
Now, the unique capabilities of the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope are providing new insights into the Jovian aurorae.

Evidence is mounting that a secret lies beneath the dusty red plains of Mars, one that could redefine our view of the Red Planet: a vast reservoir of liquid water, locked deep in the crust.

Planetary scientists research the complex asteroid Vesta which may possess the same fundamental architecture as Earth such as the crust.

New research finds that despite large rivers and seas of liquid methane, Saturn's moon Titan seems mostly devoid of river deltas.
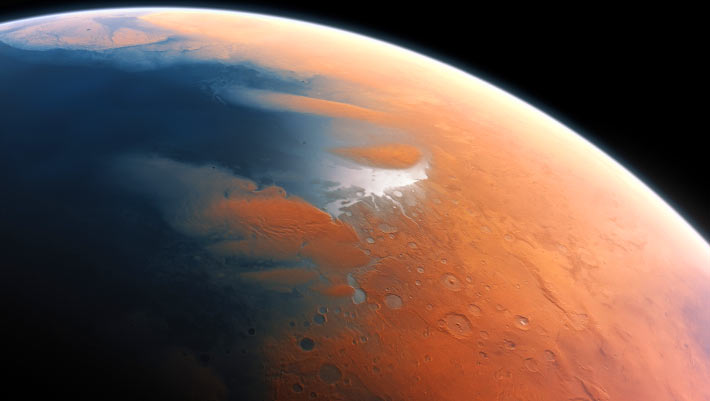

The distribution of valley heads on Mars matches predictions for a climate that includes precipitation rather than just runoff from melting ice caps.
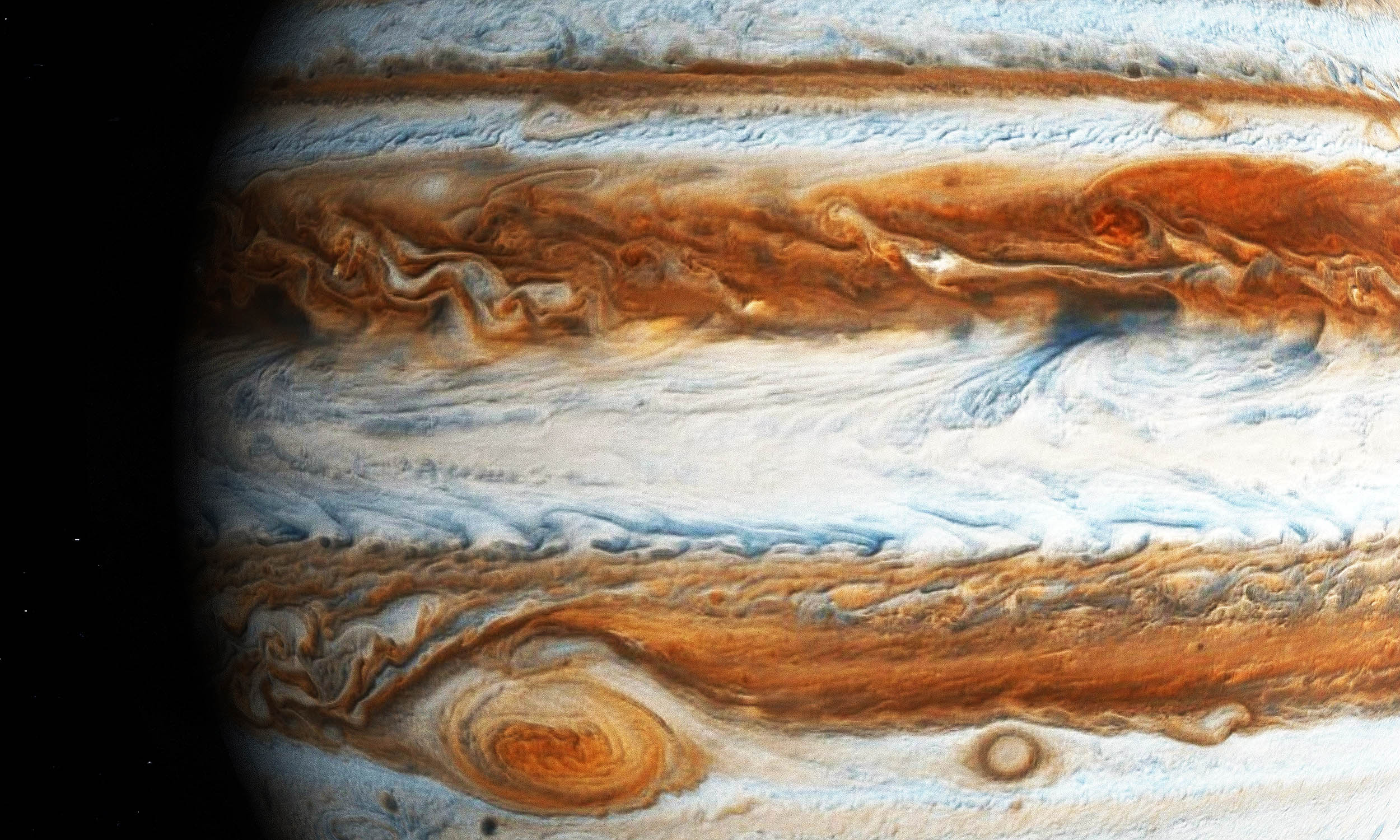

