
A supermassive black hole in the center of the radio quasar RACS J032021.44-352104.1 (RACS J0320-35 for short) is growing at one of the fastest rates ever recorded.

Dark dwarfs are hypothetical dark matter-powered objects that formed from the cooling of brown dwarfs.
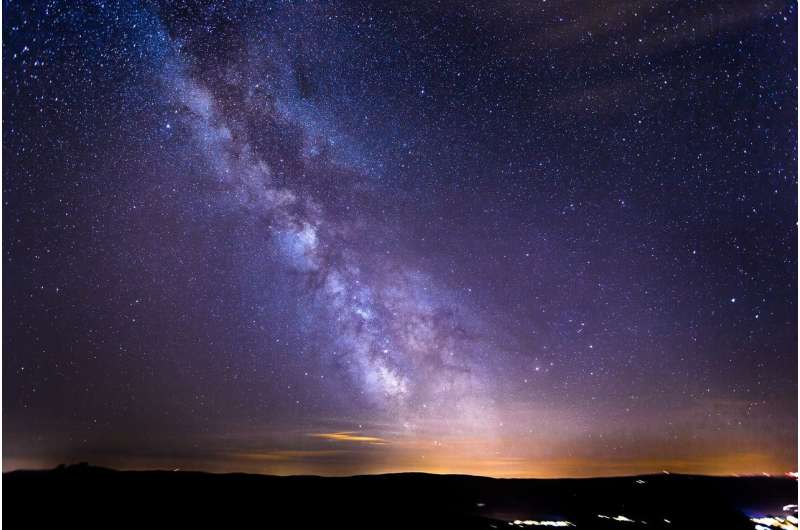

New research has uncovered a striking link between the structure of our galaxy and the evolution of Earth's crust, showing its development was shaped by the impact of meteorites during its journey through the Milky Way.
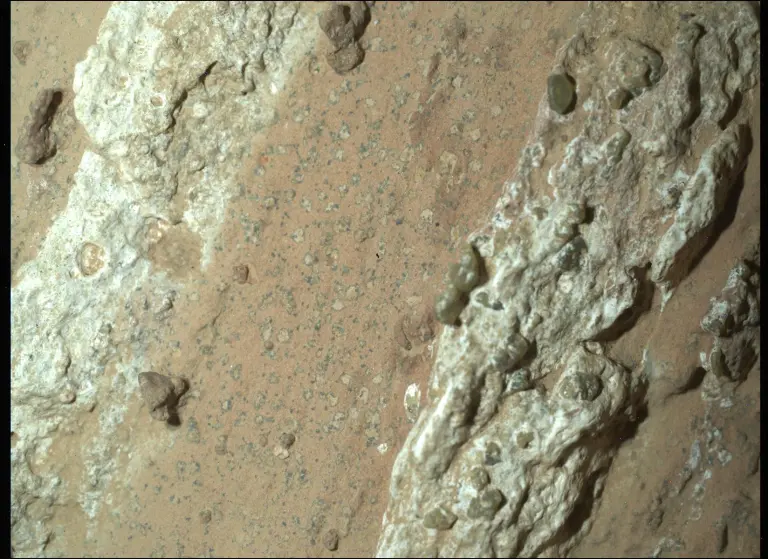

A sample collected by NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover from an ancient dry riverbed in Jezero Crater could preserve evidence of ancient microbial life.

78 million years ago, a 1.6 km asteroid slammed into what is now Finland, creating a crater 23 km (14 mi) wide and 750 m deep. The catastrophic impact created a fractured hydrothermal system in the shattered bedrock under the crater.

