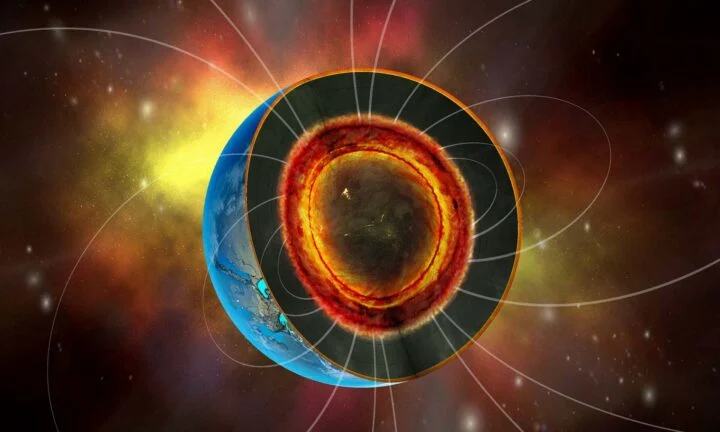

Deep beneath the surface of super-earths, oceans of molten rock may be doing something extraordinary: powering magnetic fields strong enough to shield entire planets from dangerous cosmic radiation.
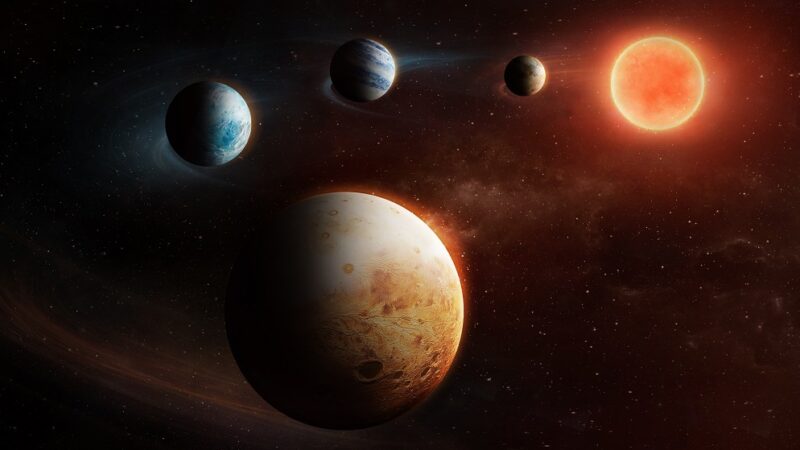

