A Canadian study finds that the human brain emits a faint glow known as bio-photons, which vary with mental activity.

Understanding how the brain processes moral responsibility is important because of the implications it can have for ethics, justice, and the psychology of human behavior.

A new study of older adults suggests it can lead to brain shrinkage and cognitive issues, irrespective of how much exercise you're managing to fit in.

Findings indicate rising microplastic concentrations in human brains and organs, urging deeper investigation into their health effects and distribution.
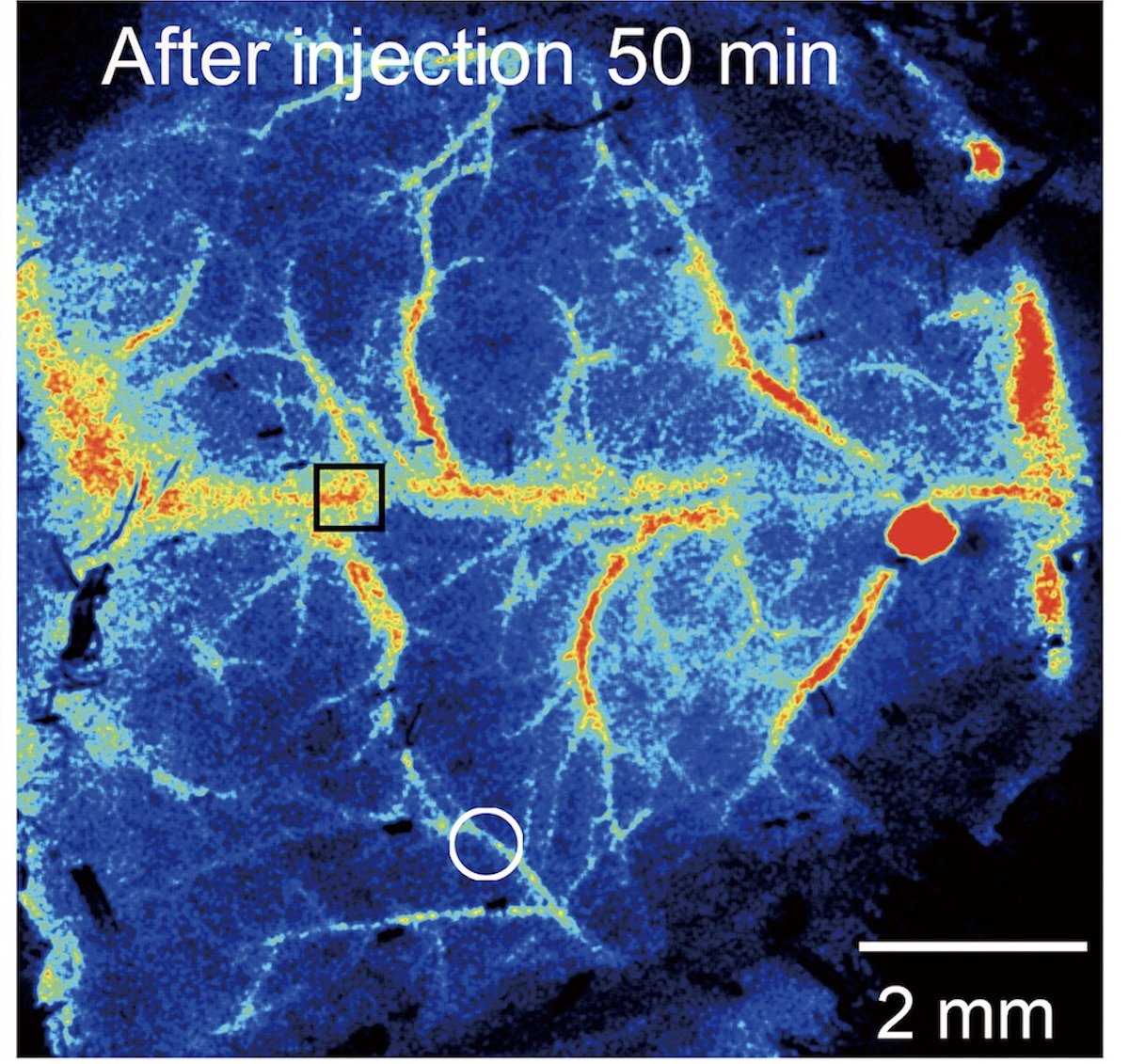
Scientists have found in lab experiments that microplastics can block blood flow in mice brains, raising concerns about human health impacts.

Brain imaging of fetuses and infants reveals a rapid increase in functional brain connectivity at birth, aiding adaptation to the external world.
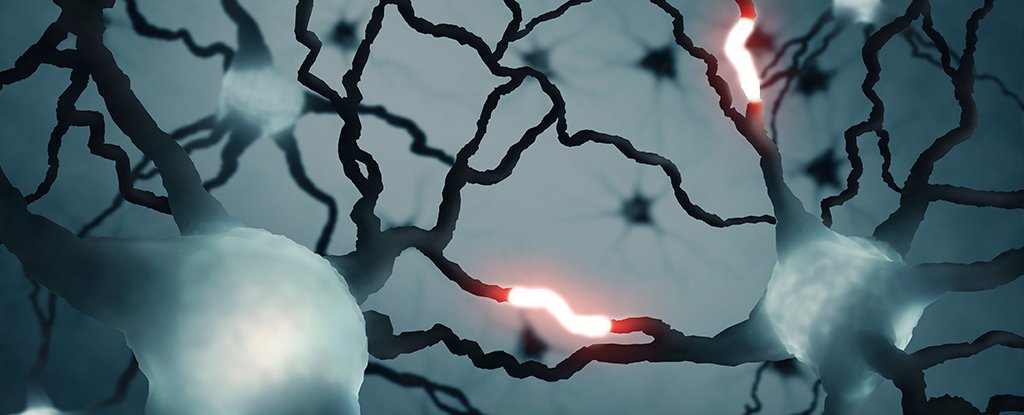

Scientists have identified a unique form of cell messaging occurring in the human brain, revealing just how much we still have to learn about its mysterious inner workings.

