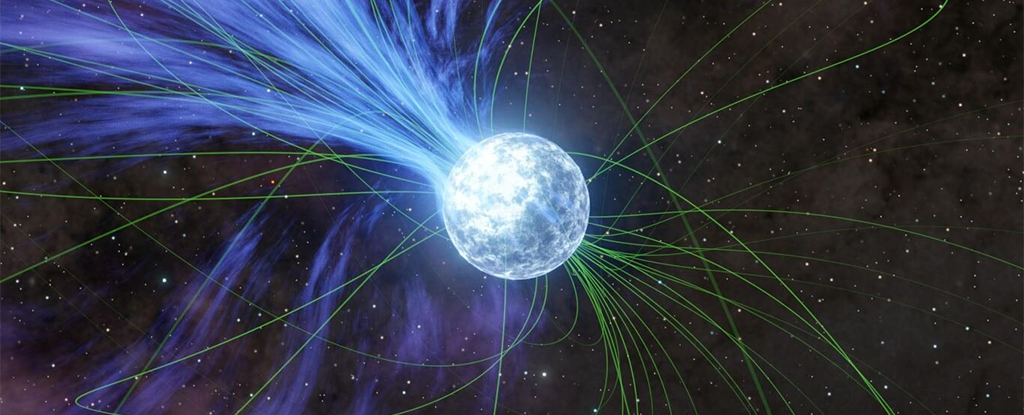
Scientists have long been trying to determine how elements heavier than iron, including gold and platinum, were first created and scattered through the Universe, and new research may give us another part of the answer: magnetars.
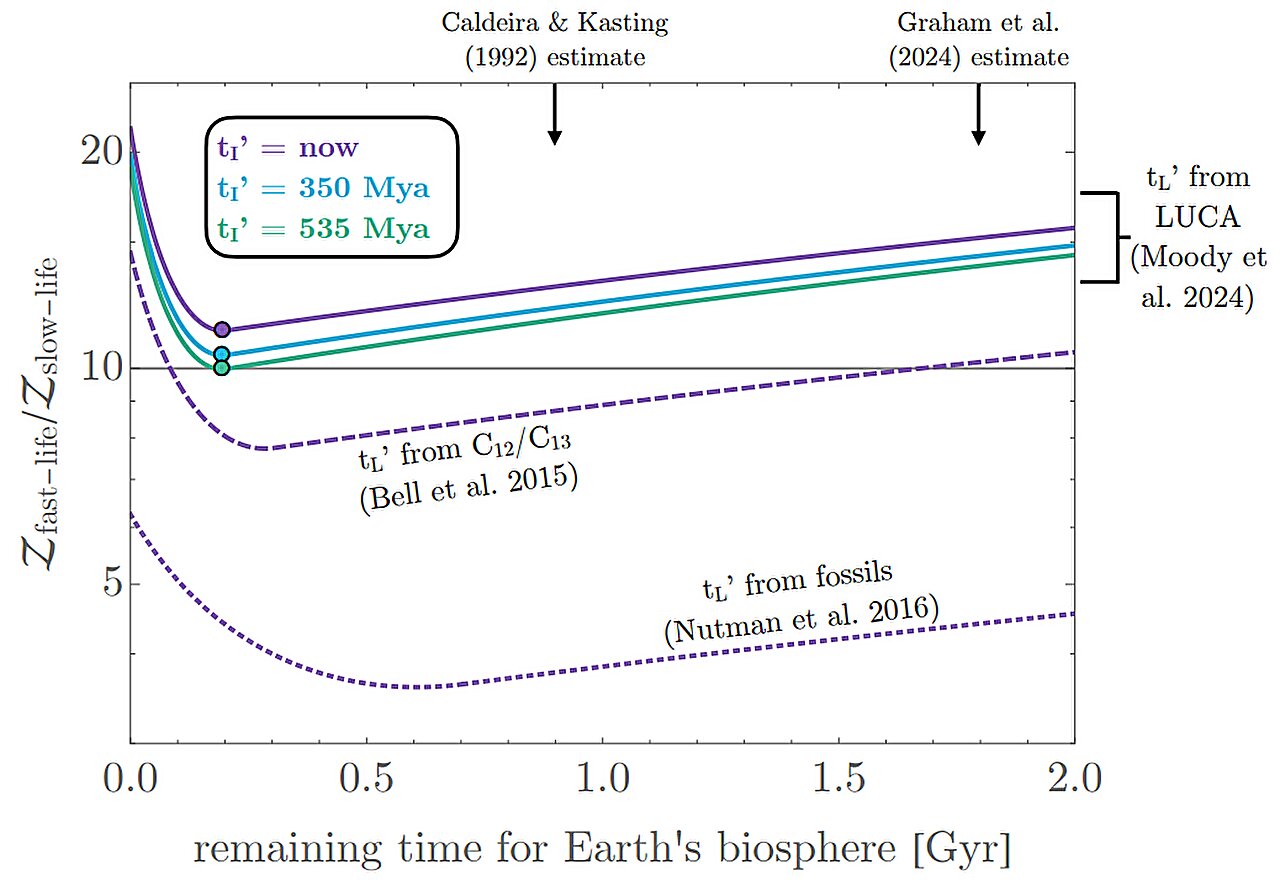
An astronomer at Columbia University is suggesting that because life emerged so soon on Earth after its formation, it may emerge rapidly on Earth-like planets after the right conditions arise in general.

