Astronomers have discovered another potentially habitable exoplanet orbiting a nearby star. The planet – GJ 251 c – is in the habitable zone of its red dwarf star.
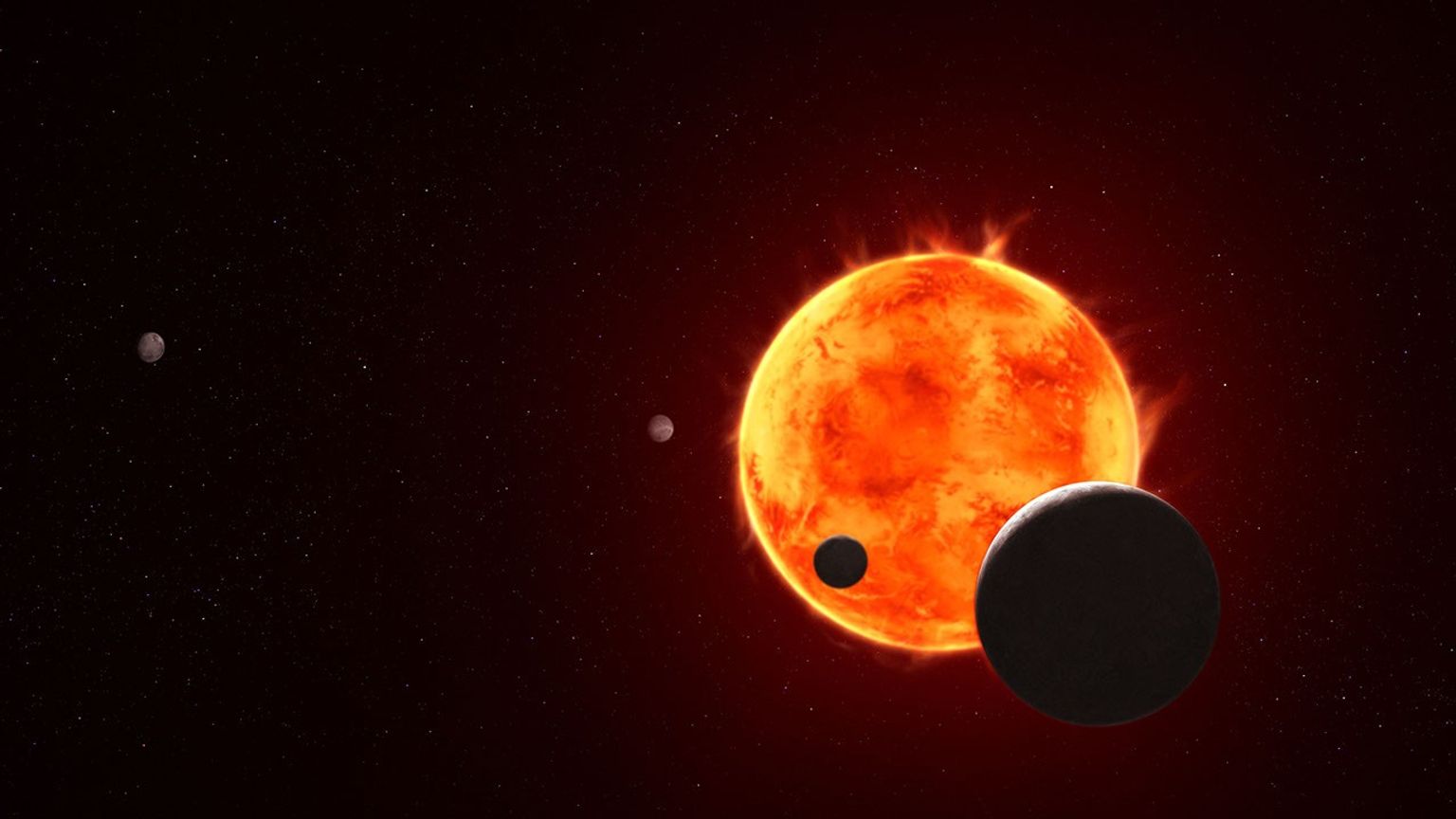