The planets around LHS 1903 – a cool faint red dwarf star – begin as expected with a rocky planet orbiting close by and then two gas worlds. A surprising 4th planet at the system’s outer edge that is rocky, rather than gaseous.
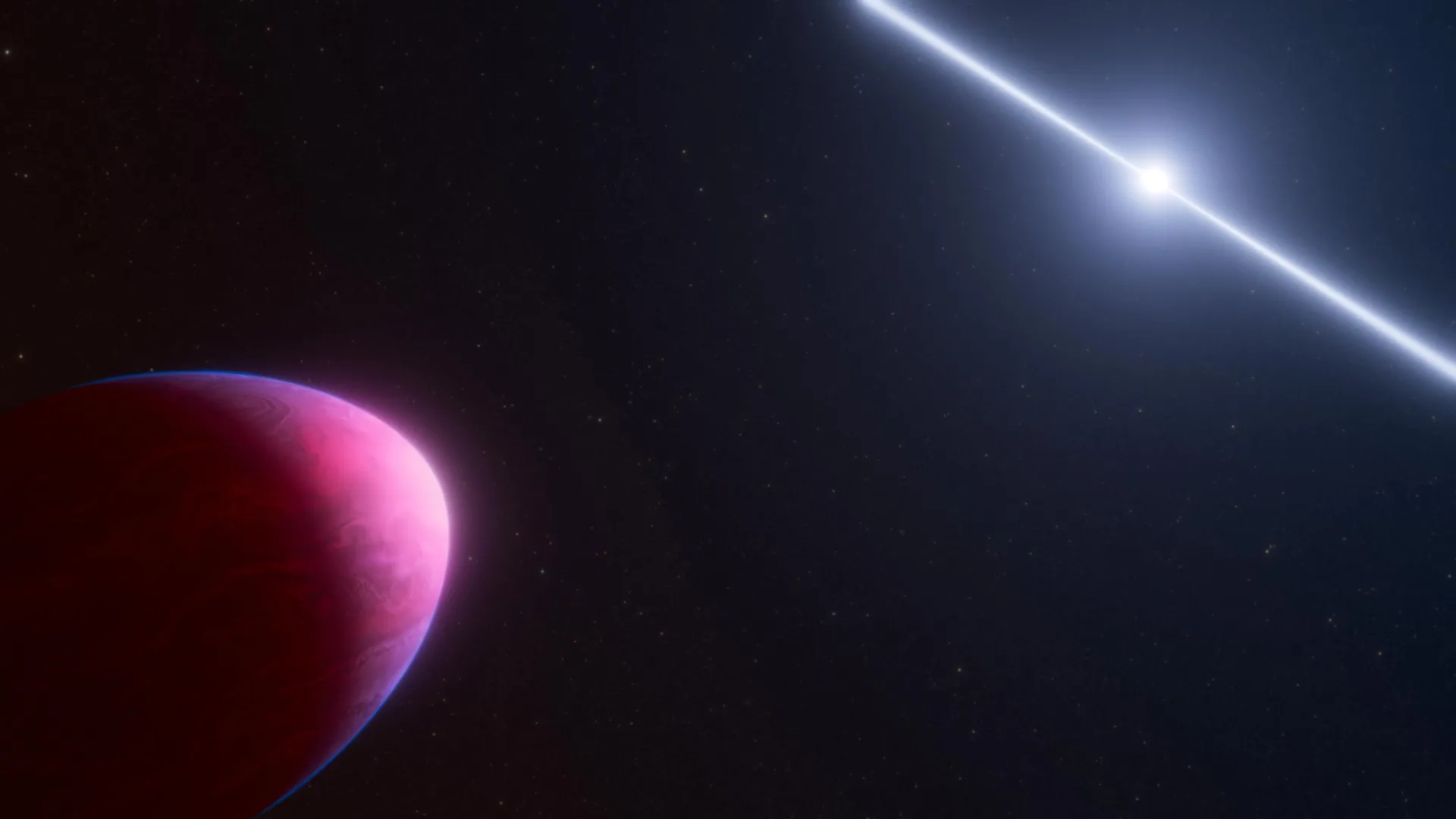

