
Life may have started in sticky, rock-hugging gels rather than inside cells. Researchers suggest these primitive, biofilm-like materials could trap and concentrate molecules, giving early chemistry a protected space to grow more complex.

Vast amounts of hydrogen could also be locked away in our planet's core, attached to the densely packed alloyed iron that lurks therein

By firing tiny projectiles of iron-carbon alloy from a high-speed cannon, scientists have finally demonstrated that a weird part-solid, part-liquid-like state thought to exist inside Earth's inner core is indeed possible.

New research has uncovered a striking link between the structure of our galaxy and the evolution of Earth's crust, showing its development was shaped by the impact of meteorites during its journey through the Milky Way.
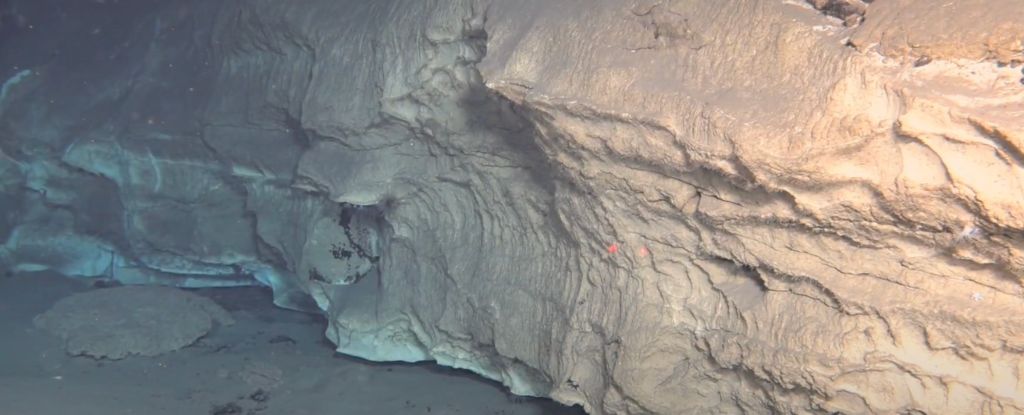

At 11.1 square kilometers (4.3 square miles), the newly discovered hydrothermal field is over a hundred times larger than its Atlantic counterpart.
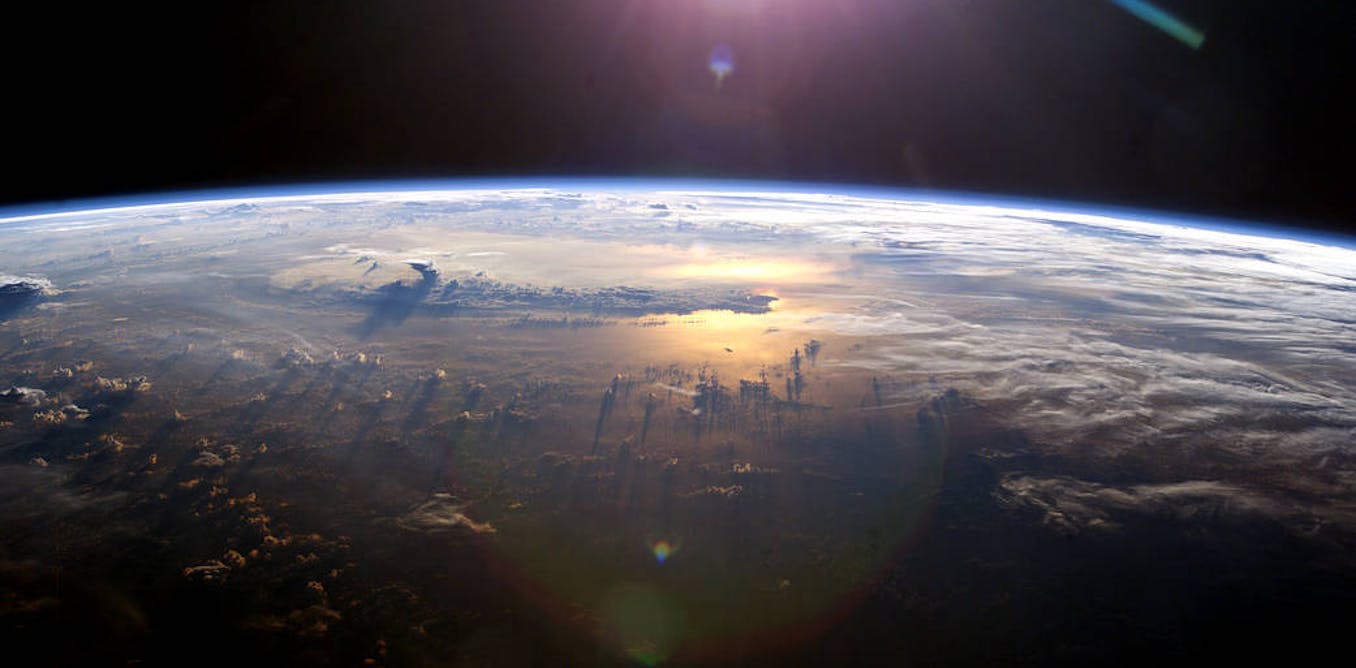