Scientists are in the midst of observing the exoplanet TRAPPIST-1 e with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope.
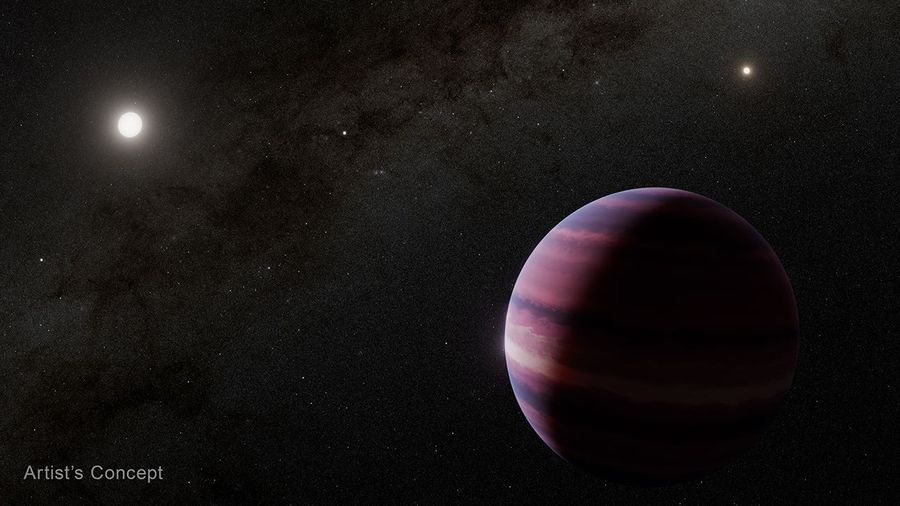

Astronomers using NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope have found strong evidence of a giant planet orbiting a star in the stellar system closest to our own Sun.
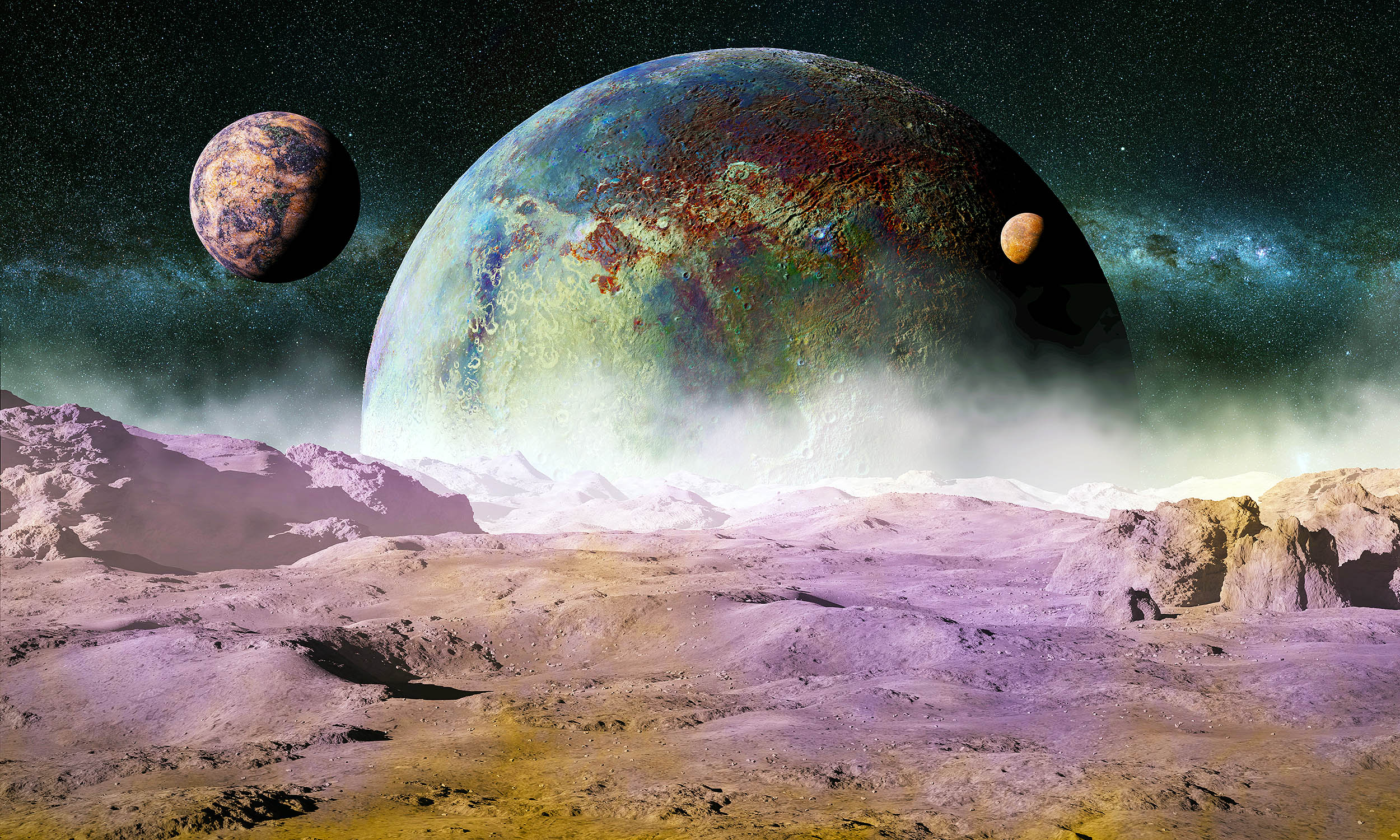

