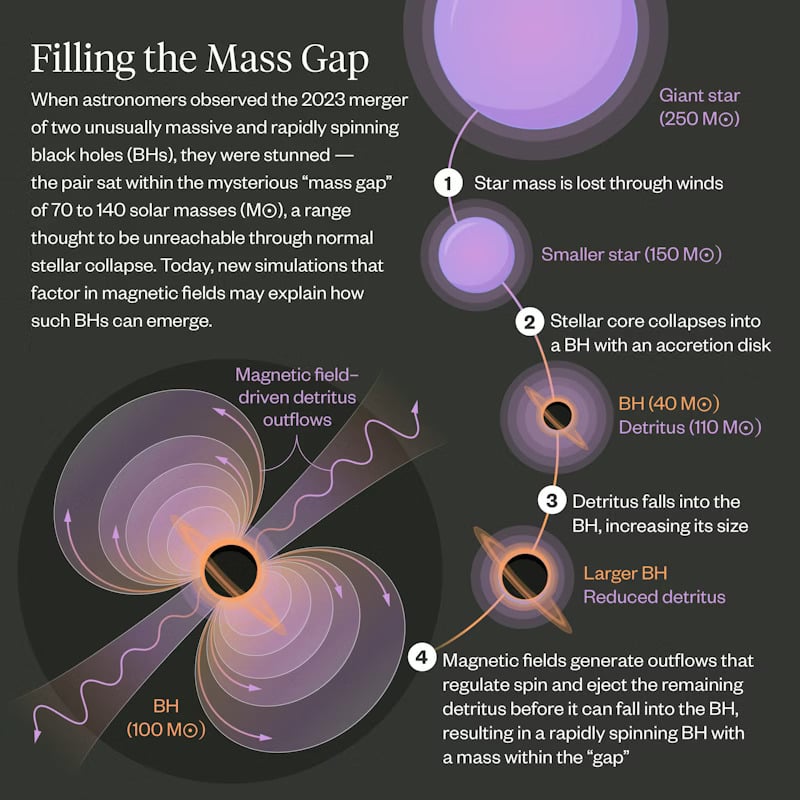
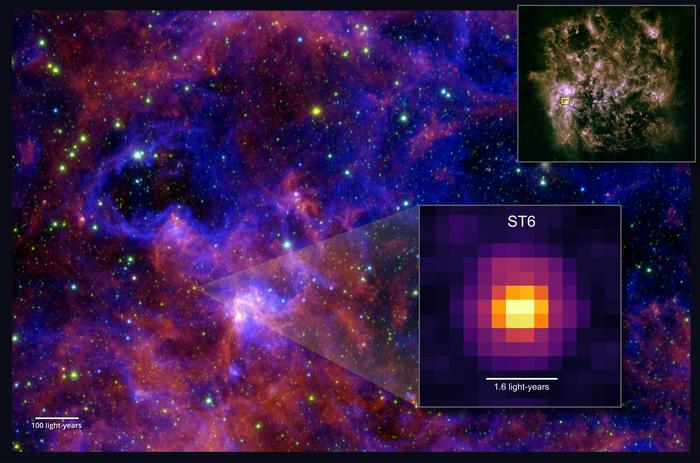
The black hole was bigger than expected, and while the answer was hiding in plain sight, it still rewrites what we thought was possible.
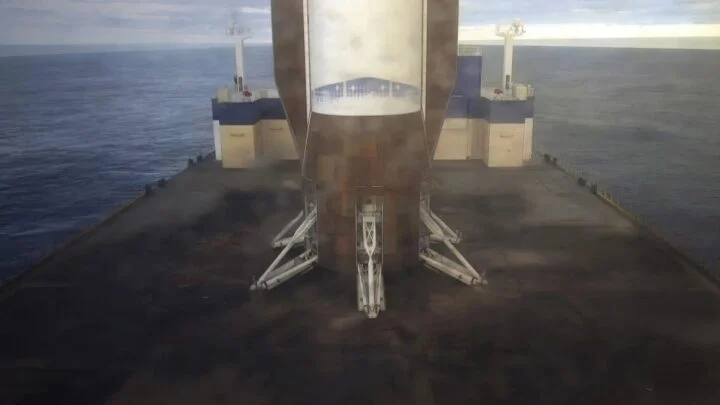

Jeff Bezos's Blue Origin successfully launched its New Glenn rocket on Thursday with NASA twin spacecraft destined for Mars aboard, and in a breakthrough, nailed the landing of its booster.

