
The microbes could potentially pose a threat to the health of astronauts on board Tiangong.

Martian dust storms can potentially cause respiratory issues and elevated risk of disease, making them yet another health hazard space agencies need to prepare for, according to new research.

Astronauts often experience immune dysfunction, skin rashes, and other inflammatory conditions while traveling in space. These issues could be due to the excessively sterile nature of spacecraft.
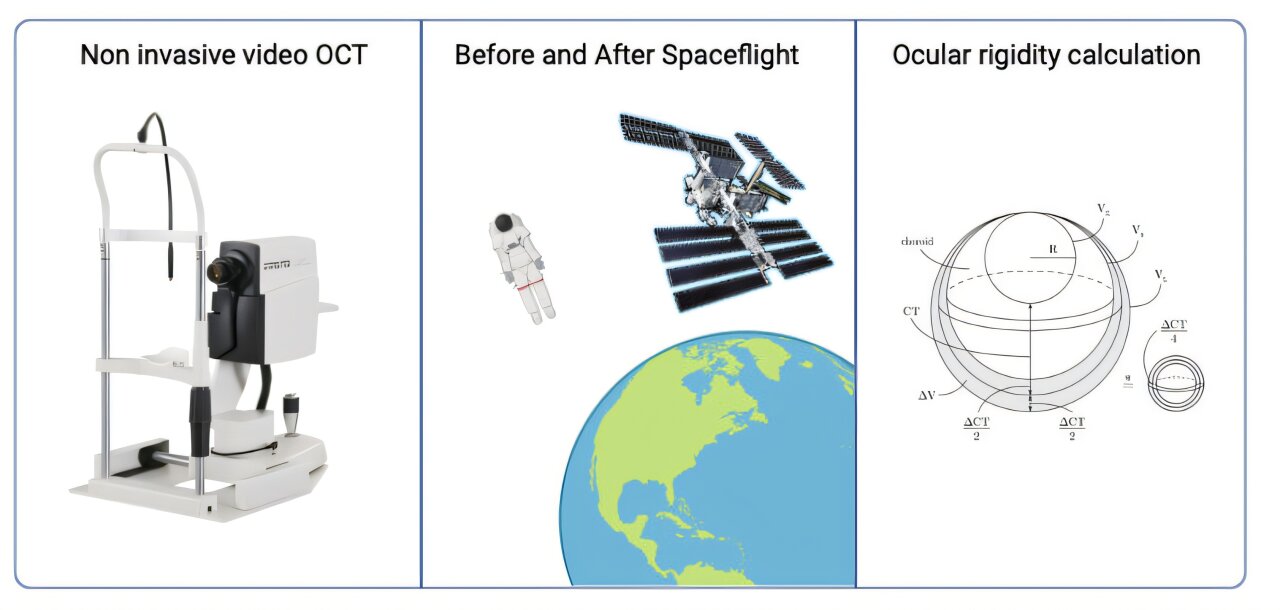
The low levels of gravity (microgravity) in space cause significant changes in astronauts' eyes and vision after six to 12 months aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
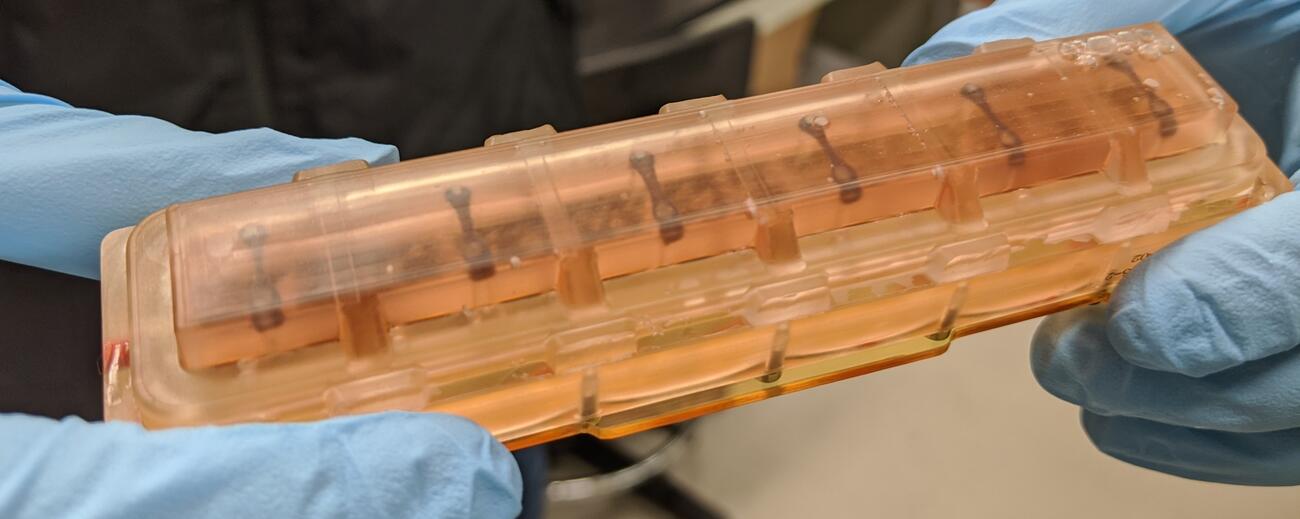
New research finds that heart tissues aboard the space station beat about half as strong as on Earth.

Motorcyclists have long ridden on an apparatus called the “wall of death,” which involves driving in circles parallel to the ground. Scientists are theorizing that something similar could be used for astronauts to exercise on the Moon.

It is clear that going to space exploration will not be reserved for astronauts and government space agencies for much longer. But before the 'Great Migration' can begin, there are a lot of questions that need to be addressed.

Using MRI scans of 30 astronauts, the researchers built on those earlier studies to discover that the longer the spaceflight, the greater the increase in brain fluid volume.

Astronauts lose decades' worth of bone mass in space and many do not recover even after a year back on Earth after their missions on the International Space Spation, - a new study finds.

Overall, astronauts remain in excellent mental and physical health relative even after their return from long-term missions. And yet some develop cardiovascular deconditioning, vision problems and ovary problems (women).