Real world measurements of how much extra heat the Earth is trapping are well beyond most climate models. That's a real problem.
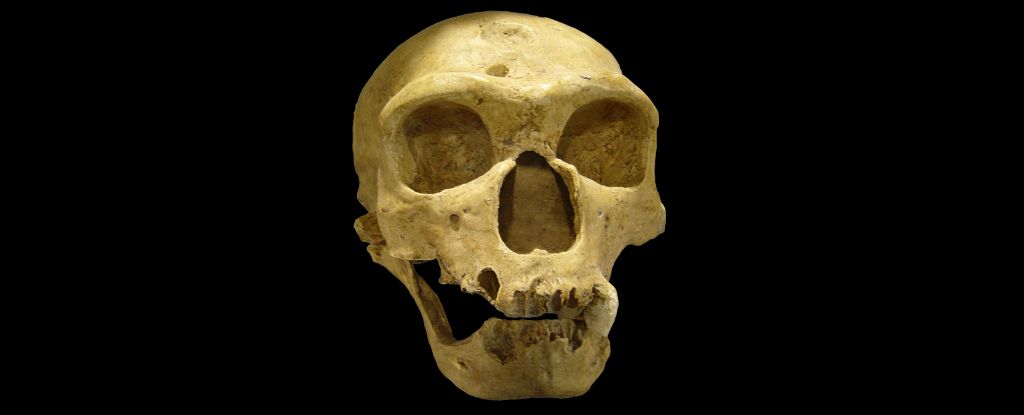
A new research suggests that a shift in the Earth's magnetic poles around 41,000 years ago, known as the Laschamp event, may have contributed to the extinction of Neanderthals.
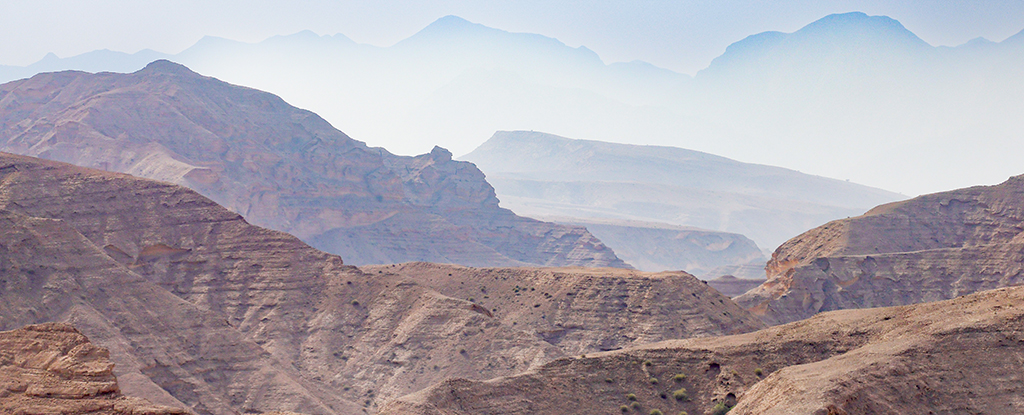