Exciting new research suggests there are four miniature planets orbiting Barnard's Star, each thought to be just 20 to 30% the mass of Earth.

Data from 2023 soured hopes that a nearby exoplanet had a habitable atmosphere. That disappointment might have been premature.
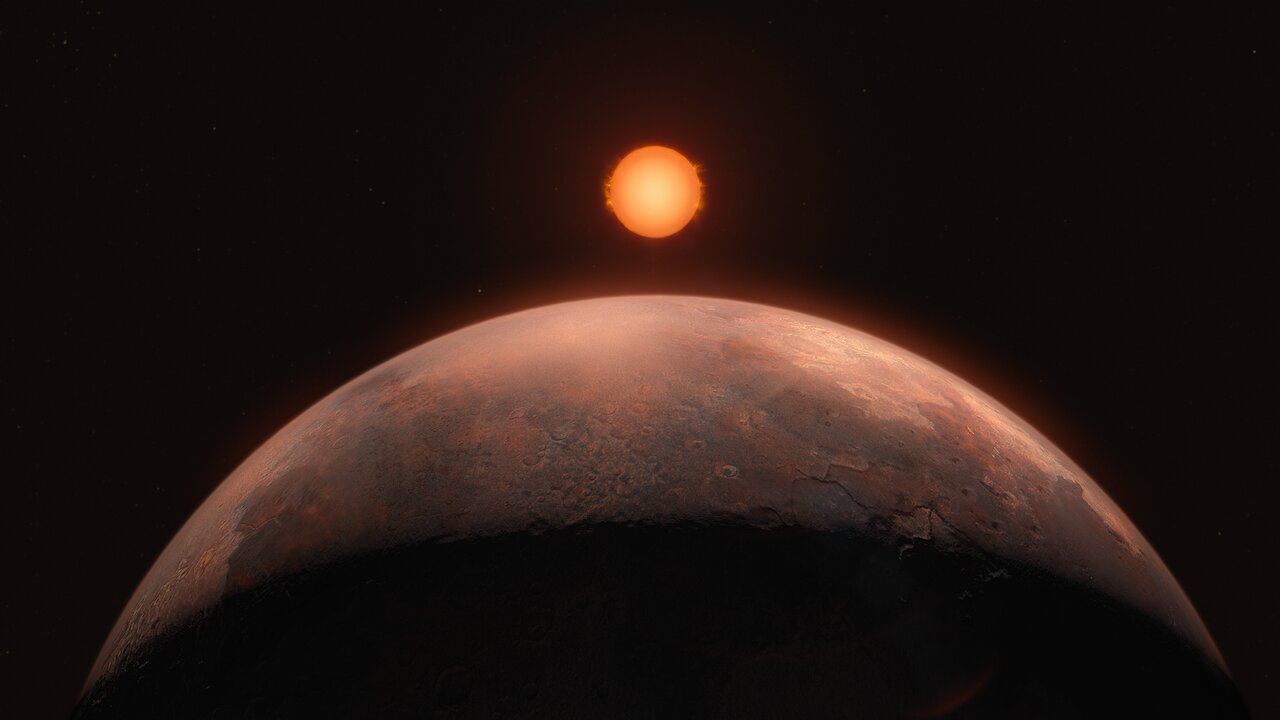

