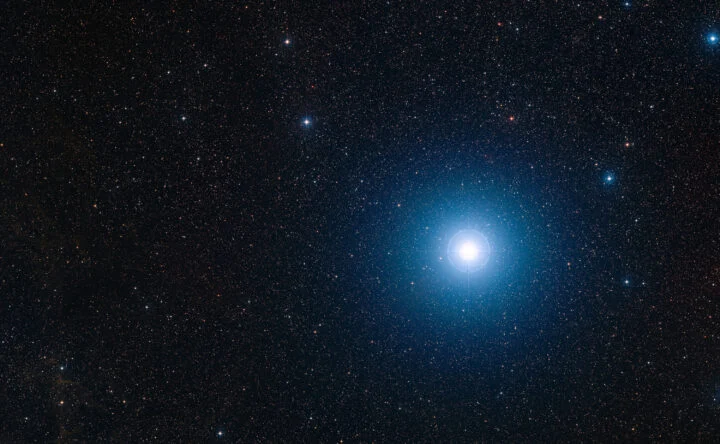

Astronomers have discovered a mysterious shock wave around a dead star – something they say has never been seen before.
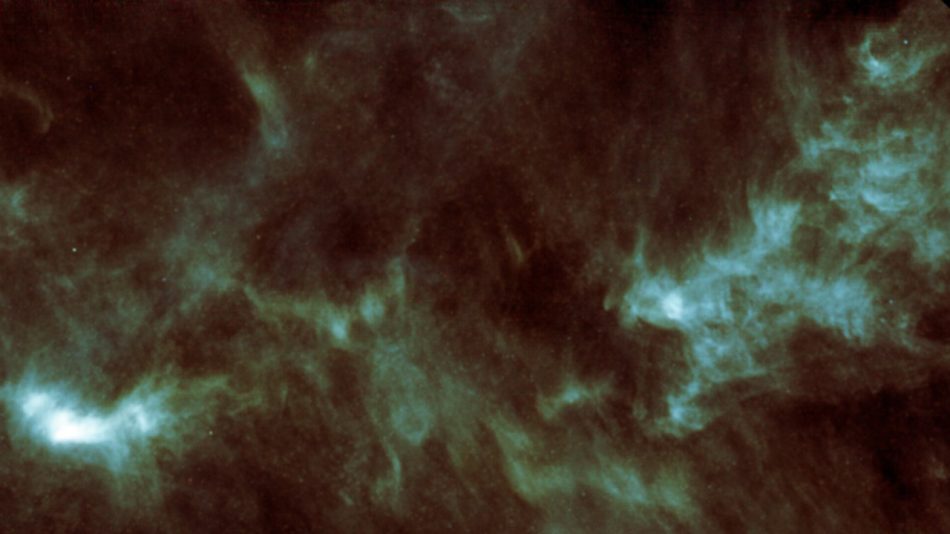
While looking through a developing star called L1544, a team of astronomers found methanimine, an organic molecule scattered throughout the clump of gas.