A newly discovered exoplanet is rewriting the rules of what planets can be. Orbiting a city-sized neutron star, this Jupiter-mass world has a bizarre carbon-rich atmosphere filled with soot clouds and possibly diamonds at its core.
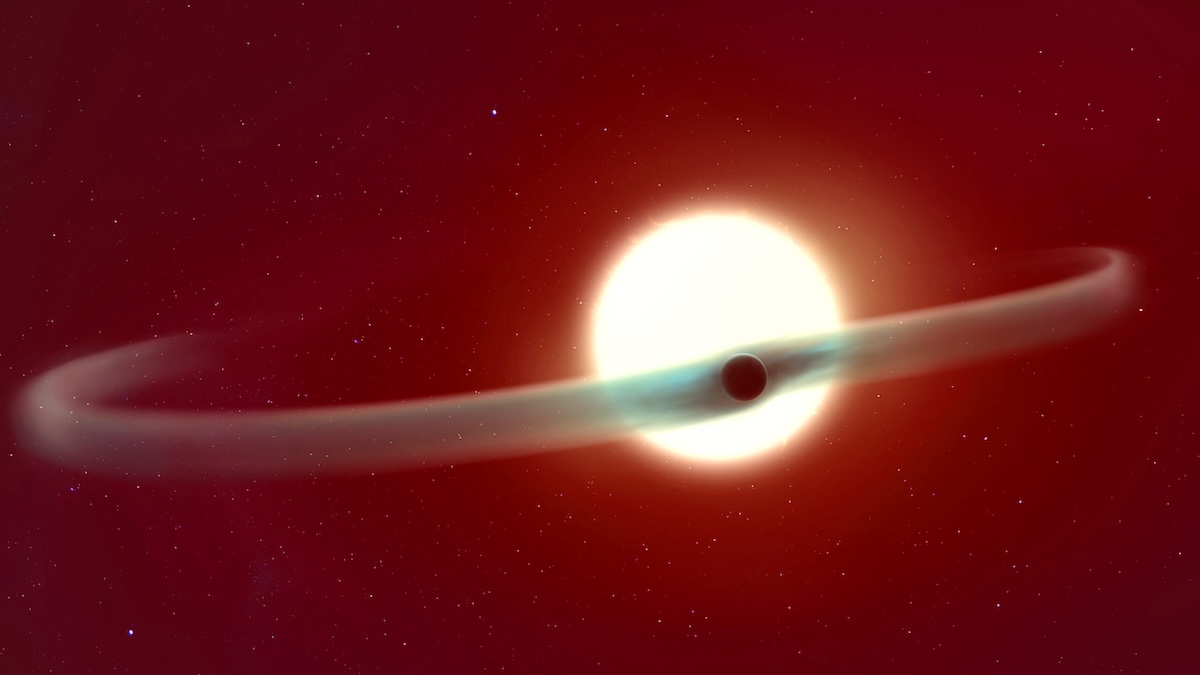

About 880 light-years from Earth, a hot mess of an exoplanet is slowly spilling its atmosphere into space, creating two enormous tails of helium that stretch more than halfway around its star.
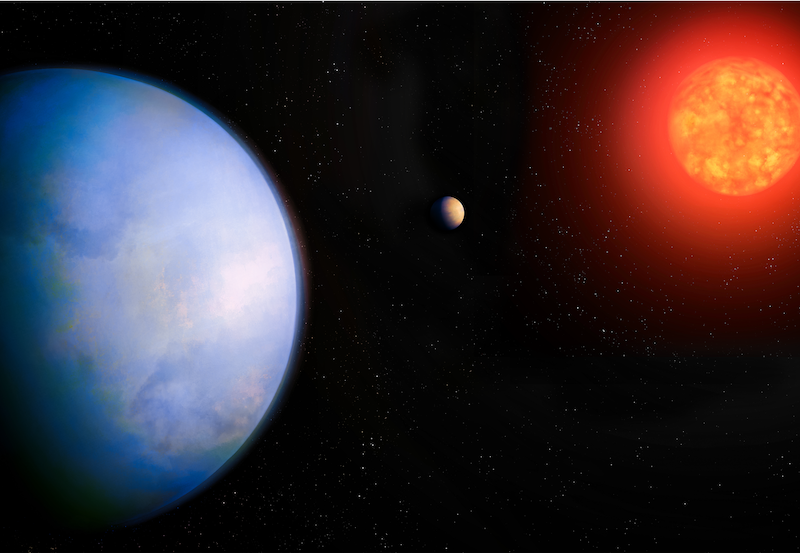
Astronomers have discovered another potentially habitable exoplanet orbiting a nearby star. The planet – GJ 251 c – is in the habitable zone of its red dwarf star.
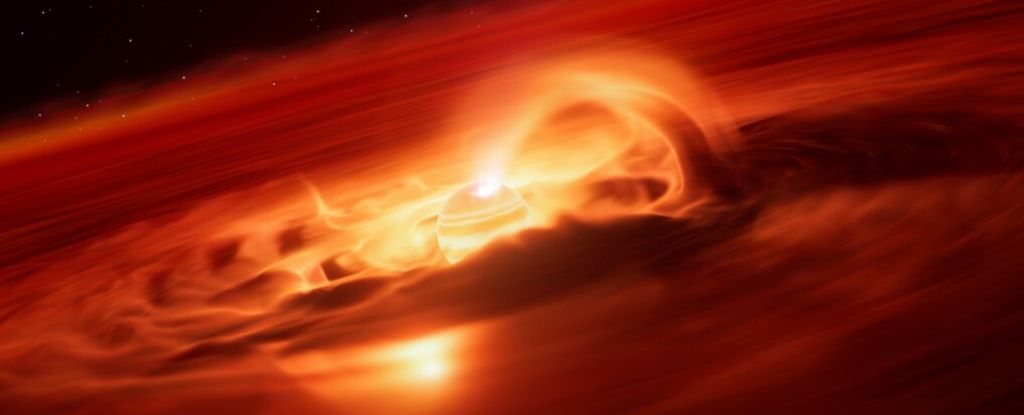