Slushy hail, made of water and ammonia, may form during lightning-packed storms, giving researchers fresh clues about what lurks beneath the planet’s colorful cloud tops.
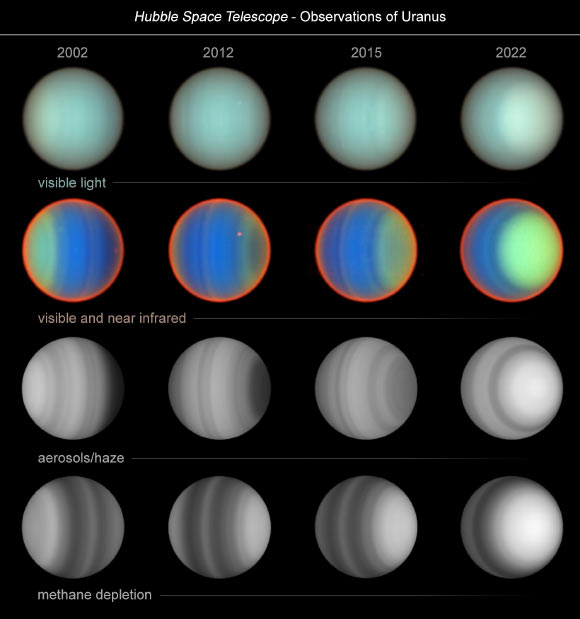
A 20-year Hubble study of Uranus provide valuable data for understanding the atmospheric dynamics of this distant ice giant, which can serve as a proxy for studying exoplanets of similar size and composition.
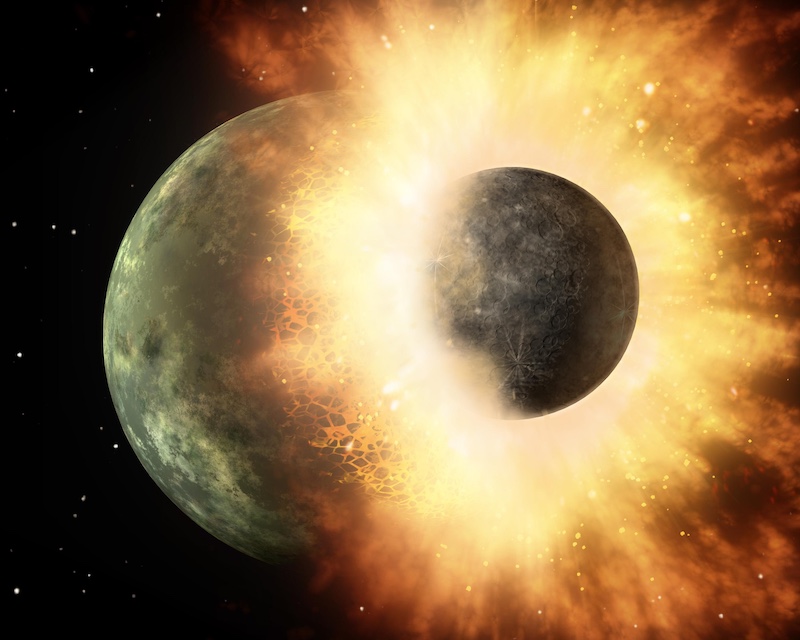