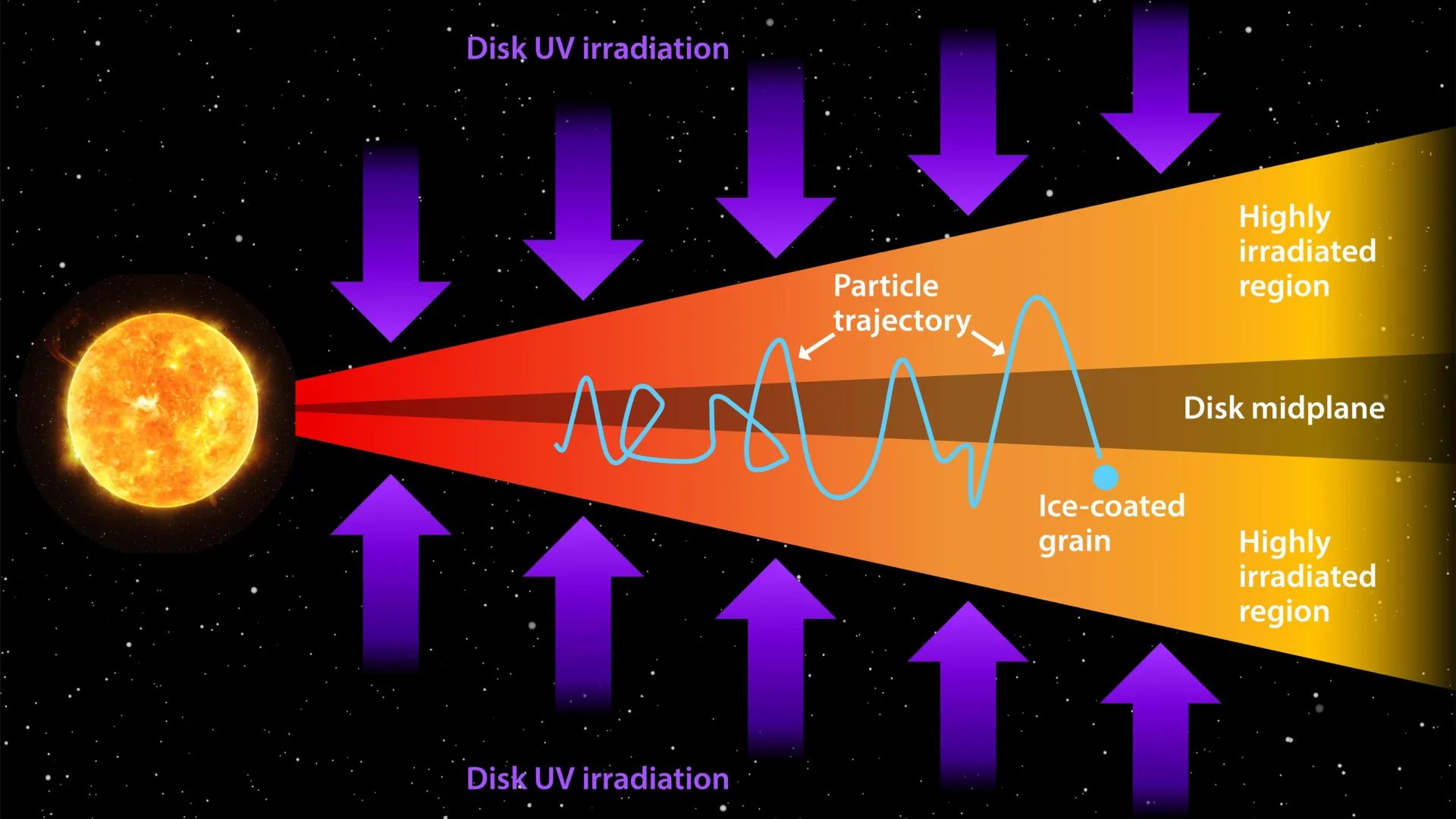
Jupiter’s icy moons may have been seeded with the chemical ingredients for life from the very beginning.

For the first time ever, scientists have uncovered a vast field of tektites in Brazil — mysterious glassy fragments forged when a powerful extraterrestrial object slammed into Earth about 6.3 million years ago.