Astronomers have detected a storm on a star other than our Sun for the first time, discovering an explosion so violent it could have stripped away the atmosphere of any planets unlucky enough to be nearby.

The Moon has no atmosphere, yet it faces an invisible bombardment more relentless than any terrestrial storm, a constant rain of micrometeoroids, tiny fragments of rock and metal traveling at speeds up to 70 kilometers per second.

Astronomers have discovered traces of ancient “heavy water” around a young star, revealing that some of the water found in our Solar System and even on Earth could be older than the Sun itself.
Something massive is lurking in the darkness of space, a mysterious object with the weight of a million Suns but no light to give it away.

Gravitational waves from the birth of two newborn black holes caught the attention of scientists last year. Scientists have discovered something spectacular about the birth of one of the black holes.
A new study shows that the Universe has already entered a phase of decelerated expansion at the present epoch and that dark energy evolves with time much more rapidly than previously thought.

Our home galaxy also has a colossal wave rippling through it, pulling and pushing an ocean of stars and cosmic dust in its wake.
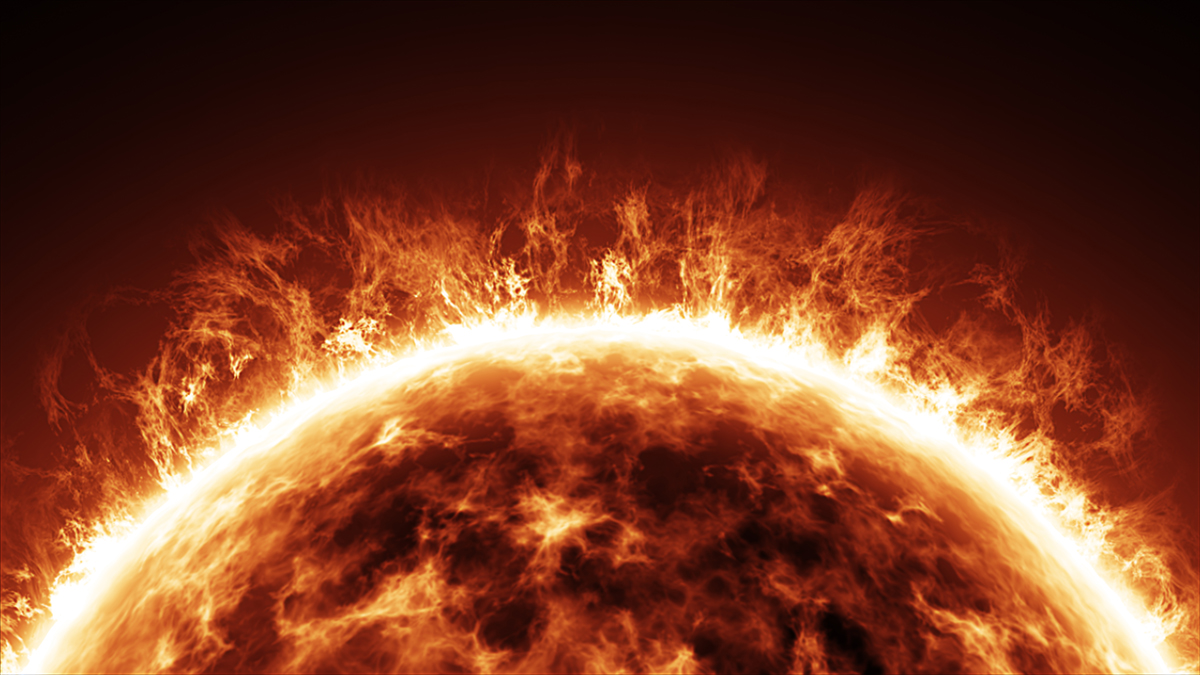