Physicist Melvin Vopson offered a new interpretation of gravity, arguing that it could be evidence that reality is a computer simulation.
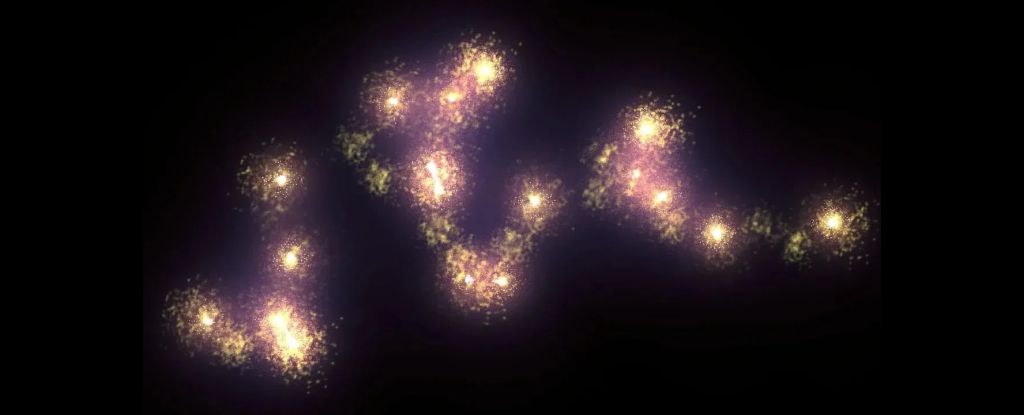

The largest known structure in the Universe may be even larger than the large we thought it was.
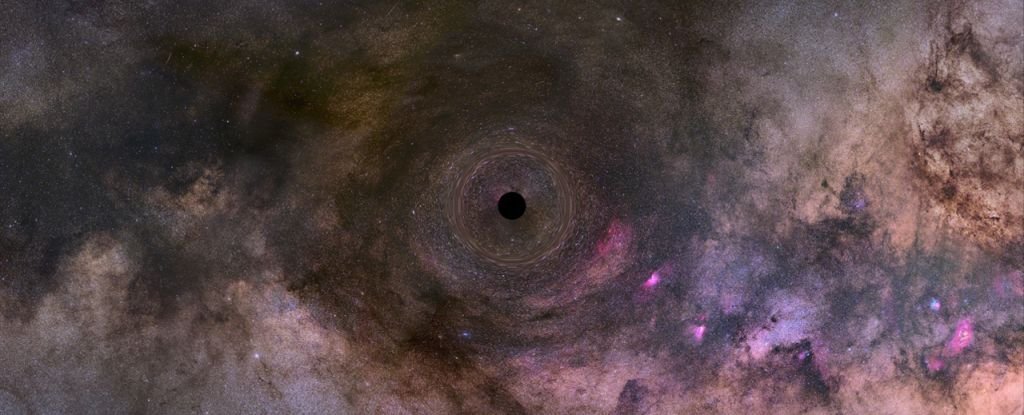

A lonely black hole roaming the cosmos in solitude has been confirmed for the first time.