Rising from Earth's core beneath Oman, the unusually elusive column of hot rock shows no surface volcanic activity, unlike typical plumes.
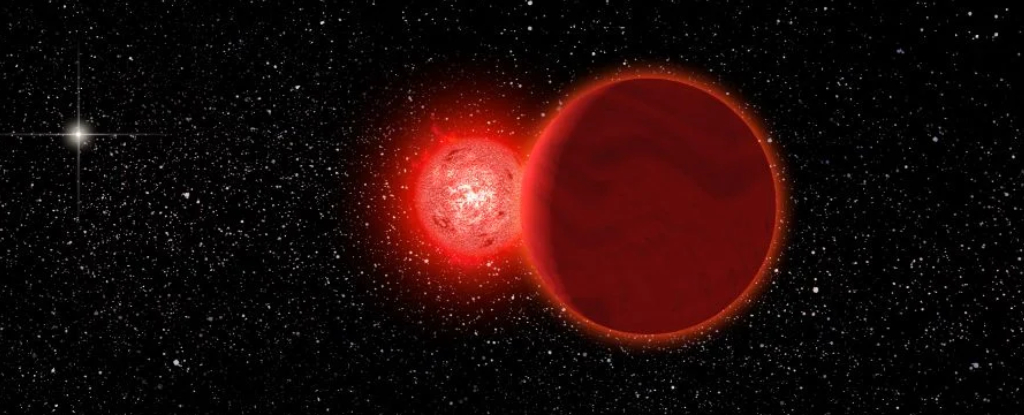

About 70,000 years ago Scholz's star passed through the Oort Cloud. It may have perturbed some comets from the Oort Cloud. But we won't know for a couple of million years because that's how long it would take for a comet to reach us.
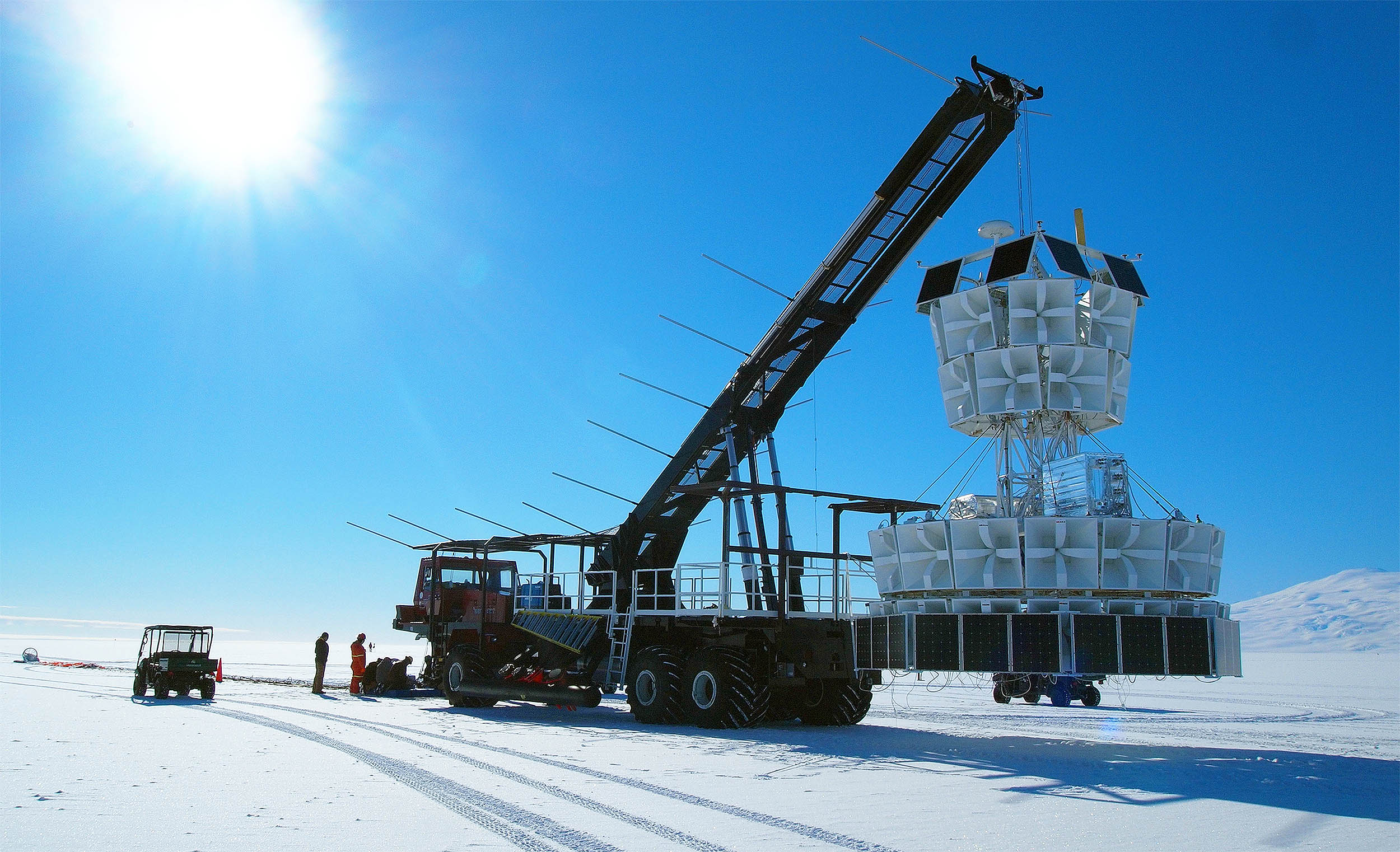