A young rogue planet about 620 light-years away from Earth has experienced a record-breaking "growth spurt," hoovering up some six billion tons of gas and dust each second over a couple of months.
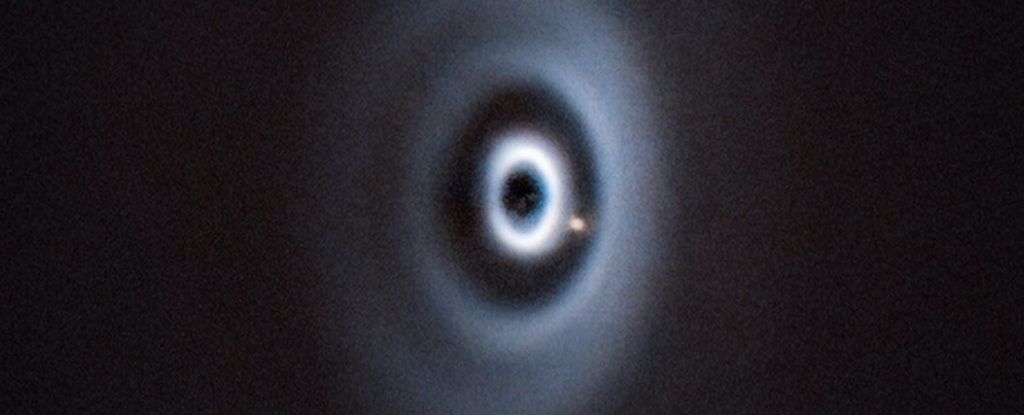
For the first time, astronomers have actually found a baby planet responsible for carving out gaps in the dusty disk surrounding a newborn star.
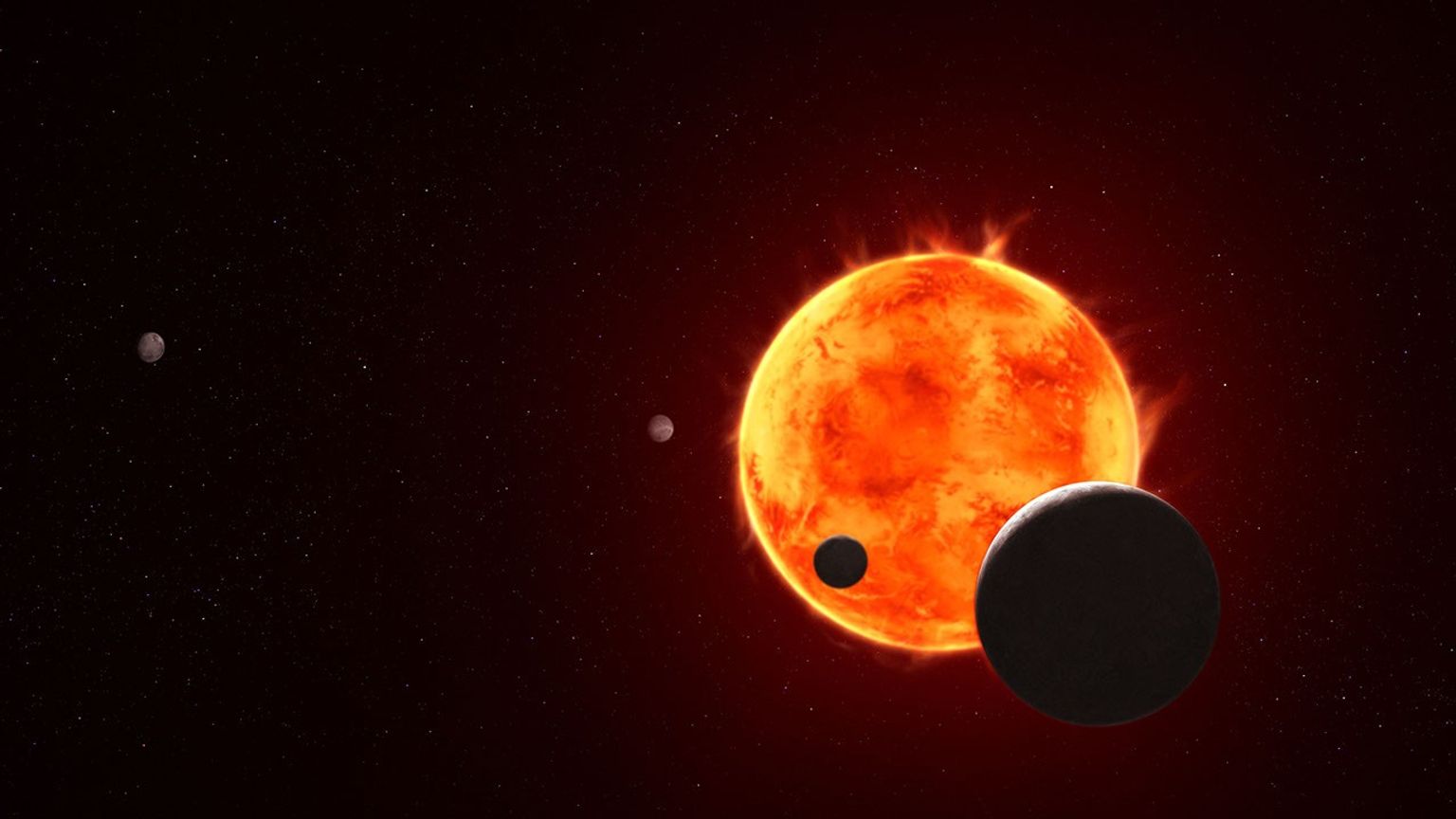