Using the European Southern Observatory's Very Large Telescope, astronomers have discovered an exoplanet orbiting Barnard's star, the closest single star to our Sun.
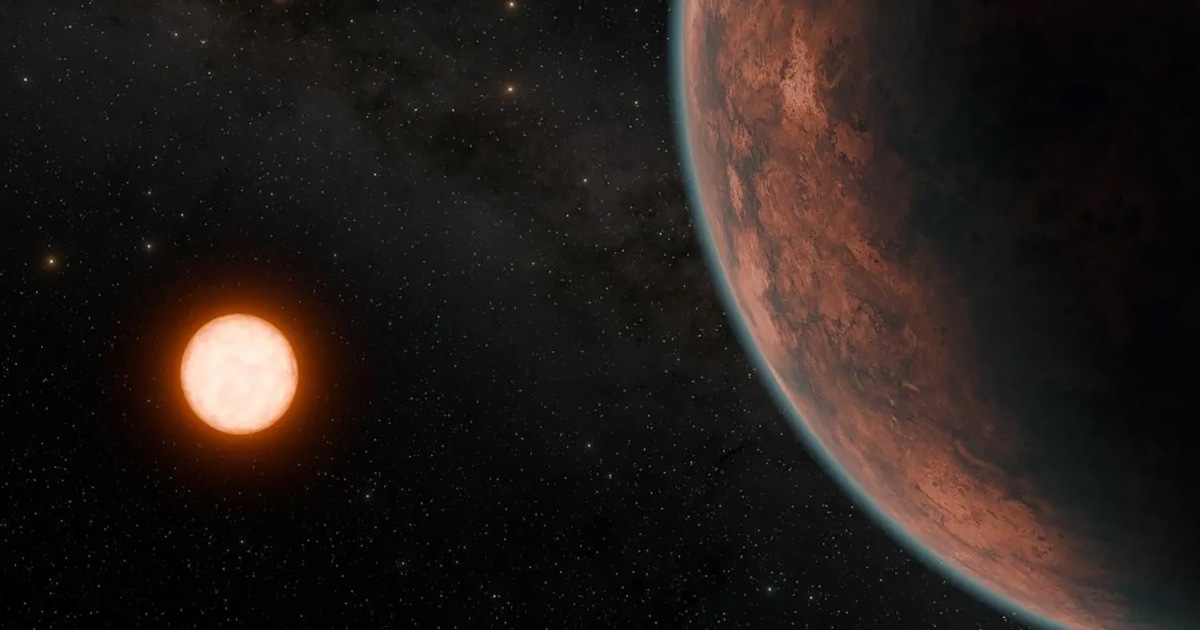

Dubbed Gliese 12 b, the planet takes 12.8 days to orbit a star that is 27% of the sun's size. The planet is about the size of Venus, so slightly smaller than Earth, and may be temperate enough to support life, the researchers said.
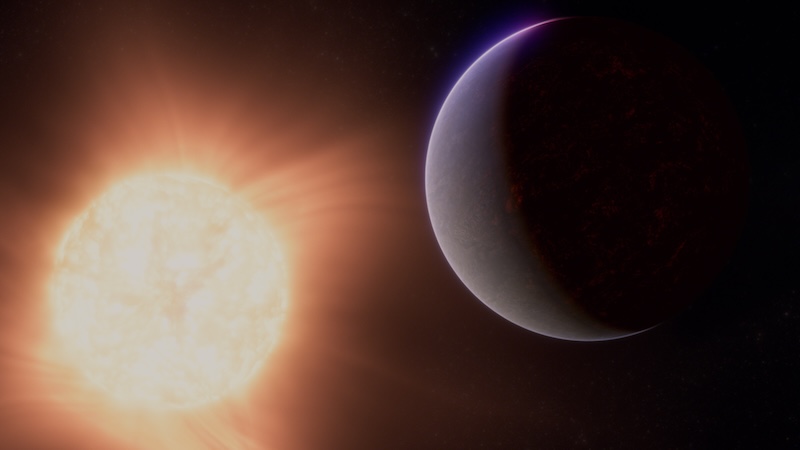

For the first time, astronomers say that they have detected a possible atmosphere on a rocky exoplanet. This smaller rocky world, 55 Cancri e, is only 41 light-years from Earth. But unlike our planet it is extremely hot.