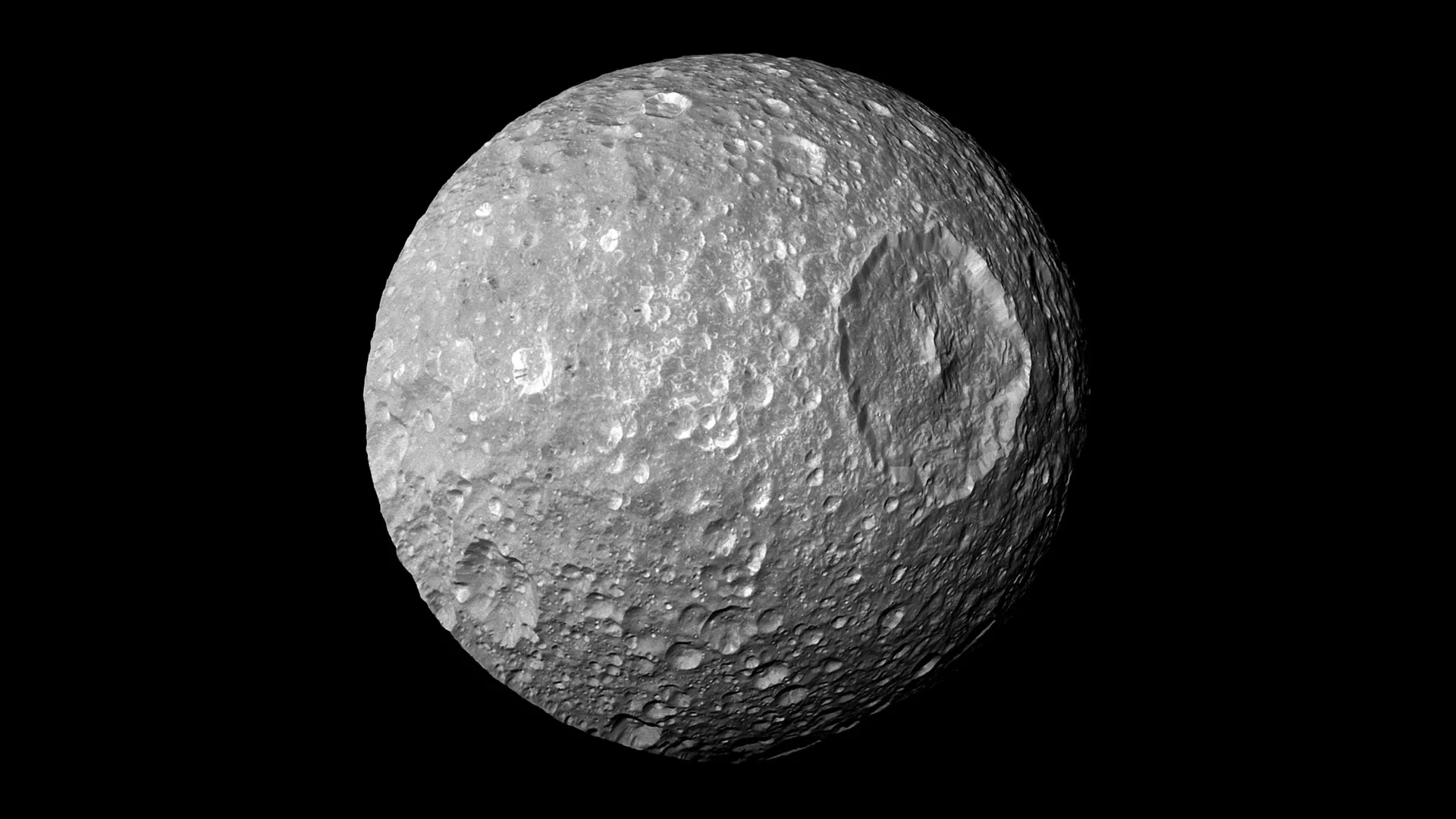

Icy moons circling the outer planets may be far more dynamic. New research suggests that when heat from tidal forces melts their ice shells from below, the sudden drop in pressure could cause hidden oceans to boil beneath the surface.

Using archival radar data from NASA’s Magellan spacecraft, planetary researchers have identified a vast underground conduit beneath the surface in the Venusian region of Nyx Mons.