Scientists are in the midst of observing the exoplanet TRAPPIST-1 e with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope.
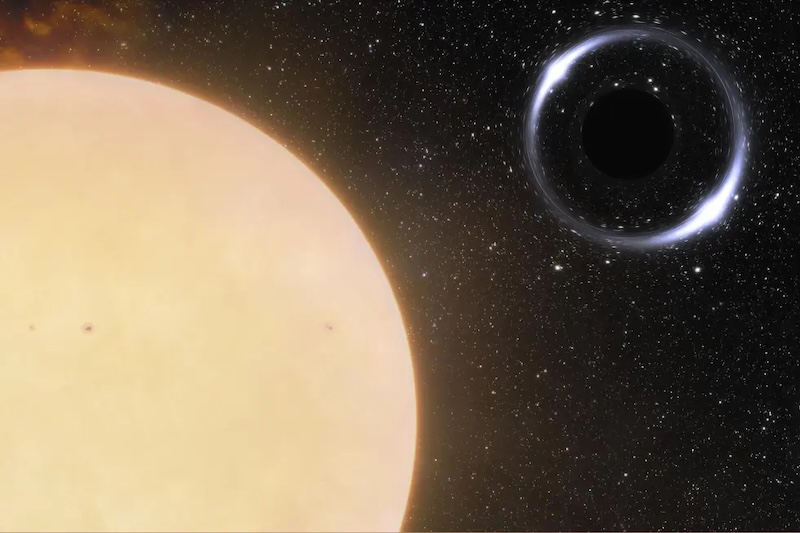

