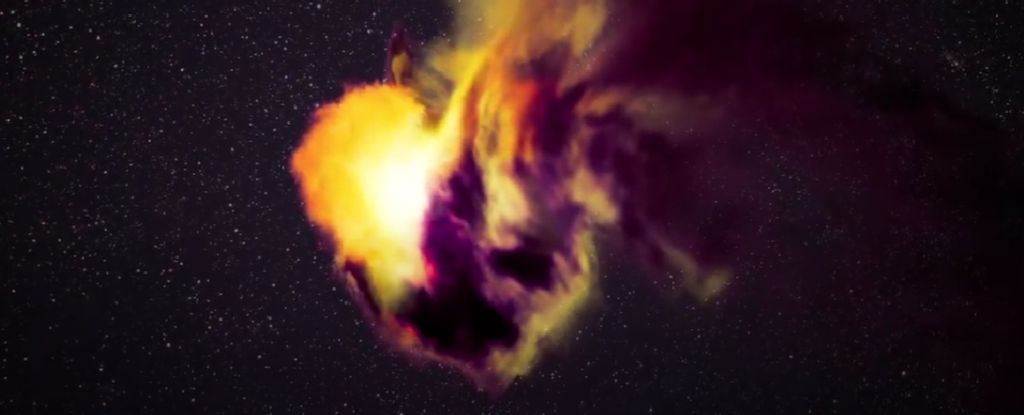

In 2021, astronomers watched in astonishment as a supernova 2.2 billion light-years away named SN2021yfj bloomed, rich with silicon, sulfur, and argon – something never before seen in an exploding star.
Astronomers in Hawaii detected three different stars being devoured by supermassive black holes that released more energy than 100 supernovas. These are the largest explosions since the Big Bang.

Scientists have traced radioactive elements on the seafloor back to the cosmic explosions they might have come from – and potentially linked the event to evolutionary changes in viruses in a lake in Africa.
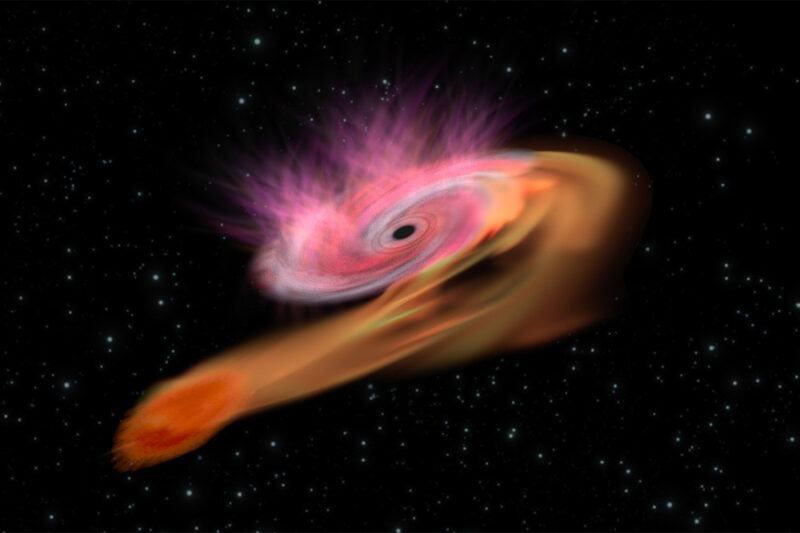

