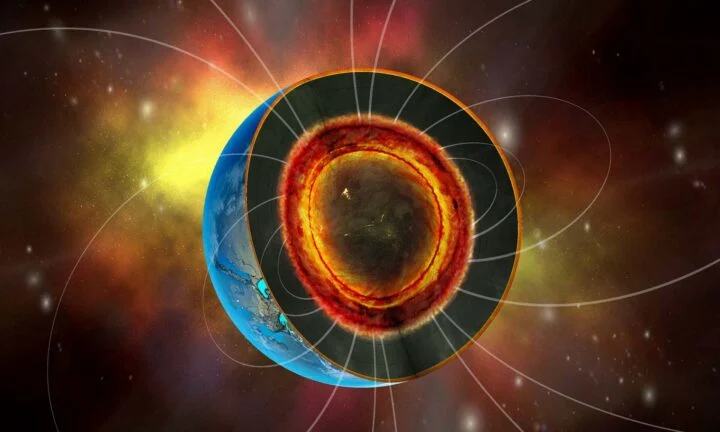

Deep beneath the surface of super-earths, oceans of molten rock may be doing something extraordinary: powering magnetic fields strong enough to shield entire planets from dangerous cosmic radiation.
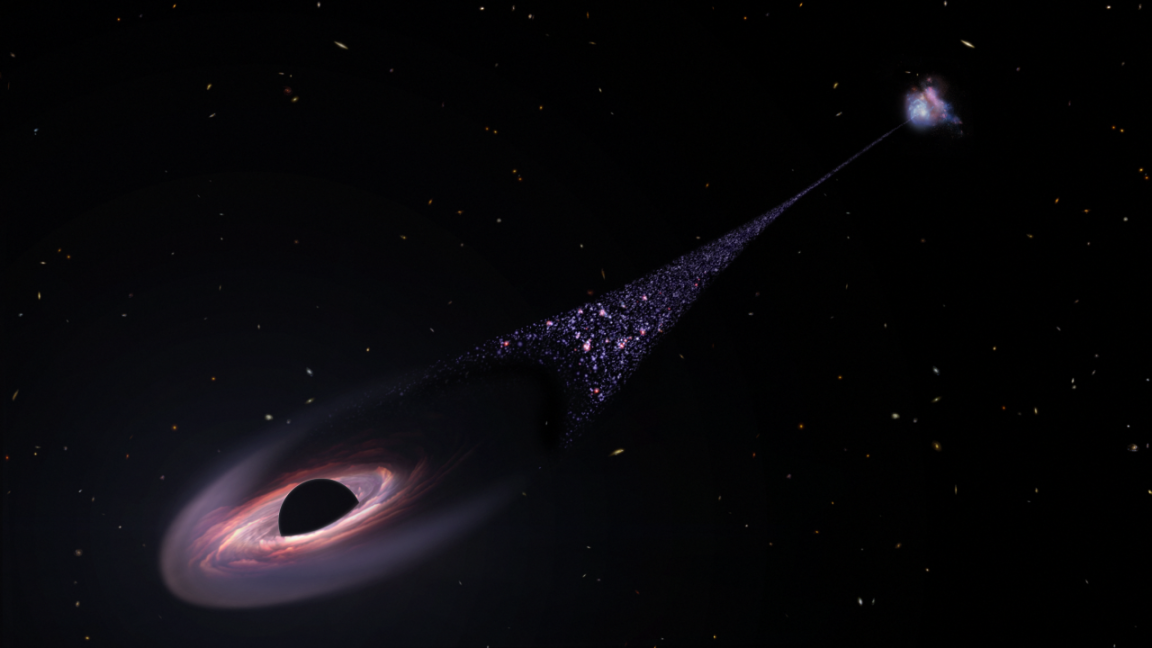
A new study suggests a solution to the Little Red Dots mystery. Scientists think young supermassive black holes may go through a “cocoon phase,” where they grow surrounded by high-density gas they feed on.