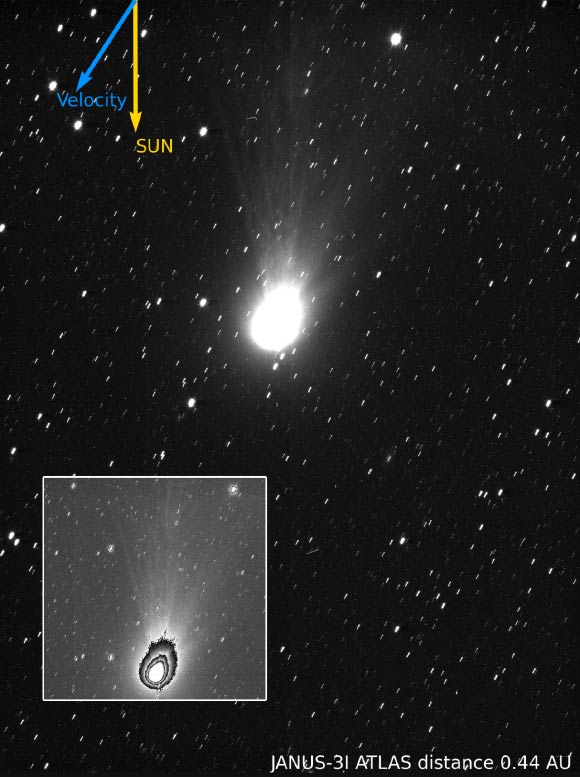

The JANUS science camera aboard ESA’s Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (Juice) has captured new images of the interstellar object 3I/ATLAS. The image displays jets coming out of the nucleus of 3I/ATLAS opposite to the direction of the Sun.
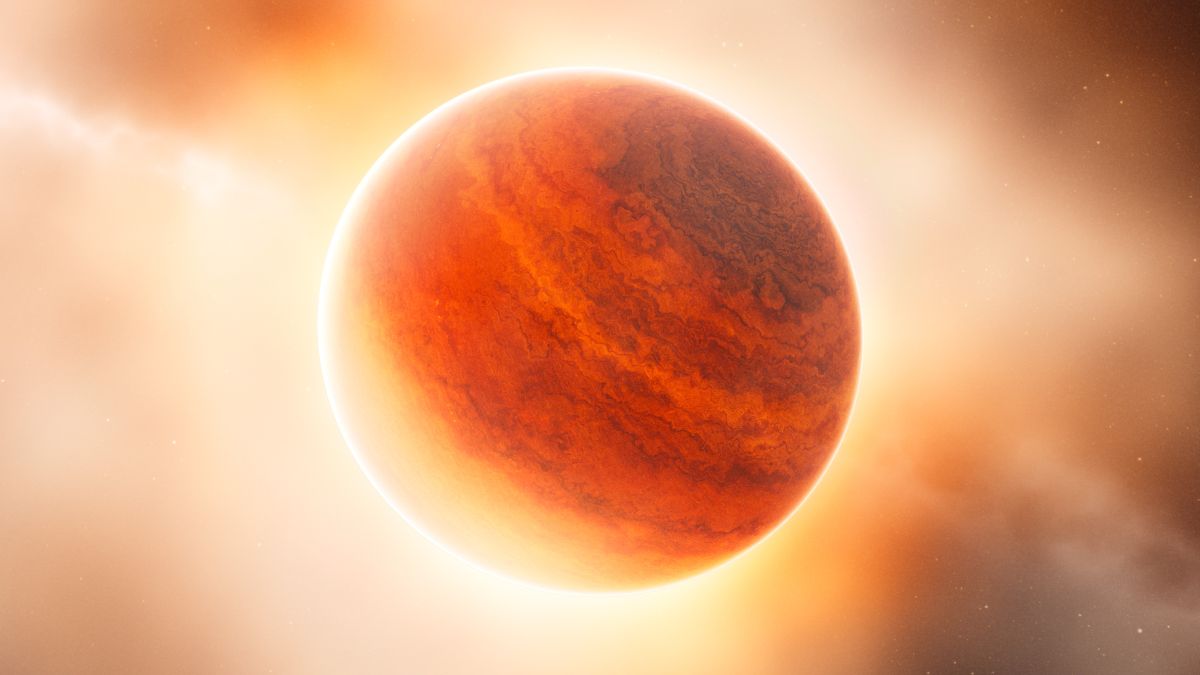

In a new study, researchers examine three massive gas giants about 130 light-years away, using their atmospheric chemistry to probe how such enormous planets form.