Dark matter particles could accumulate inside giant Jupiter-like exoplanets. Dense dark matter particles could eventually collapse to form a black hole inside a planet. The black hole could then ultimately consume the entire planet.
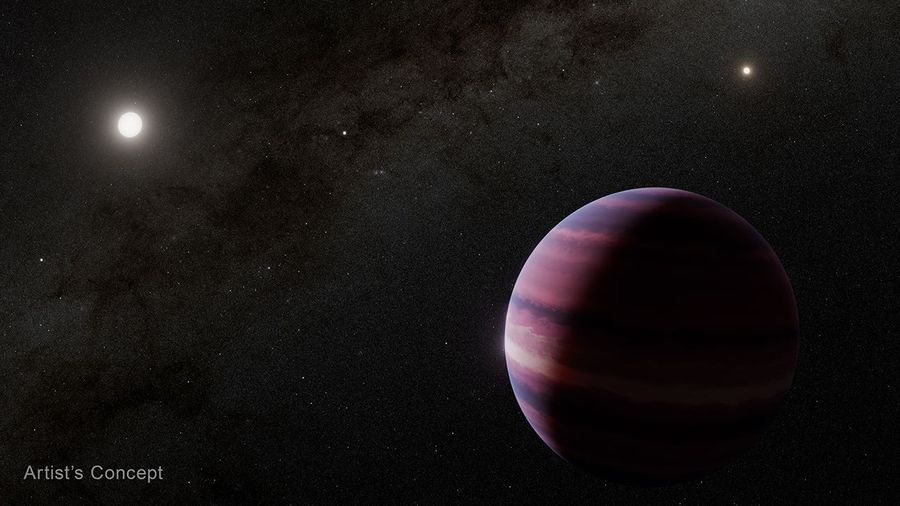

Astronomers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope have found strong evidence of a giant planet orbiting a star in the stellar system closest to our own Sun.
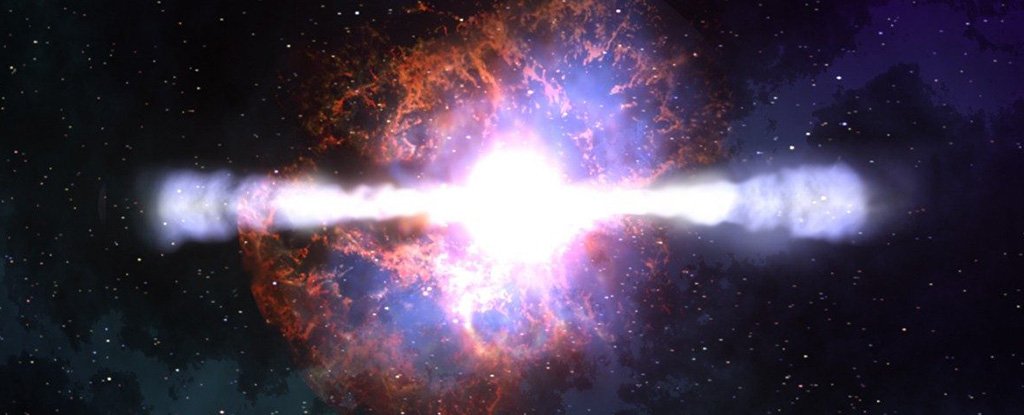

A surprising new study has found that under the right circumstances, cosmic radiation could actually make uninhabitable worlds habitable.

JWST has discovered and directly imaged its first exoplanet. It’s the first one Webb has found that other telescopes hadn’t previously found.

Astronomers have detected the smallest and most solar system-like planet ever directly imaged around another star.
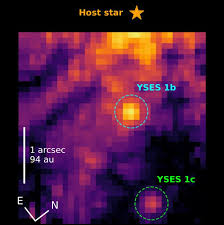
Astronomers using the James Webb Space Telescope have captured breathtakingly detailed images of two giant exoplanets orbiting a distant sun-like star.

An international team of astronomers discovered a giant planet orbiting the smallest known star to host such a companion. It’s a finding that defies current theories of planet formation.