After over three decades of scrutinising our Universe, Hubble remains a household word as the most well-recognised telescope in scientific history.

New research finds that despite large rivers and seas of liquid methane, Saturn's moon Titan seems mostly devoid of river deltas.

Astronomers have detected the most promising signs yet of a possible biosignature outside the solar system, although they remain cautious.
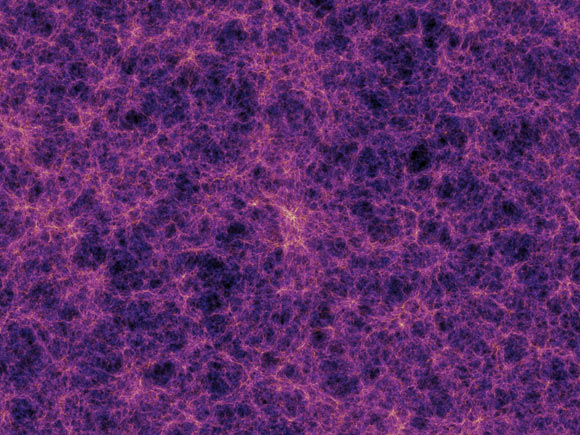

New research led by University of Hawaii astronomers suggests our Universe may rotate - just extremely slowly.
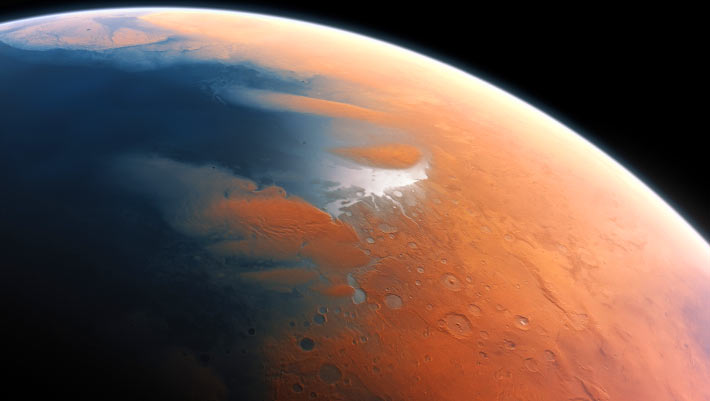

The distribution of valley heads on Mars matches predictions for a climate that includes precipitation rather than just runoff from melting ice caps.

Astronomers at MIT have discovered a rocky exoplanet orbiting the bright K-dwarf star BD+05 4868A and observed variable transit depths that are characteristic of comet-like tails.

In a new image from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, a galaxy named for its resemblance to a broad-brimmed Mexican hat appears more like an archery target.
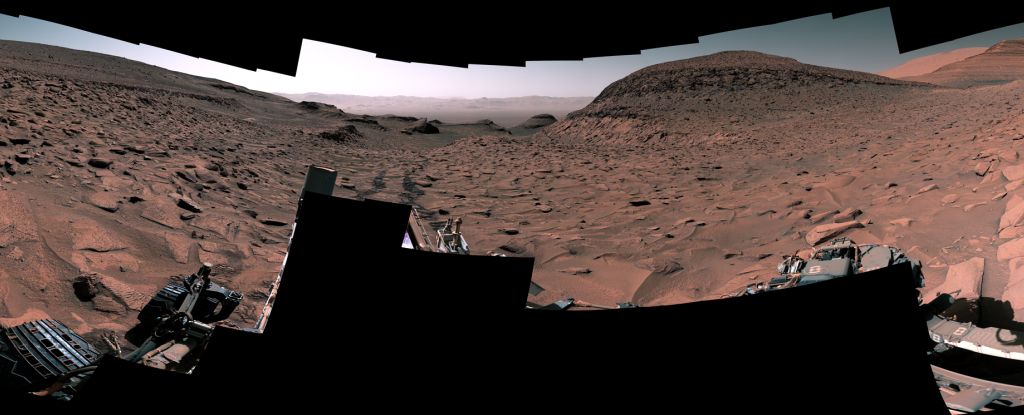