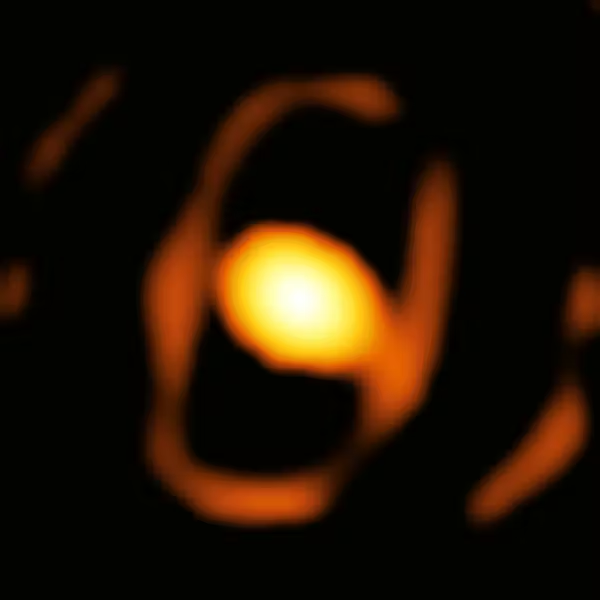
The enormous star WOH G64 in the Large Magelanic Cloud has transitioned from a red supergiant to a rare yellow hypergiant – in what may be evidence of impending supernova.
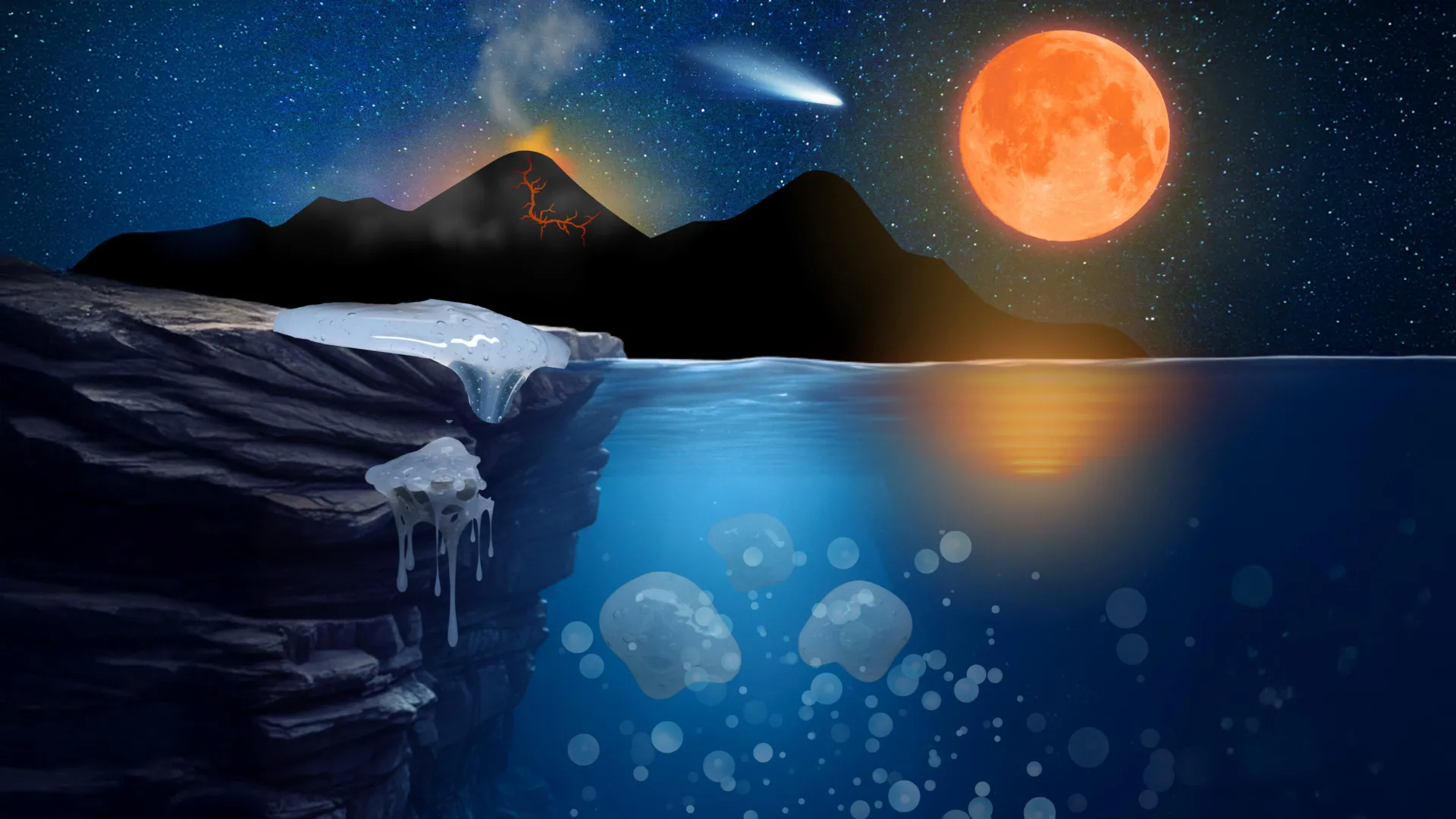

Life may have started in sticky, rock-hugging gels rather than inside cells. Researchers suggest these primitive, biofilm-like materials could trap and concentrate molecules, giving early chemistry a protected space to grow more complex.