The gamma-ray burst (GRB) recorded on 2 July 2025 is the longest of its kind ever observed, lasting about a day. By comparison, GRBs normally last on the scale of milliseconds to minutes at most.
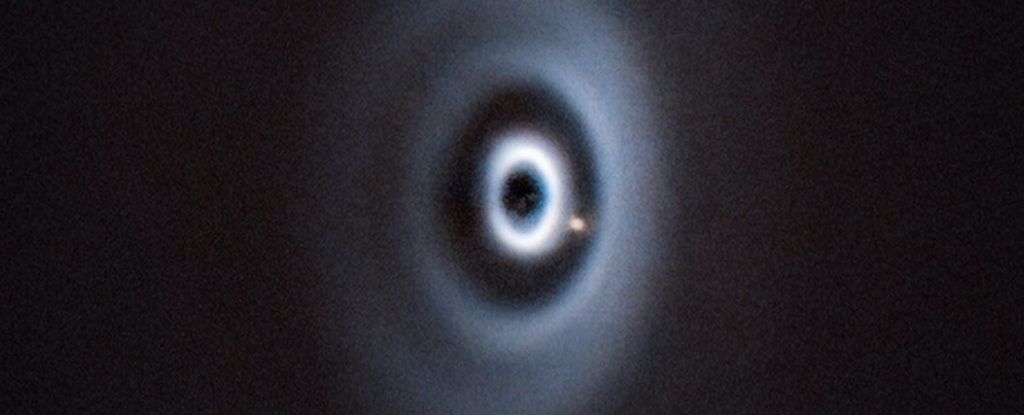
For the first time, astronomers have actually found a baby planet responsible for carving out gaps in the dusty disk surrounding a newborn star.
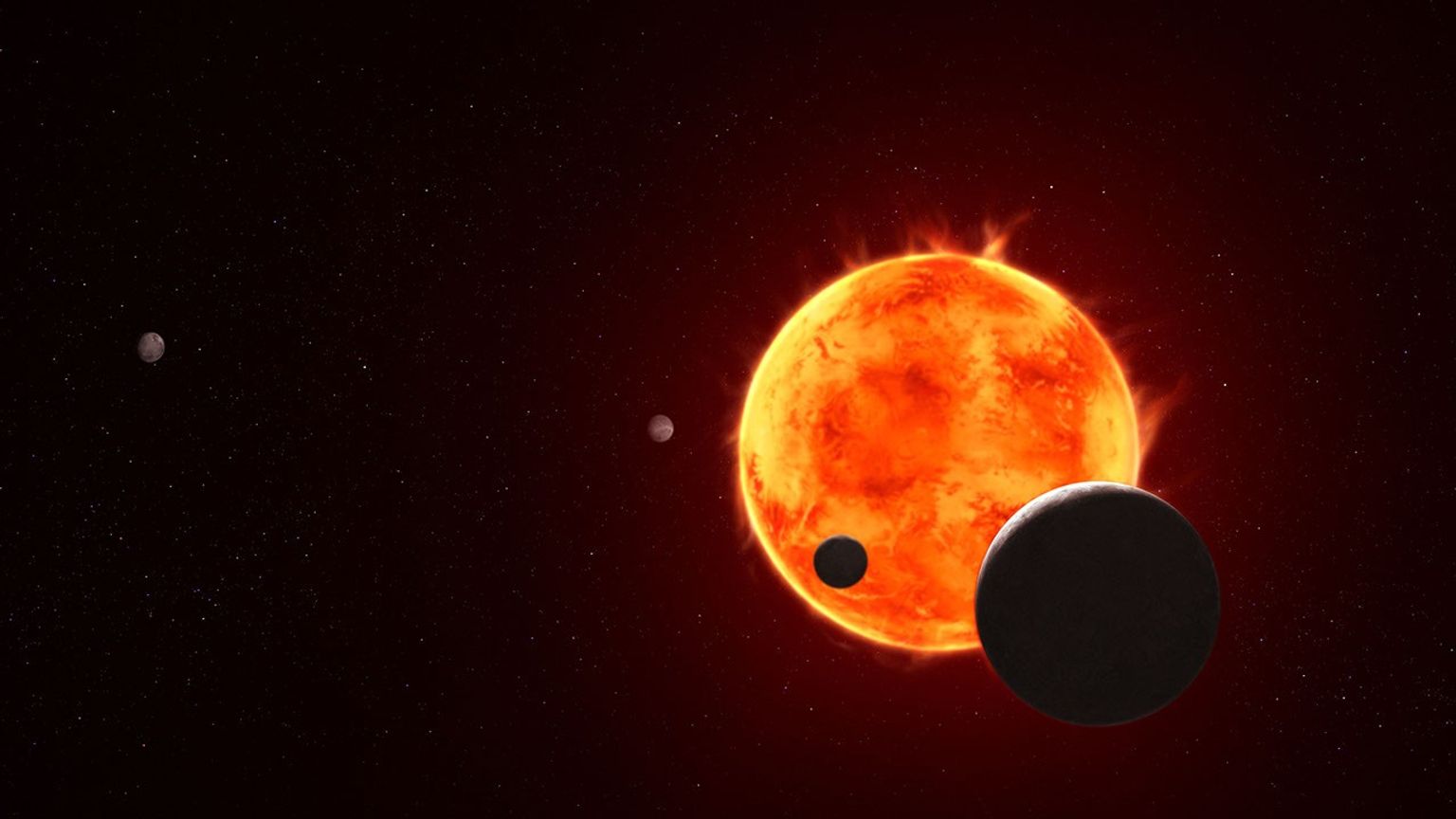