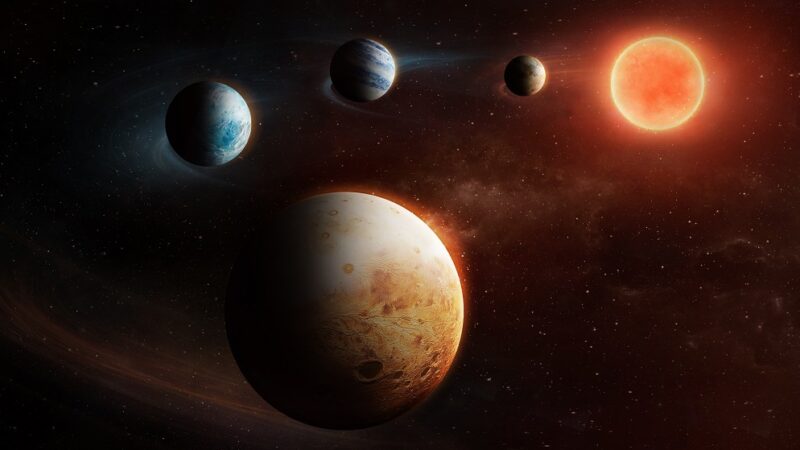

The planets around LHS 1903 – a cool faint red dwarf star – begin as expected with a rocky planet orbiting close by and then two gas worlds. A surprising 4th planet at the system’s outer edge that is rocky, rather than gaseous.
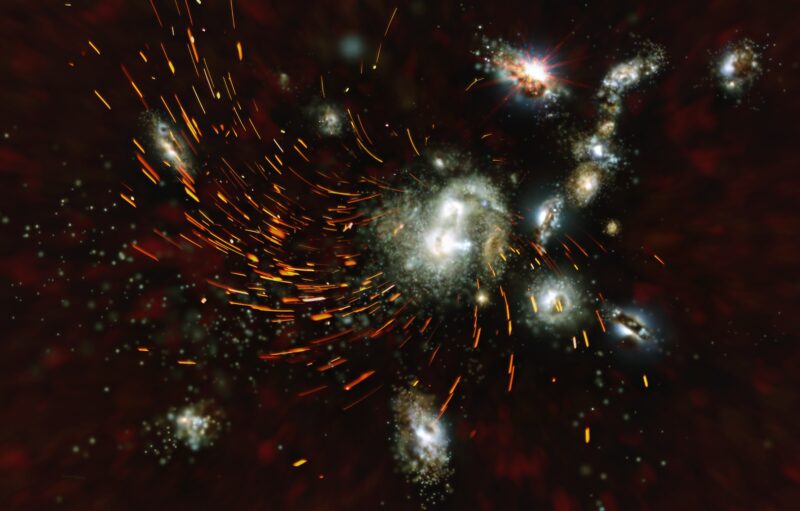
Astronomers found evidence a giant elliptical galaxy may form through the rapid collapse of a young galaxy cluster.
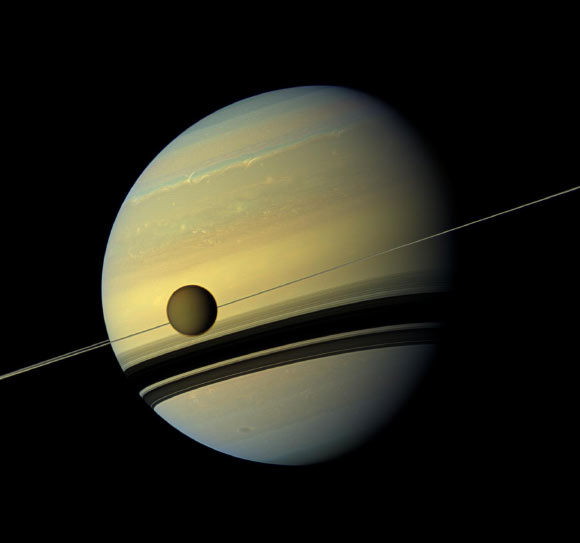

Scientists argue that two Saturnian moons, Titan and Hyperion, are not primordial worlds, but the result of a dramatic merger between two ancient moons.