The ANITA experiment, built to detect neutrinos, has detected very strange radio waves coming from deep below the Antarctic ice.
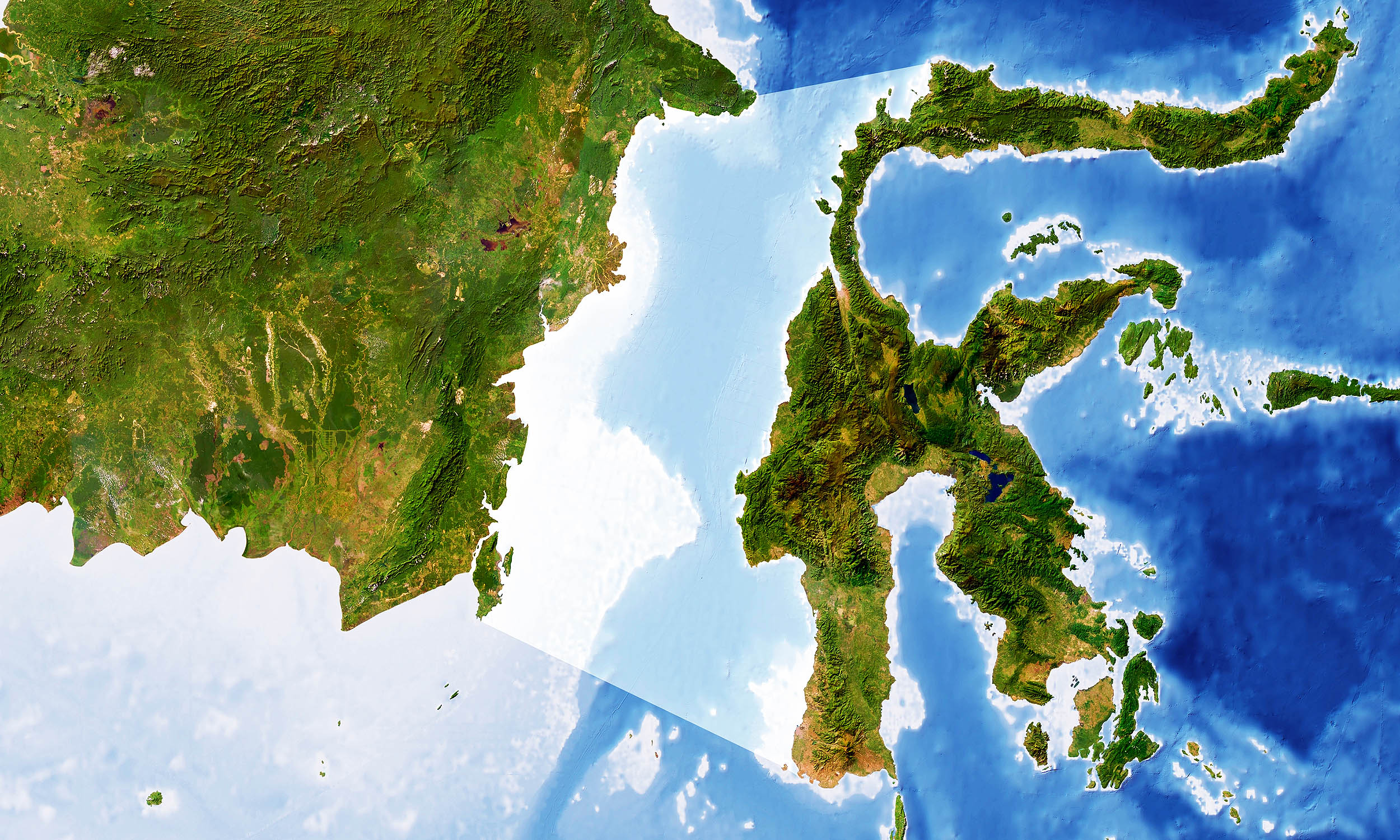
The Wallace Line divides species in Southeast Asia. A deep ocean trench prevents animal migration. Even flying birds rarely cross it.
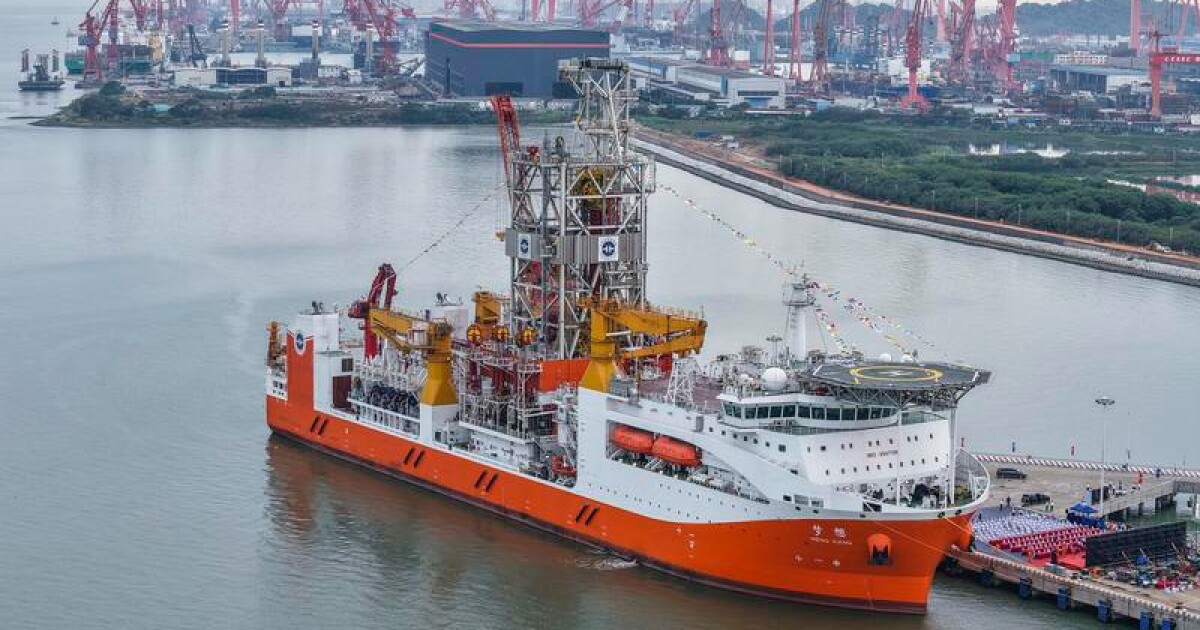