In April of 2024, astronomers spotted an unusual event that astronomers named EP240408a. While the explosion was originally thought to be a gamma-ray burst, it now appears it might represent a new class of powerful cosmic explosion.
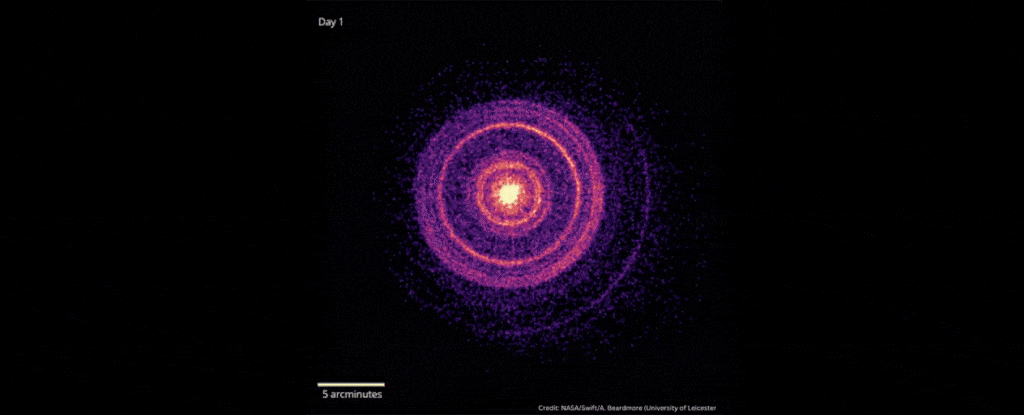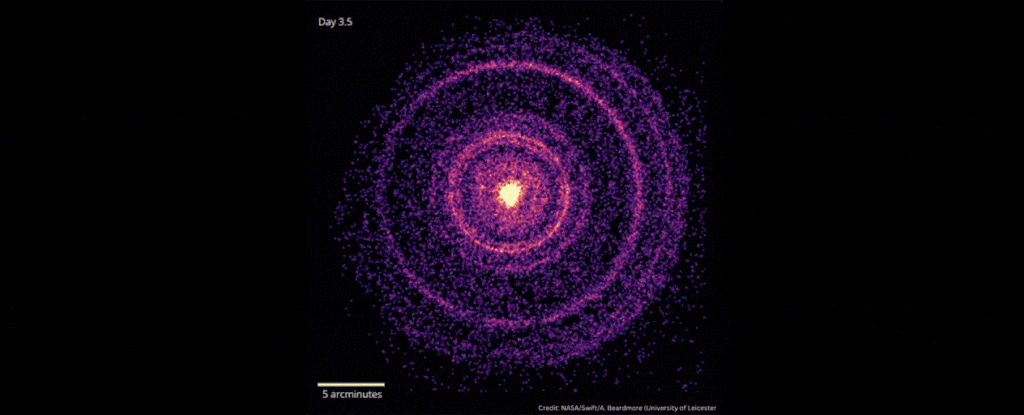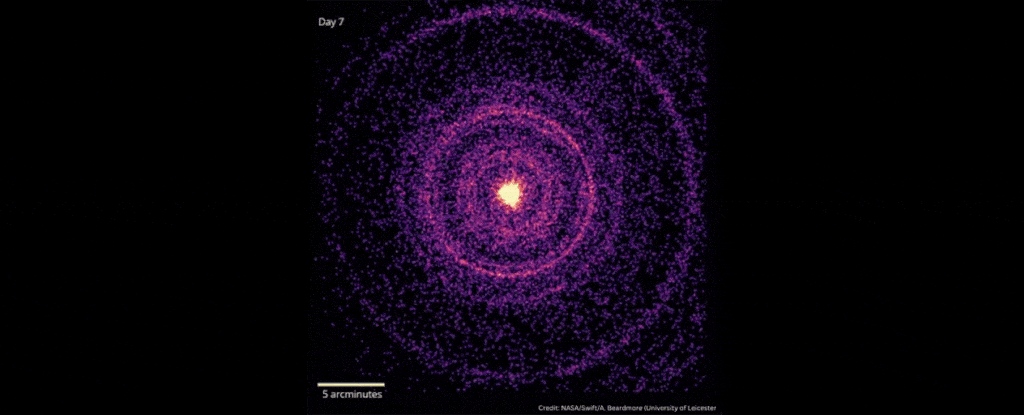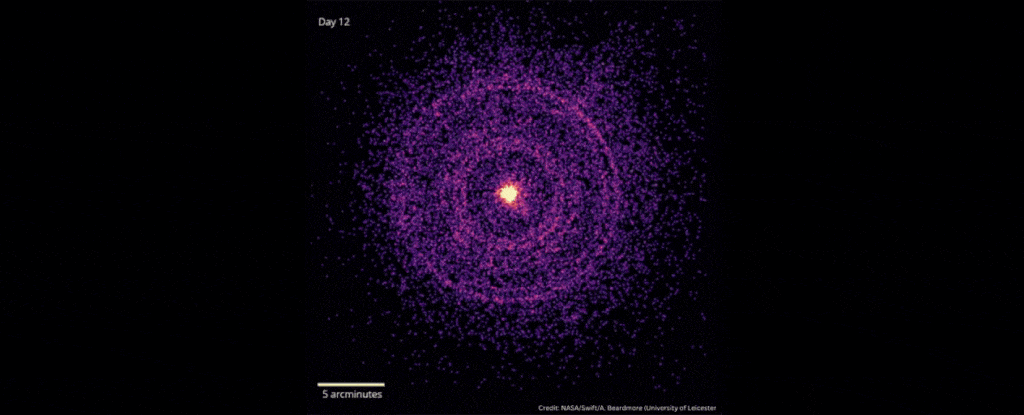
In October 2022, scientists detected the explosive death of a star 2.4 billion light-years away that was brighter than any ever recorded.