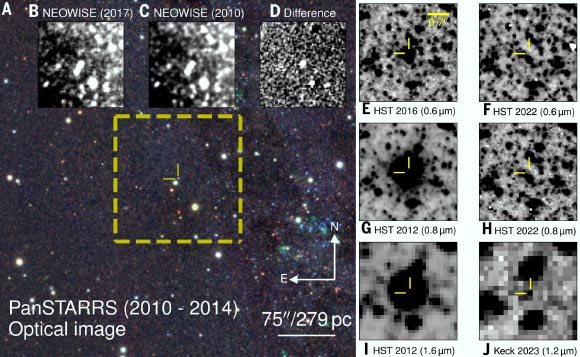
astronomers identified the clearest observational record yet of a massive star fading and vanishing into a black hole — an event once theorized but rarely seen.
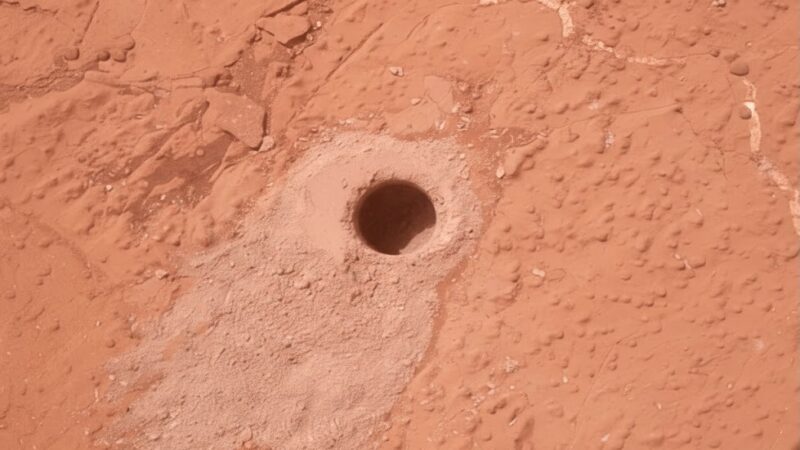

The researchers found that additional studies of the data from Curiosity show that non-biological sources they had considered don’t fully explain the organics. They conclude, therefore, that a biological source is a reasonable hypothesis.