For decades, scientists have tried to understand how the Sun's corona (outer atmosphere) gets so blisteringly hot while its surface stays relatively balmy – and now a new study has delivered a big clue.
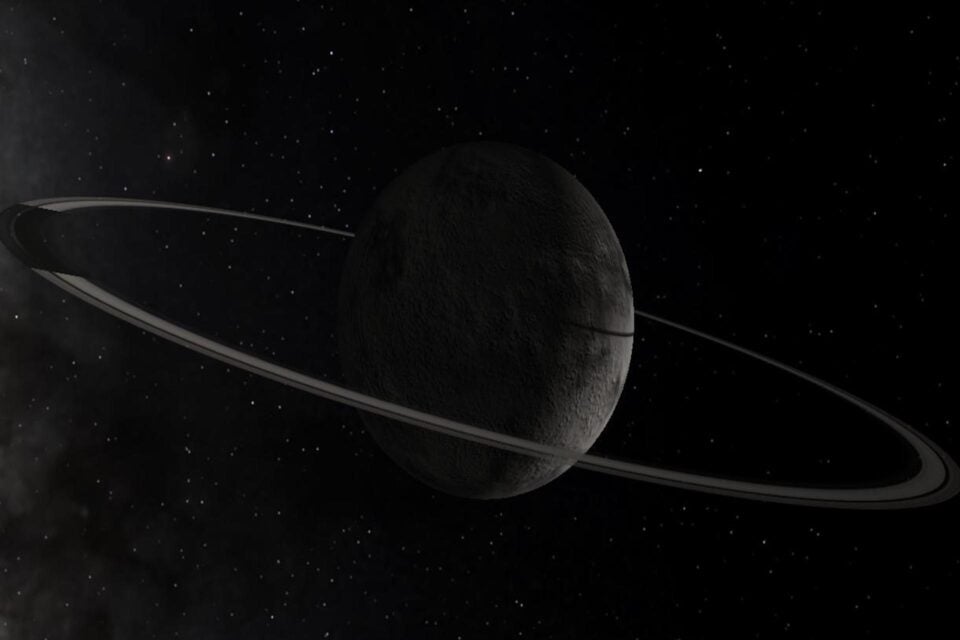