China is going full Jules Verne as it prepares to go where no drill has gone before. As part of its Deep Ocean Drilling Program, the special-built Meng Xiang ("Dream") drill ship is gearing up for a multi-year effort to pierce the Earth's crust.
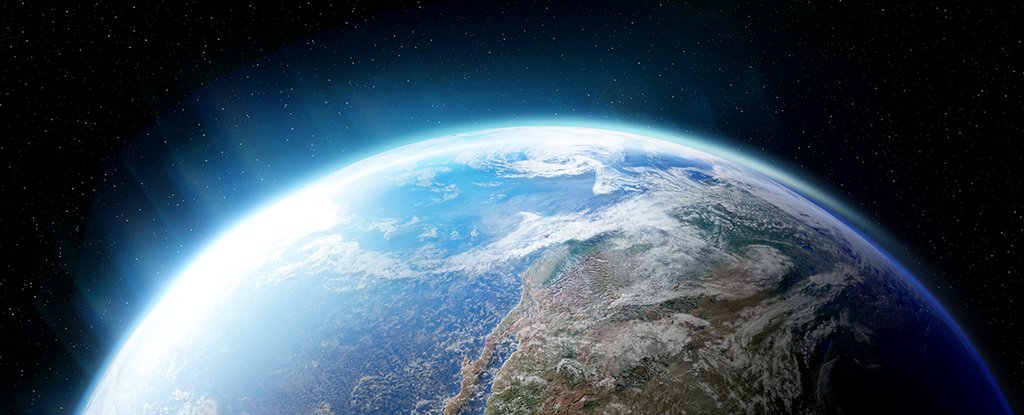

But Earth's atmosphere wasn't always like it is today, and scientists predict that in the future, it will revert back to one that's rich in methane and low in oxygen.

Here are nine natural mysteries across the world that scientists have yet to fully explain.

New research uncovers the strongest solar event ever detected - rewriting our understanding of space weather and radiocarbon dating.