The brain is a marvel of efficiency, honed by thousands of years of evolution so it can adapt and thrive in a rapidly changing world.
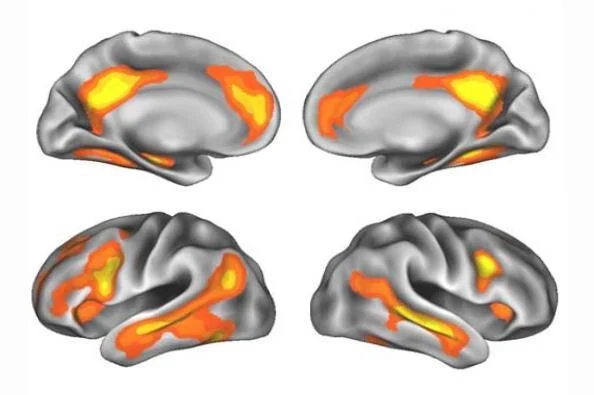
Neuroscientists scanned the brain of a pregnant woman and captured a 'widespread reorganization' of her brain before, during and after pregnancy.

Chinese scientists explain how entangled photons emitted by carbon-hydrogen bonds in nerve cell insulation could synchronize activity within the brain.

A research team discovered that obesity causes chronic changes in the brain which affects sperm count.

A longitudinal study by UQ researchers has found high-intensity interval exercise improves brain function in older adults for up to 5 years.
Once maligned for their psychedelic properties, magic mushrooms are increasingly attracting attention for their same mind-altering potential as a therapy for a wide variety of mental health issues.
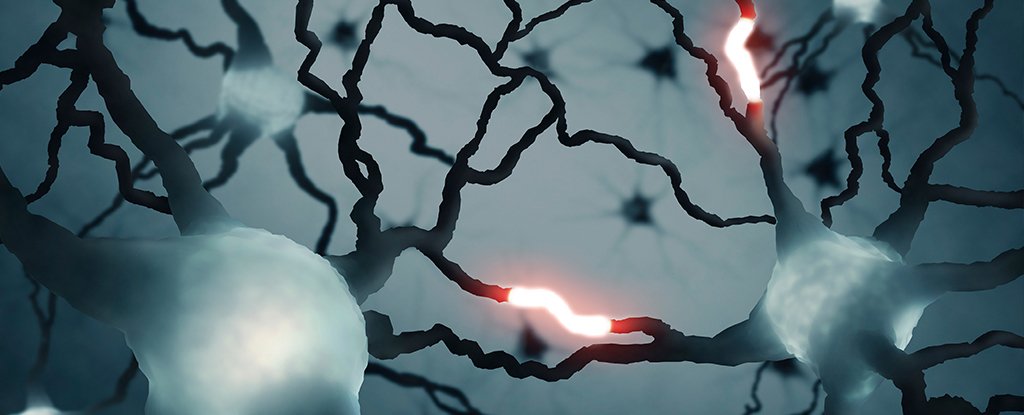

Scientists have identified a unique form of cell messaging occurring in the human brain, revealing just how much we still have to learn about its mysterious inner workings.
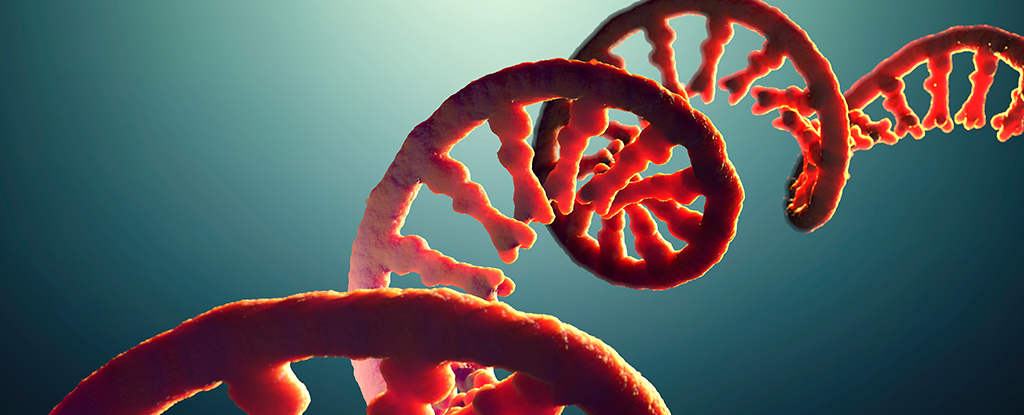

A comparison of post-mortem brain tissue and samples taken from living patients has revealed for the first time significant differences in the way strands of RNA are modified.