A grazing giant collision between two similar-sized rocky bodies likely created Mercury a few billion years ago.
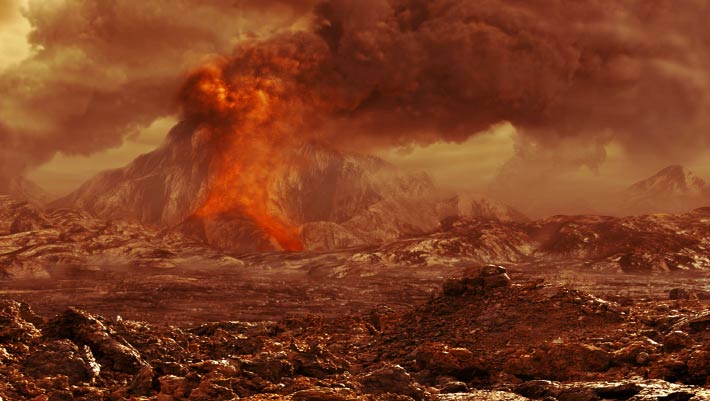

An unexpected phenomenon called convection could help explain many of the volcanoes and other features of the Venusian landscape.
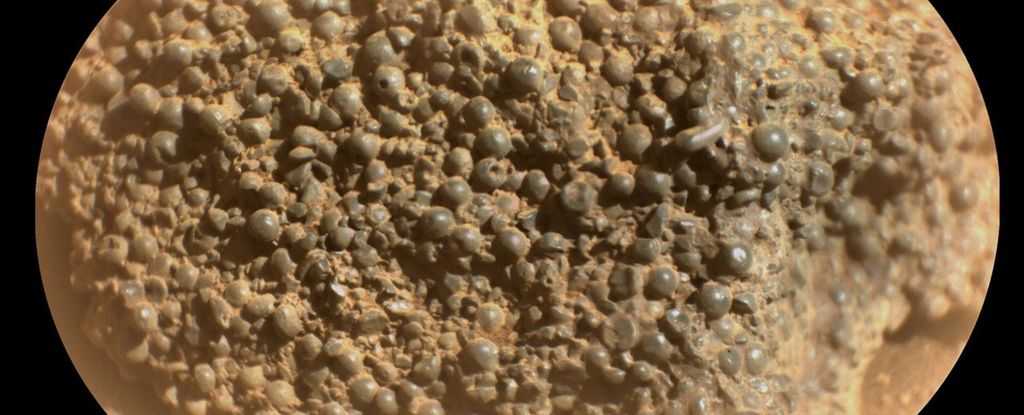

Once again, Mars has presented us with an example of something it seems to have in abundance: extremely peculiar and baffling rocks.

The main reason for space exploration is to search for life beyond Earth.

For the first time, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has captured bright auroral activity on Neptune.

Martian dust storms can potentially cause respiratory issues and elevated risk of disease, making them yet another health hazard space agencies need to prepare for, according to new research.

The discovery is one of the most significant findings in the search for evidence of past life on Mars.

The mineral content of oddly pale rocks found in Jezero Crater can only have formed under very warm, very soggy conditions – suggesting that, long ago, Mars may have been a lot more peculiar than we ever suspected.