Astronomers found evidence of three rings around Chiron, which orbits the Sun between Uranus and Saturn.
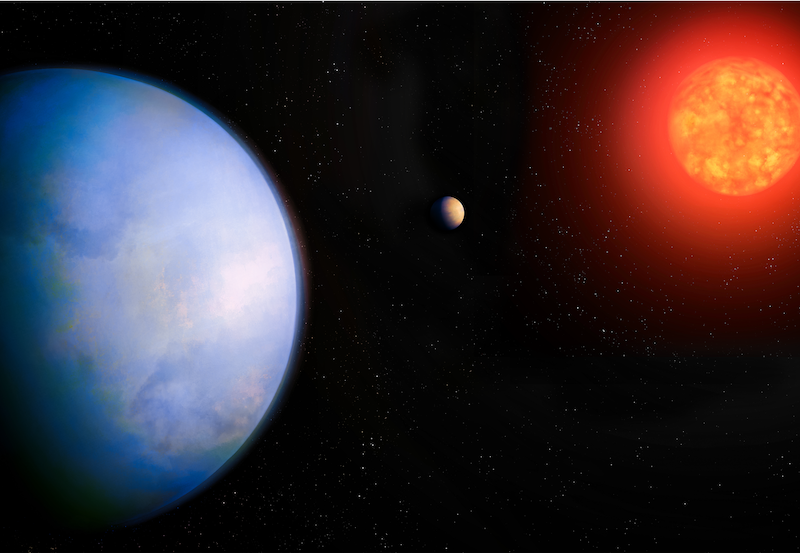
Astronomers have discovered another potentially habitable exoplanet orbiting a nearby star. The planet – GJ 251 c – is in the habitable zone of its red dwarf star.
A team led by a University of Maryland astronomer detected large complex organic molecules in ices outside of the Milky Way for the first time, offering a glimpse into the chemistry of the early universe.
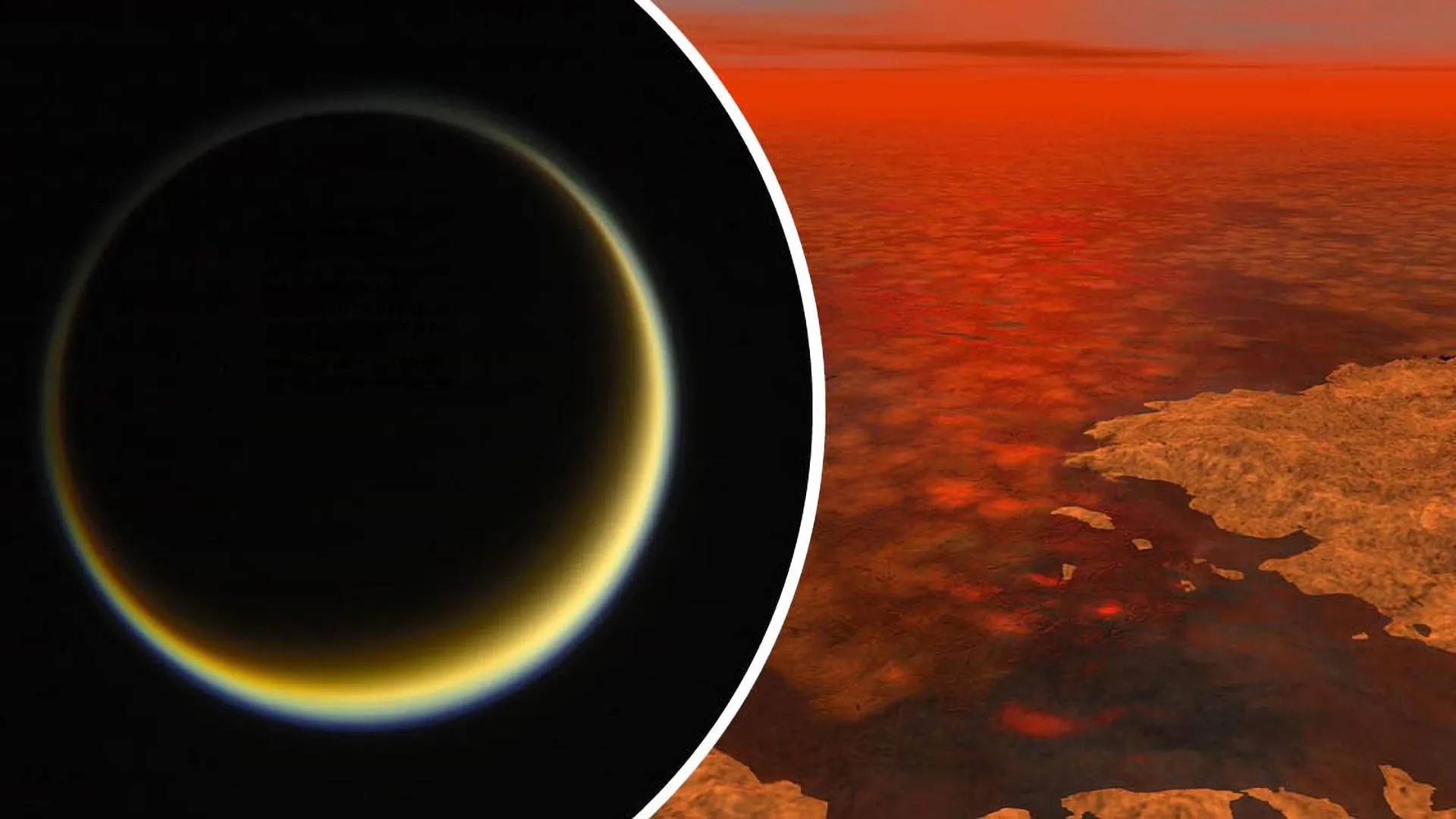