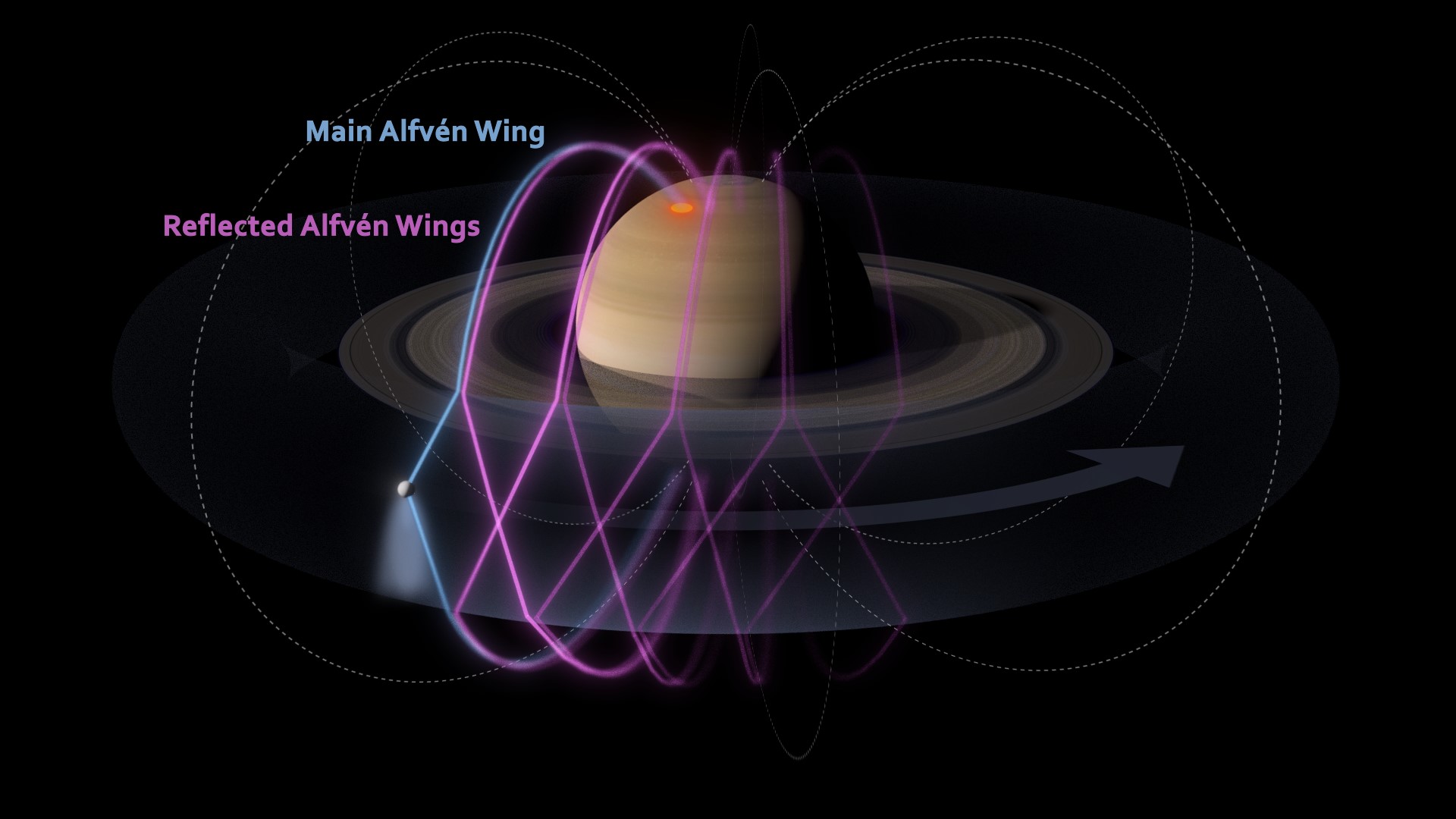
The analysis of data from four instruments aboard Cassini, collected over the mission’s 13-year duration, demonstrates the crucial role that Enceladus plays in circulating energy and momentum around Saturn’s space environment.
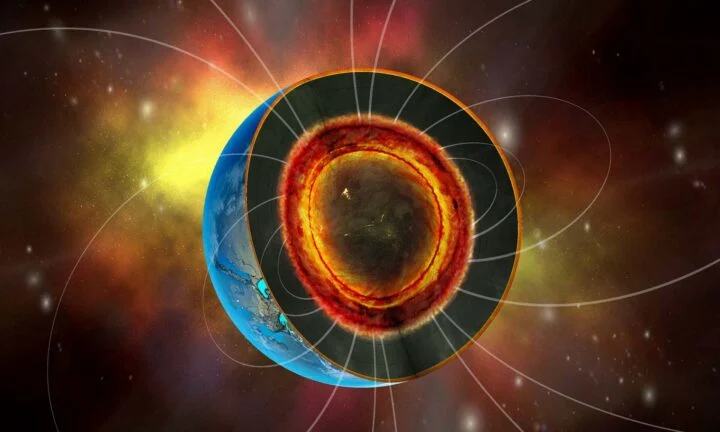

Deep beneath the surface of super-earths, oceans of molten rock may