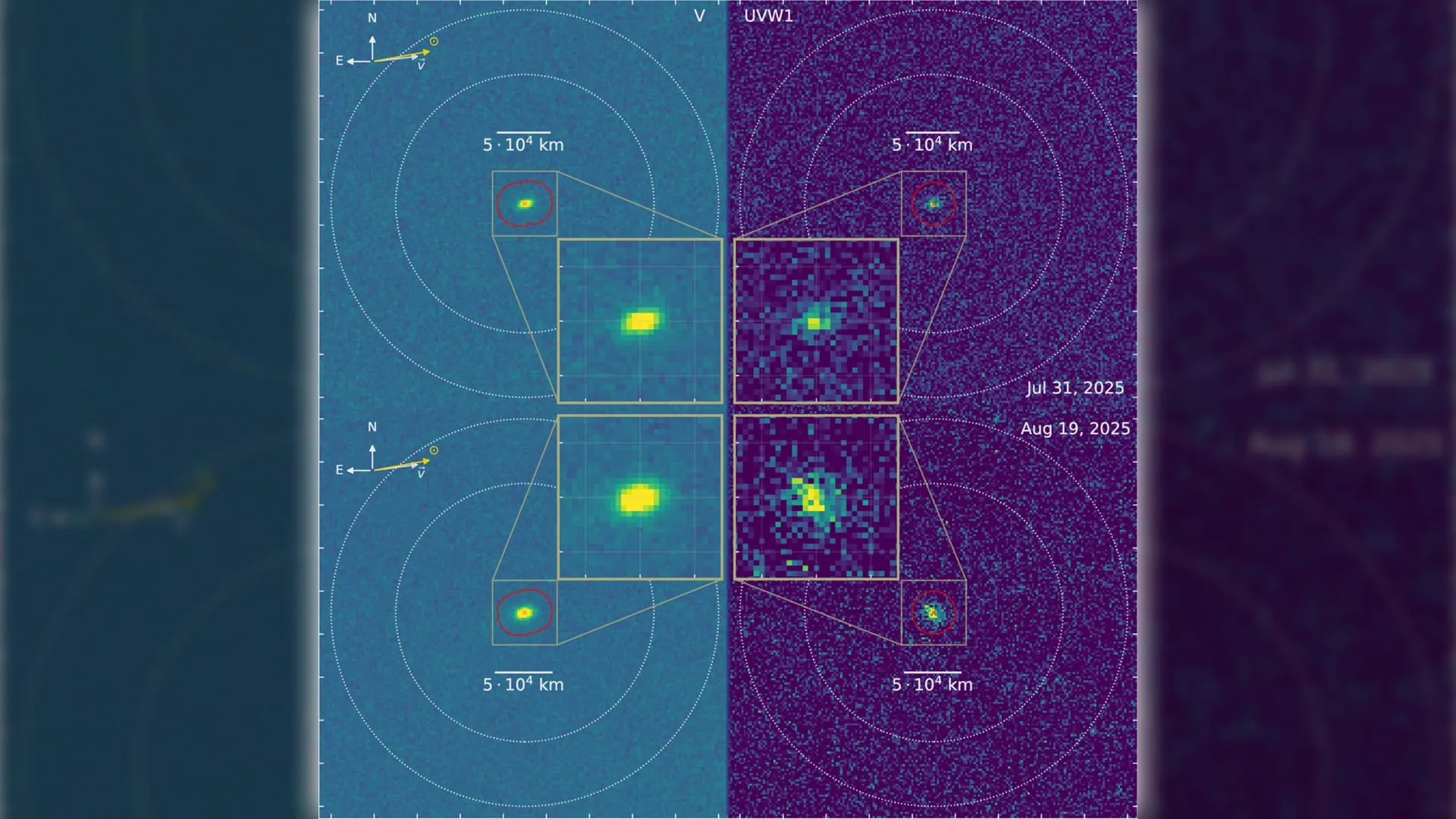
The comet is blasting out water at a rate of about 40 kilograms per second while still far from the Sun—much farther than where most comets “switch on.”
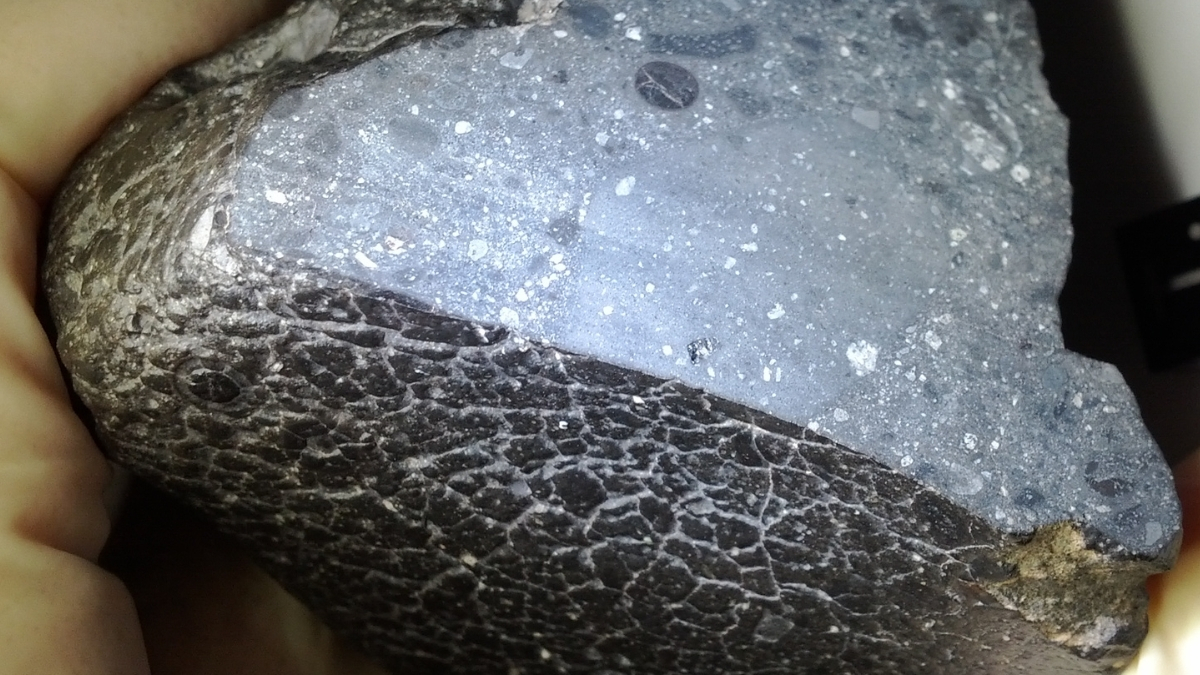

The chemical math of the interior of the meteorite Black Beauty means that those little bits of rock hold up to about 11% of the sample's total water content.