Scientists from NASA and Chalmers University have discovered that incompatible substances can mix on Titan’s icy surface, breaking the “like dissolves like” rule of chemistry.
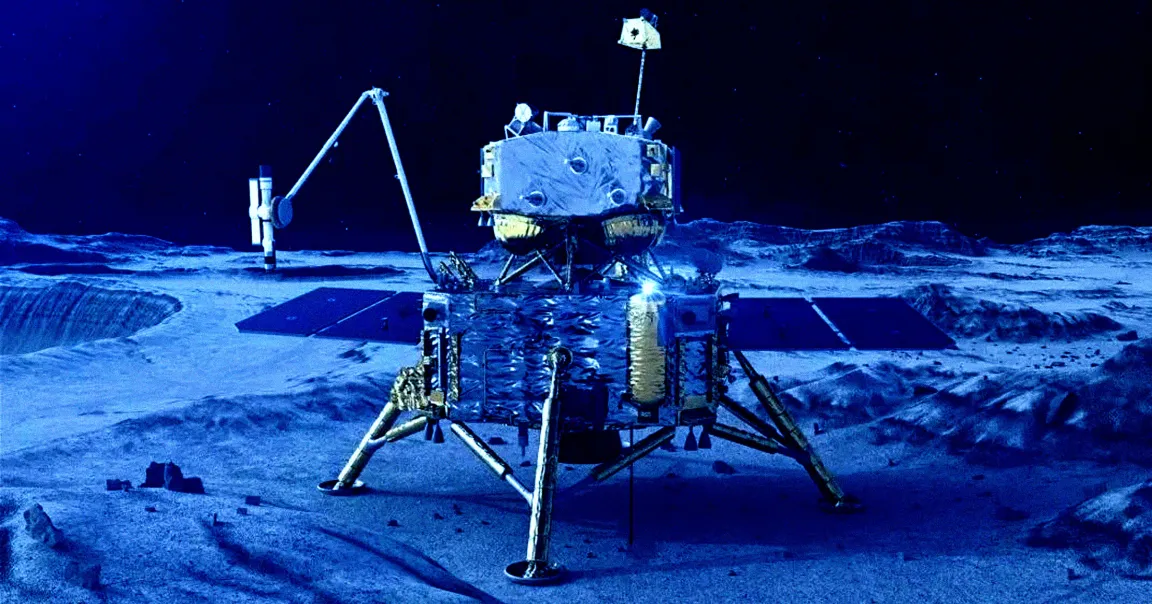

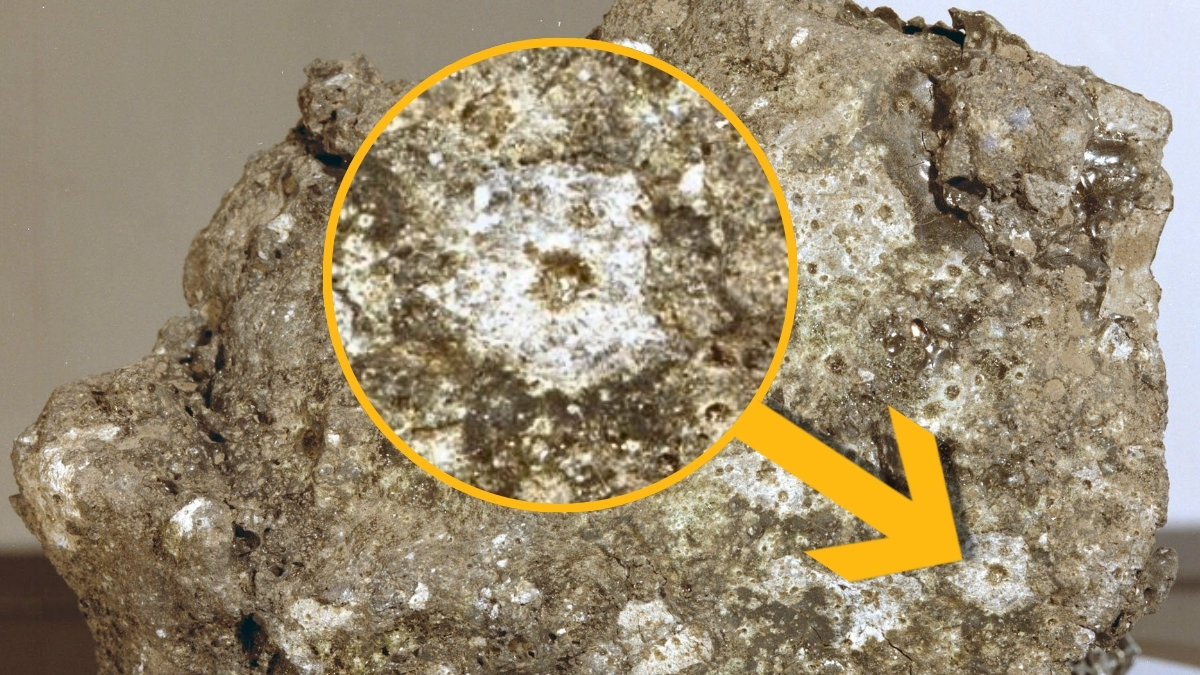
It’s the first time CI chondrite was observer on the Moon, suggesting that volatile-rich asteroids — which are very porous, with hydrated minerals making up to 20 percent of their mass — can make it all the way to the lunar surface.