be doing something extraordinary: powering magnetic fields strong enough to shield entire planets from dangerous cosmic radiation.
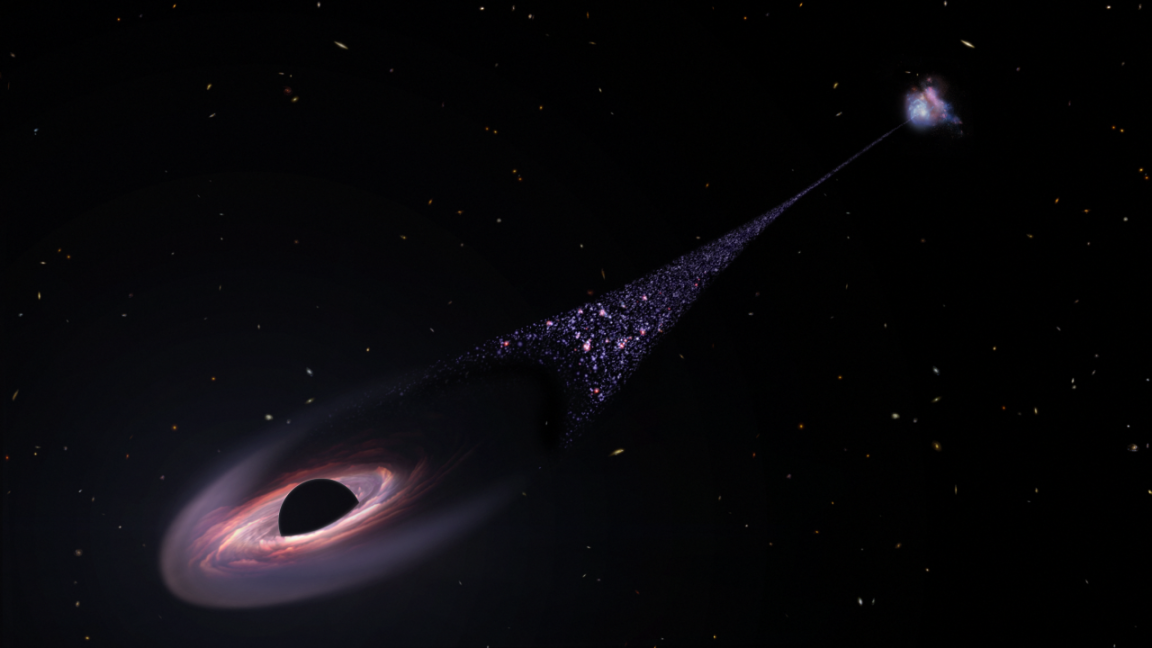
A new study suggests a solution to the Little Red Dots mystery. Scientists think young supermassive black holes may go through a “cocoon phase,” where they grow surrounded by high-density gas they feed on.