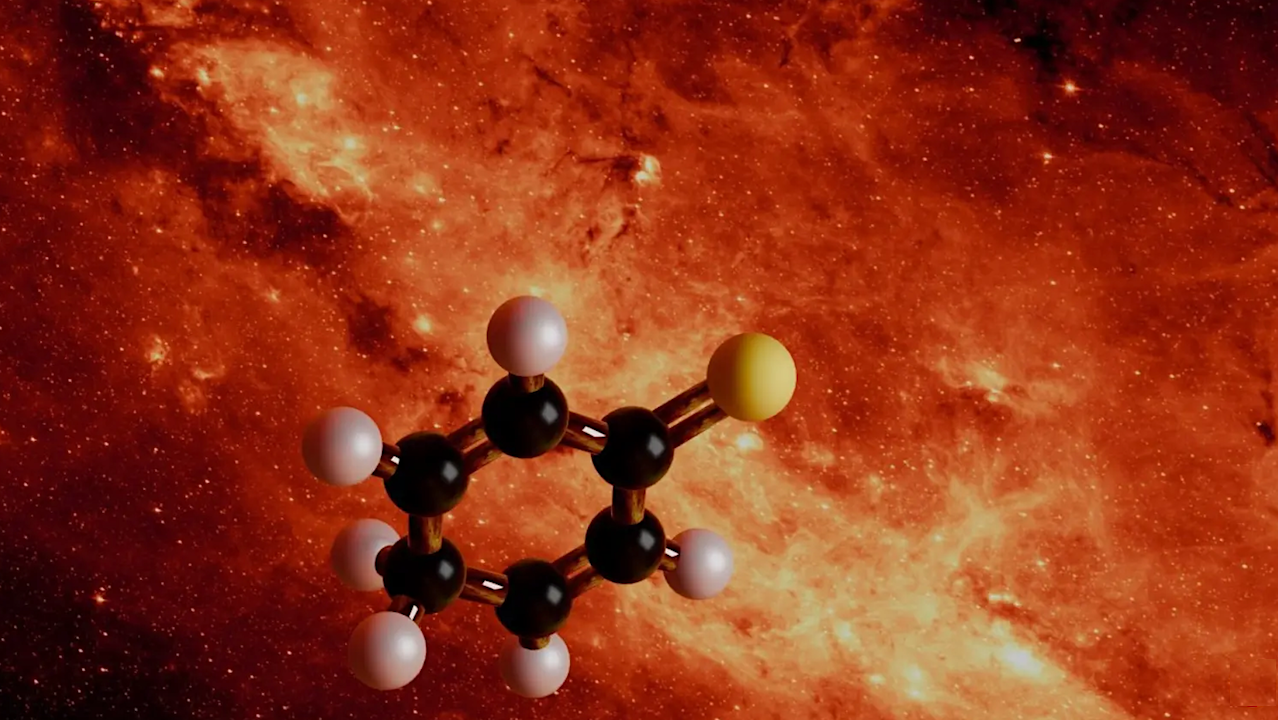
Researchers have identified the largest sulfur-bearing molecule ever found in space: 2,5-cyclohexadiene-1-thione (C6H6S).