A “super-Earth” ripe for further investigation orbits a small, reddish star that is, by astronomical standards, fairly close to us – only 137 light-years away.

Beta Pictoris has been revealed by many telescopes, even Hubble, to be home to the most amazing disk. Over the years the second disc was revealed.

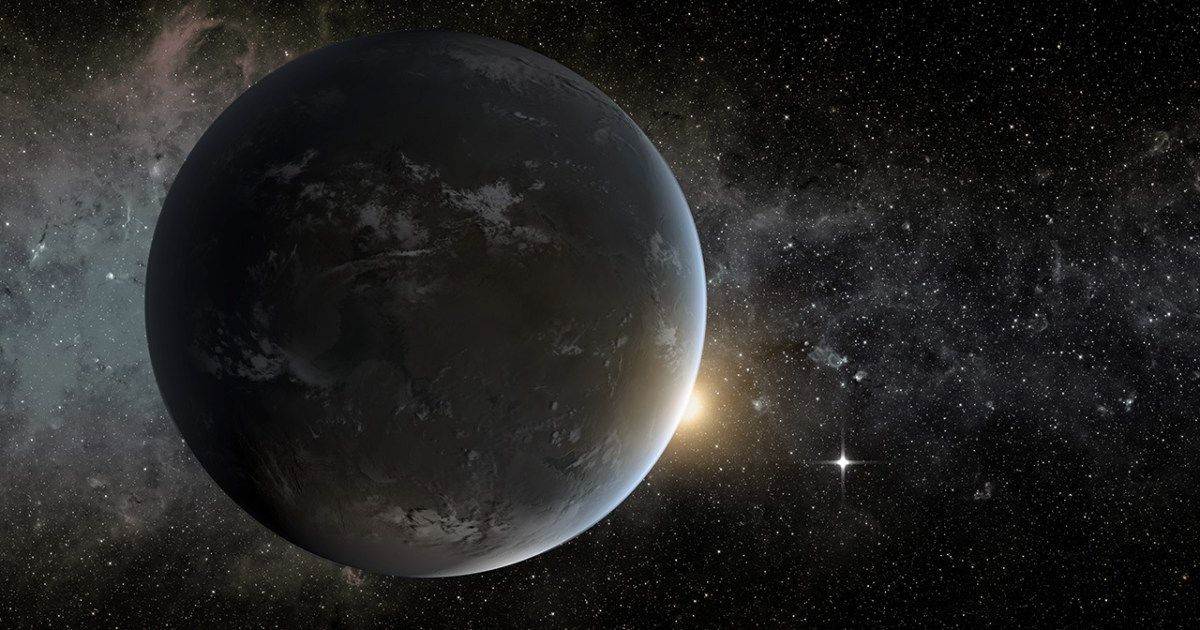
The chances of finding extraterrestrial life have improved slightly after NASA announced that its Hubble Space Telescope has confirmed the size of an Earth-sized exoplanet only 22 light-years from Earth.

Astronomers have discovered a rocky exoplanet about a few dozen light years away from Earth with conditions that could make it habitable.

An international team of astronomers has confirmed the existence of K2-415b, an Earth-sized exoplanet circling an M dwarf star, just 72 light years away from Earth.

The planet, nearly 10 times Earth’s mass, orbits a small, red-orange star about 200 light-years away. This planet is extremely hot, with an estimated temperature of 1,050 Celsius.

While observing the star system HD 23472 , researchers found three super-Earths and two super-Mercuries. This type last of exoplanet is still very rare—counting these two, there are only eight known super-Mercuries.