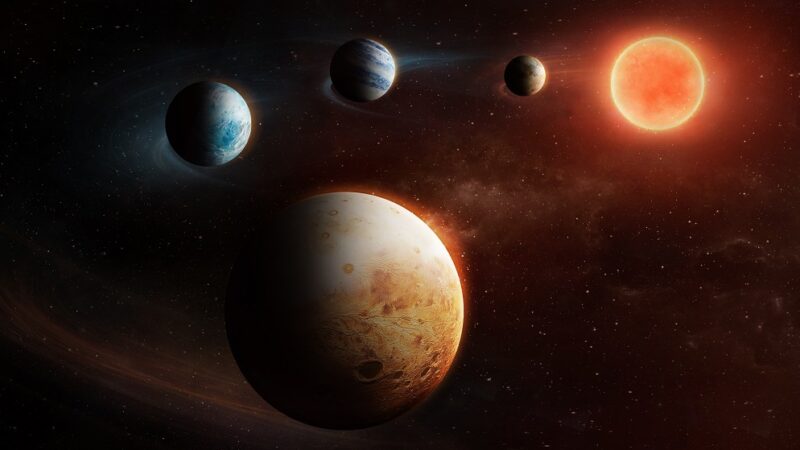

The planets around LHS 1903 – a cool faint red dwarf star – begin as expected with a rocky planet orbiting close by and then two gas worlds. A surprising 4th planet at the system’s outer edge that is rocky, rather than gaseous.
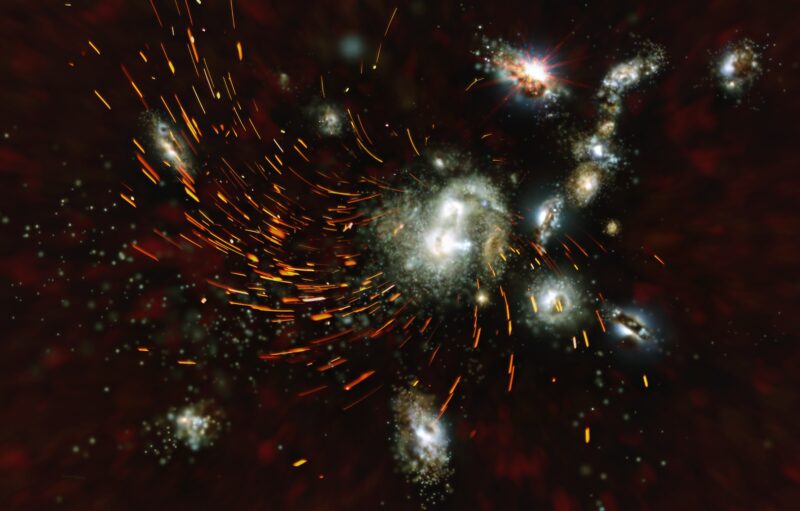
Astronomers found evidence a giant elliptical galaxy may form through the rapid collapse of a young galaxy cluster.