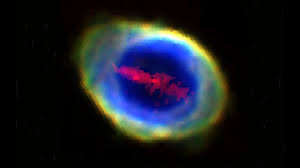
A mysterious bar-shaped cloud of iron has been discovered inside the iconic Ring Nebula.
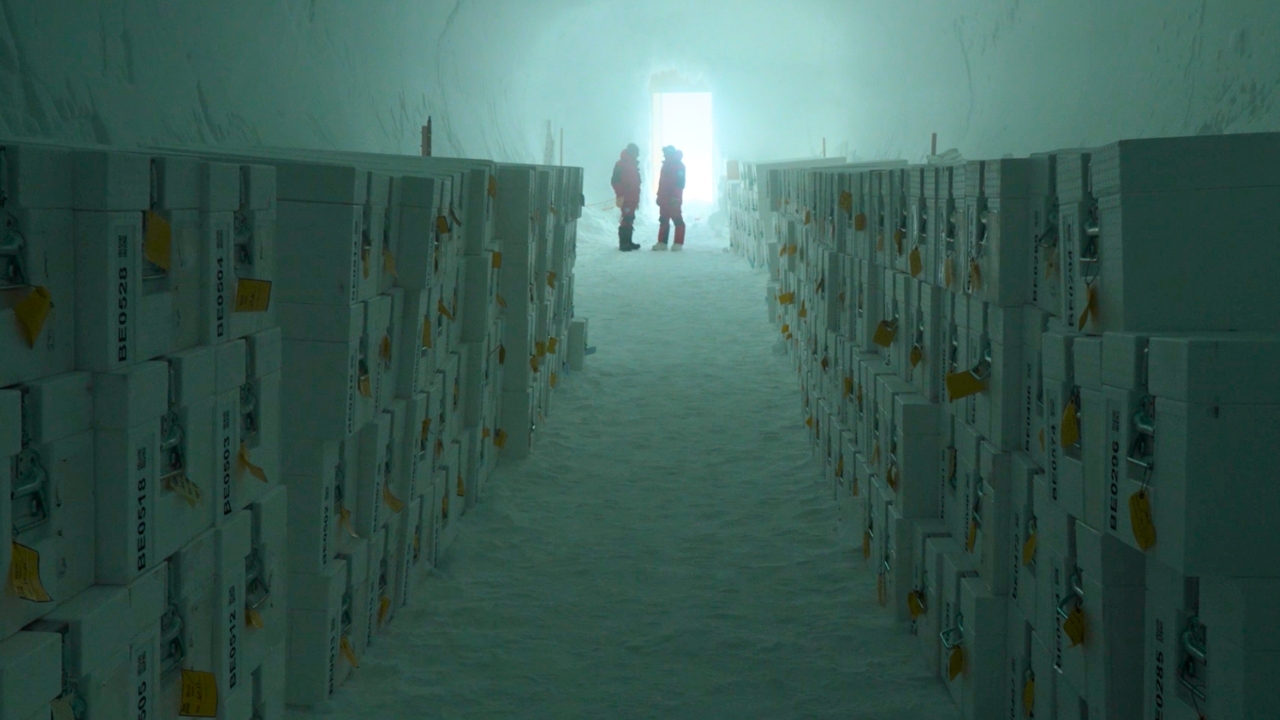

Scientists on Wednesday sealed ancient chunks of glacial ice in a first-of-its-kind sanctuary in Antarctica in the hope of preserving these fast-disappearing records of Earth's past climate for centuries to come.