Scientists are in the midst of observing the exoplanet TRAPPIST-1 e with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope.
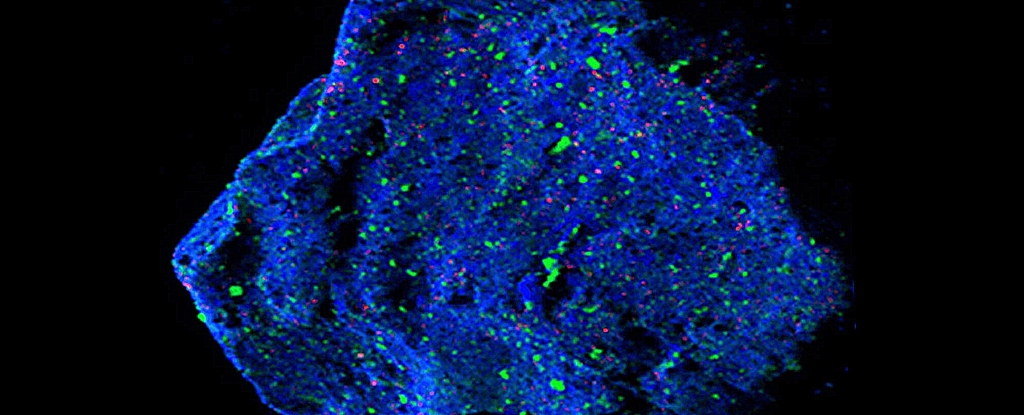
The asteroid Ryugu is an echo from the deep, distant past. Two tiny grains of the rock, delivered to Earth in 2020 by the famous Hayabusa2 mission, contain minerals older than any found on our planet.
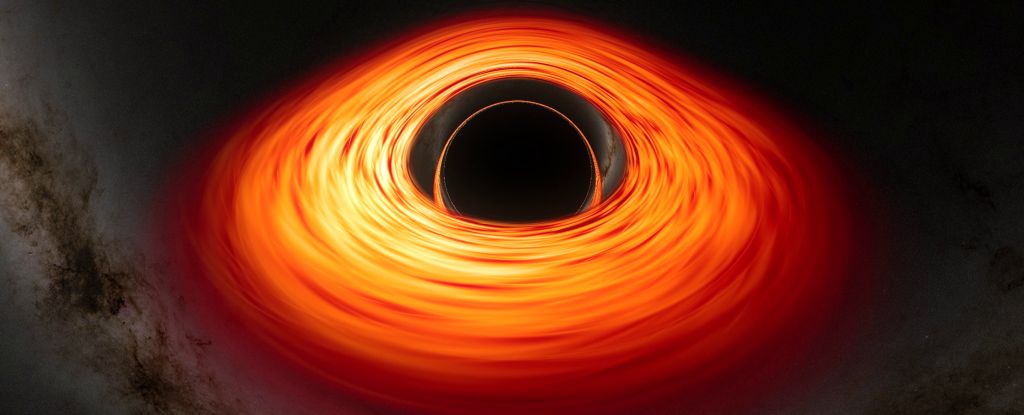

A tiny blob of red light spotted at the beginning of the Universe could represent the first direct evidence for a supermassive black hole formation pathway.
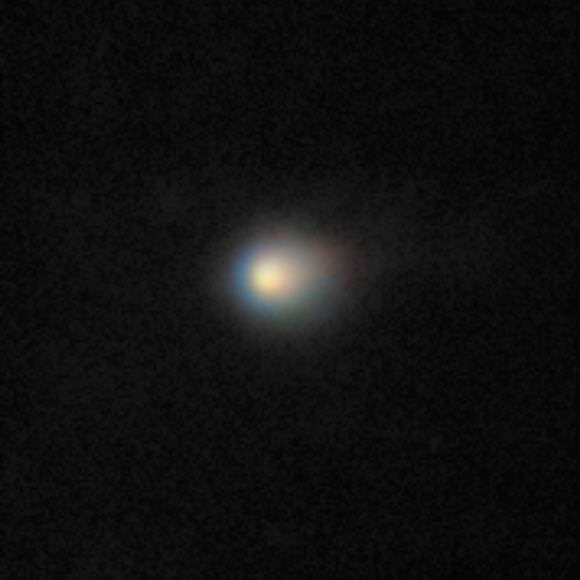

The comet is unique - not only was it made of carbon dioxide, but it had a carbon dioxide ice-to-water ice ratio that was literally out of this world, 8:1, which is among the highest ever recorded.

The NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope has revealed new details in the core of the Butterfly Nebula, NGC 6302.

Mars isn’t the neatly layered world we once imagined — its mantle is filled with ancient, jagged fragments left over from colossal impacts billions of years ago.
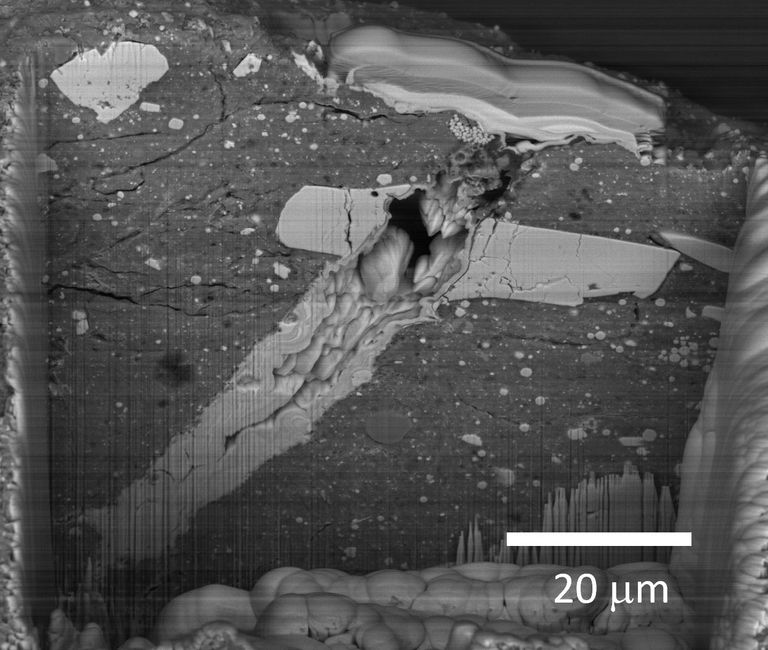
Asteroid Bennu, sampled by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission in 2020, is a mixture of dust that formed in our solar system, organic matter from interstellar space, and pre-solar system stardust.
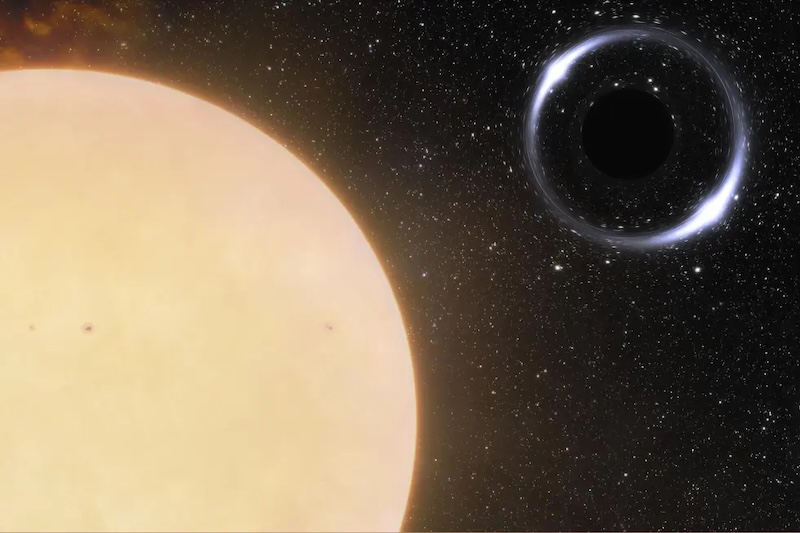

Dark matter particles could accumulate inside giant Jupiter-like exoplanets. Dense dark matter particles could eventually collapse to form a black hole inside a planet. The black hole could then ultimately consume the entire planet.