The signal could help explain why an explosion called a gamma ray burst appeared to be the most powerful ever detected.

The creation of any heavier elements would consume energy instead of releasing it. In order to explain the presence of these heavier elements today, it's necessary to find phenomena that can produce them.

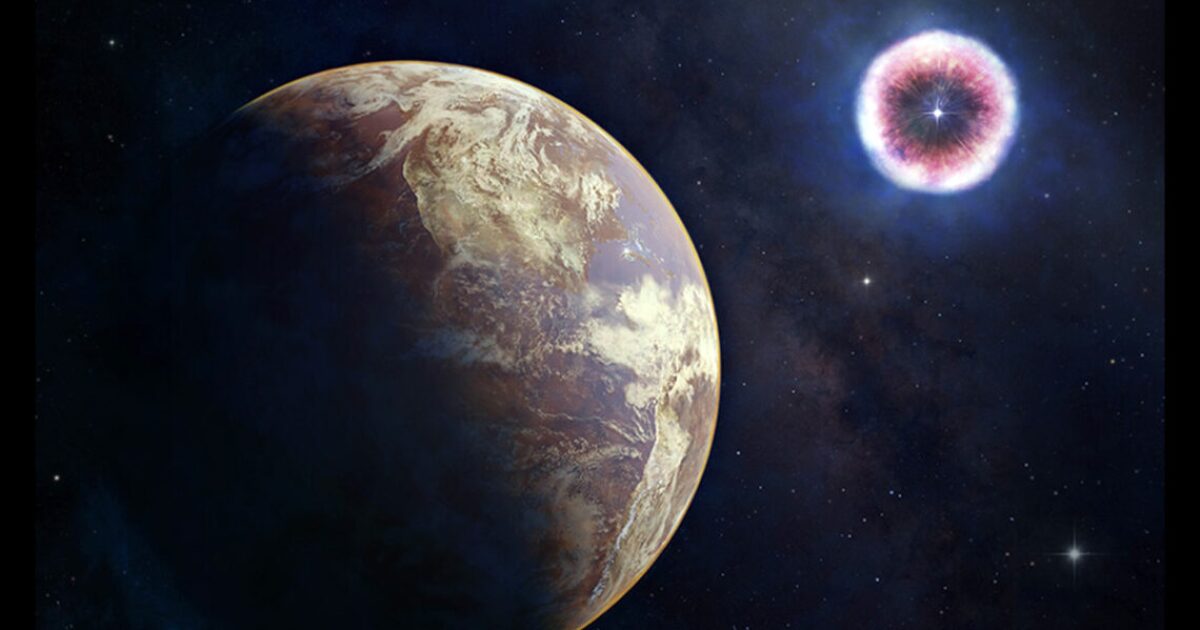
A star system, located 3,000 light-years away from Earth, is predicted to become visible to the unaided eye soon. This could be a once-in-a-lifetime viewing opportunity as the nova ouburst only occurs about every 80 years.

A strange star in the Milky Way bares the signature of a unique explosion of a giant star that once existed billions of years ago in the era of the cosmic dawn.

Last year, global astronomers picked up evidence of an explosion called a luminous fast blue optical transient, or LFBOT. But the bizarre thing about this explosion was that it kept exploding.

The burst that originated some 2.4 billion light-years away from Earth and struck the planet on 9 October last year may have led to changes in the upper ionosphere, according to a new study.

When scientists detected the gamma-ray burst known as GRB 221009A on Oct. 9, 2022, they dubbed it the brightest of all time, or BOAT. Follow-up studies showed that GRB 221009A was 70 times brighter and far more energetic than the previous record holder.

Astronomers studying black holes have serendipitously found another rarity: a dead star rocketing away from its birth supernova, leaving a comet-like trail of radio emission in its wake.

The explosive event labeled AT2021lwx was observed to be ten times brighter than any known supernova. This thing we have never, ever seen before – it just came out of nowhere.

Scientists believe the gamma-ray emission, which lasted over 300 seconds, is the birth cry of a black hole, formed as the core of a massive and rapidly spinning star collapses under its own weight.