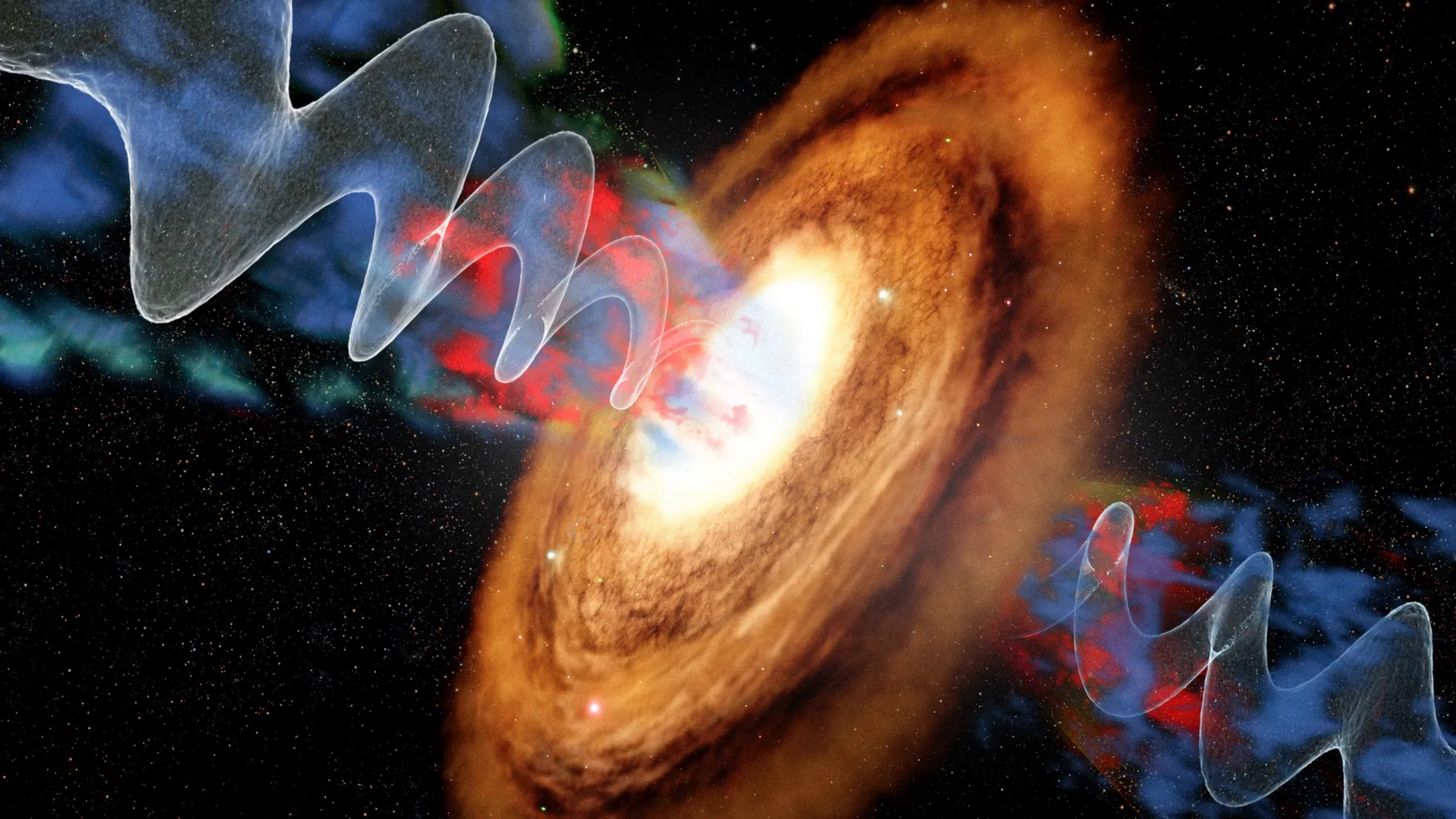

A nearby active galaxy called VV 340a offers a dramatic look at how a supermassive black hole can reshape its entire host.
