
Researchers found that time cells in the brain are crucial for learning complex tasks, acting like a personalized time code.
The human brain is said to be the most complex object in the known Universe. Its 89 billion neurons each have around 7,000 connections on average, and the physical structure of all those entities may be balanced precariously on a knife's edge.
A review of 53 placebo-controlled surgery trials found that sham surgery was as good as the real thing in over half of the studies. Sham surgery activates the wound-healing cascade.
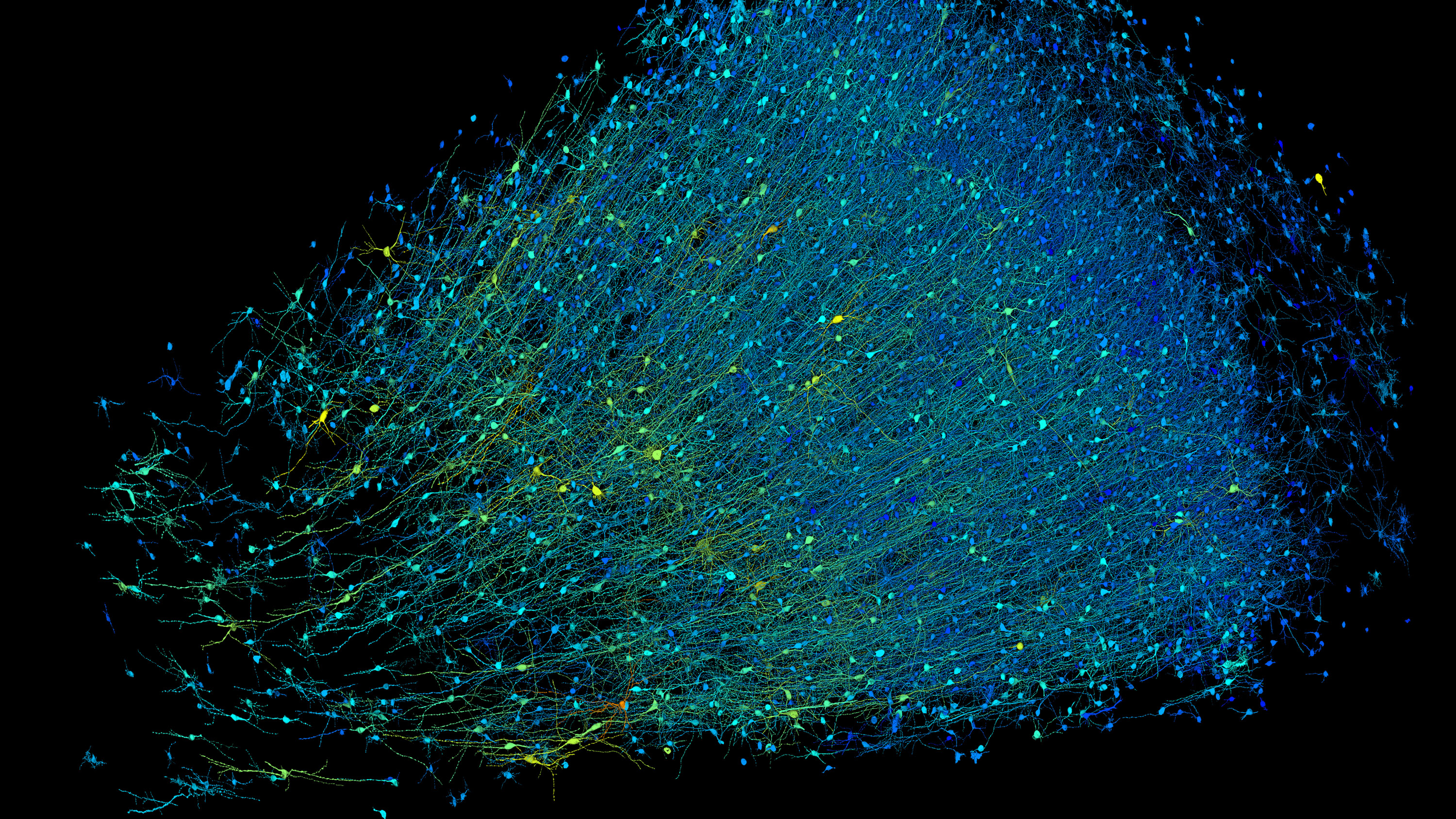
Although the map covers just a fraction of the organ—a whole brain is a million times larger—that piece contains roughly 57,000 cells, about 230 millimeters of blood vessels, and nearly 150 million synapses.

The intermittent energy restriction (IER) diet changes the human brain-gut-microbiome axis. There are highly dynamic changes in the gut microbiome and in the activity in addition-related brain regions during and after the diet.

Researchers have discovered that people born in more recent decades have larger brain volumes compared to those born in earlier decades.

Living in poorer neighborhoods is linked to higher risk of dementia and faster brain aging, according to new research.

By carefully monitoring neural activity of people who were recalling memories or forming new ones, the researchers managed to detect how a newly appreciated type of brainwave influences the storage and retrieval of memories.

Empathy, often considered a fixed trait, has been shown to be malleable in adults, influenced by observing the empathetic reactions of others.

Even small doses of LSD could have therapeutic benefits for mental health and task performance, a new study shows.

Narrowly focused soundwaves aimed at an area of the brain called the insula reduced both the perception of pain and the body’s reaction to it, according to a new study.

Millions of years ago, vertebrates were infected by a virus, which played an important role in the evolution of human beings and the development of brains and human bodies.

Discoveries over the last two decades have shed light on a crucial role for “quantumness” in human cognition – how the human brain processes information to acquire knowledge or understanding.

A supercomputer scheduled to go online in April 2024 will rival the estimated rate of operations in the human brain, according to researchers in Australia. The machine, called DeepSouth, is capable of performing 228 trillion operations per second.

Research suggests that 'time cells' – neurons in the hippocampus thought to represent temporal information – could be the glue that sticks our memories together in the right sequence so that we can properly recall the correct order in which things happened.