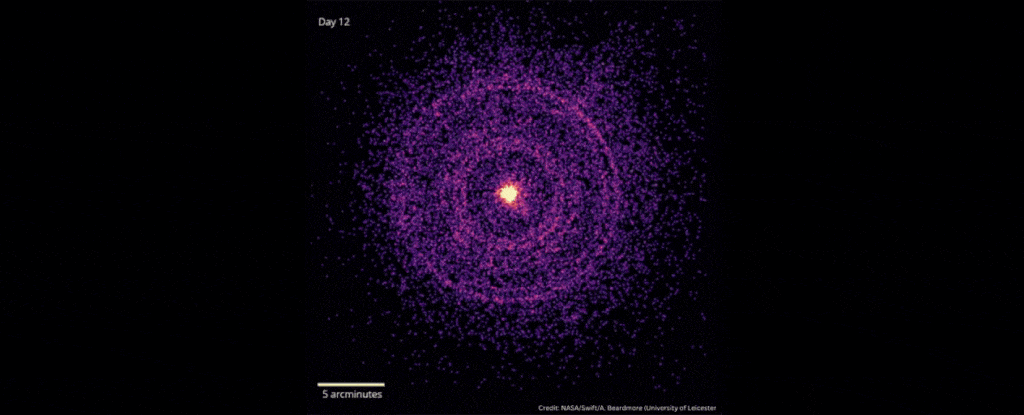
In October 2022, scientists detected the explosive death of a star 2.4 billion light-years away that was brighter than any ever recorded.

In case dark matter didn't seem mysterious enough, a new study proposes that it could have arisen before the Big Bang.

A new study suggests that dark matter may have originated from a separate "Dark Big Bang," occurring shortly after the birth of the universe.

Neutron stars with a penchant for extreme spinning could be churning out one of the most sought-after particles in the Universe.

Two giant clusters of galaxies observed in the process of colliding are going so hard that their dark matter has basically detached from normal matter and flown ahead.

Dark matter could provide supermassive black holes the brakes they need to bring them crashing together at the end of a long, spiraling journey towards their destiny.

The two new satellites, named Virgo III and Sextans II, were discovered in a region of space already crowded with more dwarf galaxies than models of dark matter predict.