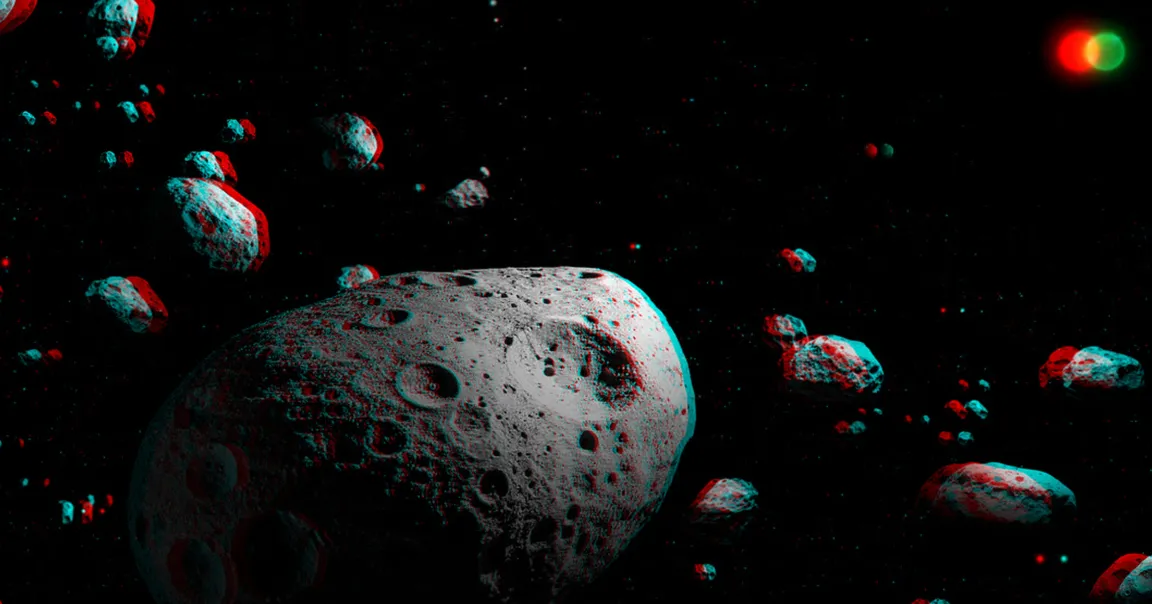

The unusual cosmic lump — dubbed 2025 MN45, 2,300 feet in diameter and located in the Main Asteroid Belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter — completes a full rotation every minute and 53 seconds.
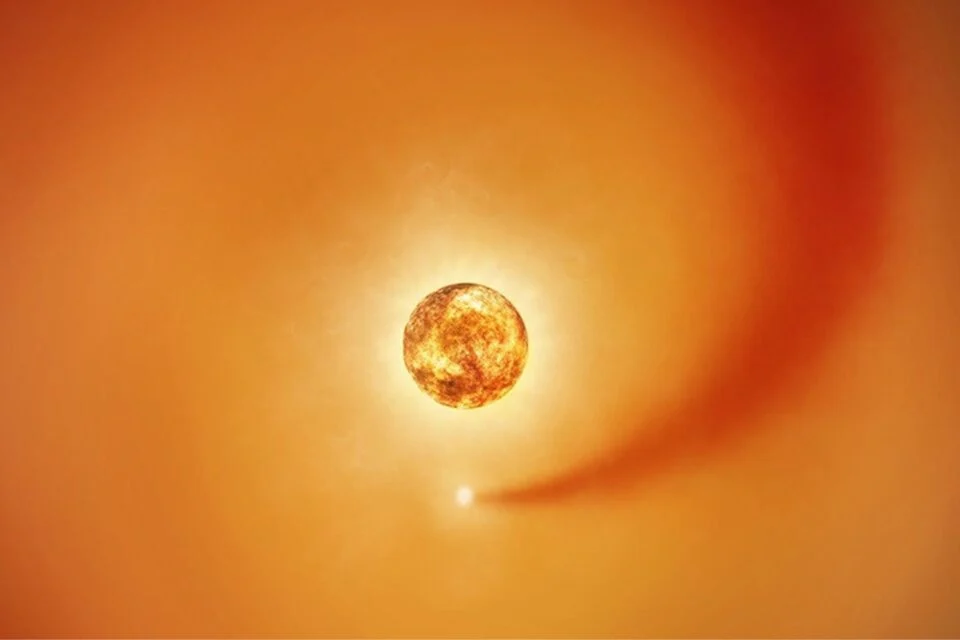
Astronomers observed changes in the star’s spectrum and these changes are the direct result of the companion star, Siwarha, plowing through Betelgeuse’s outer atmosphere.