A surprise discovery in Gale Crater is the component that was missing in the puzzle of Mars's climate history.
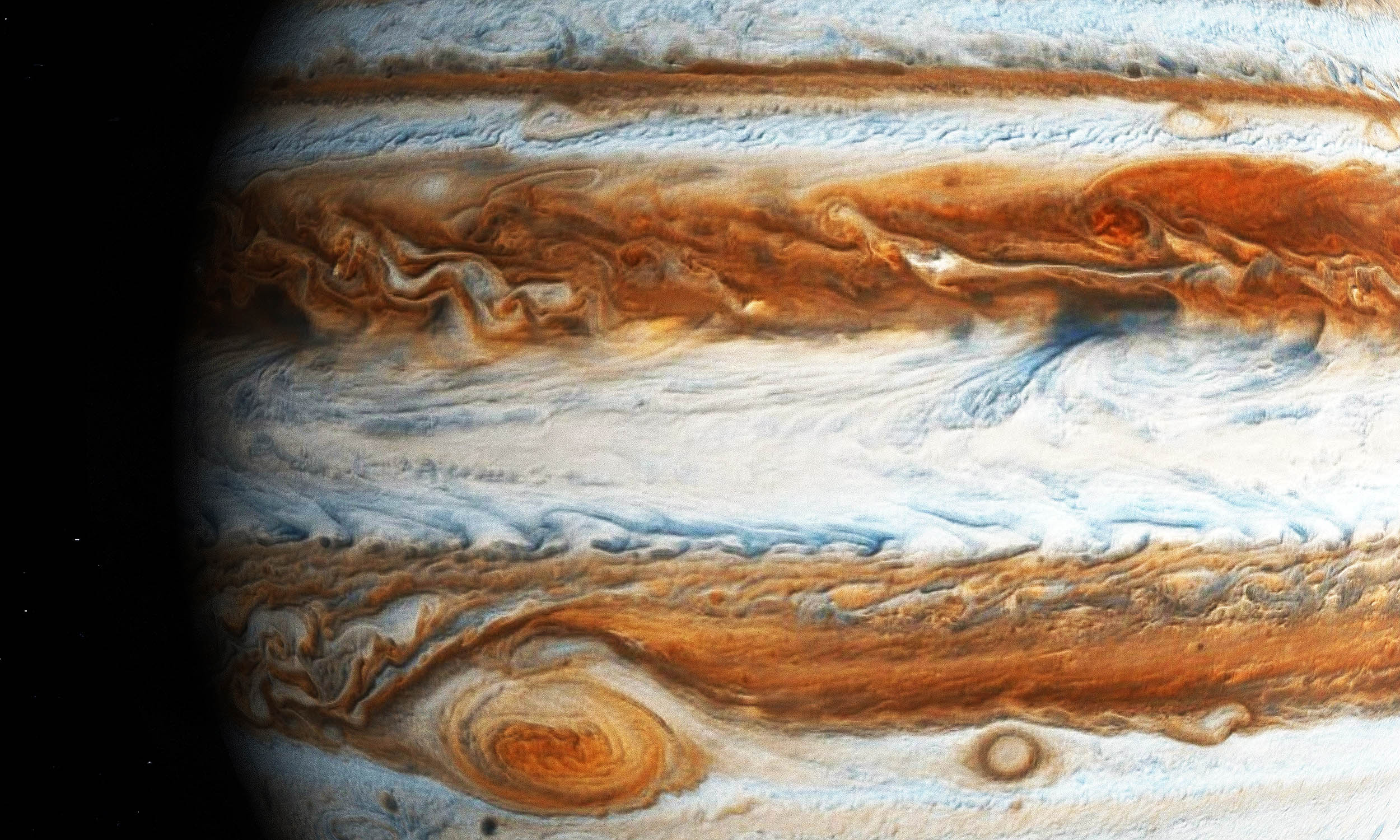

Slushy hail, made of water and ammonia, may form during lightning-packed storms, giving researchers fresh clues about what lurks beneath the planet’s colorful cloud tops.
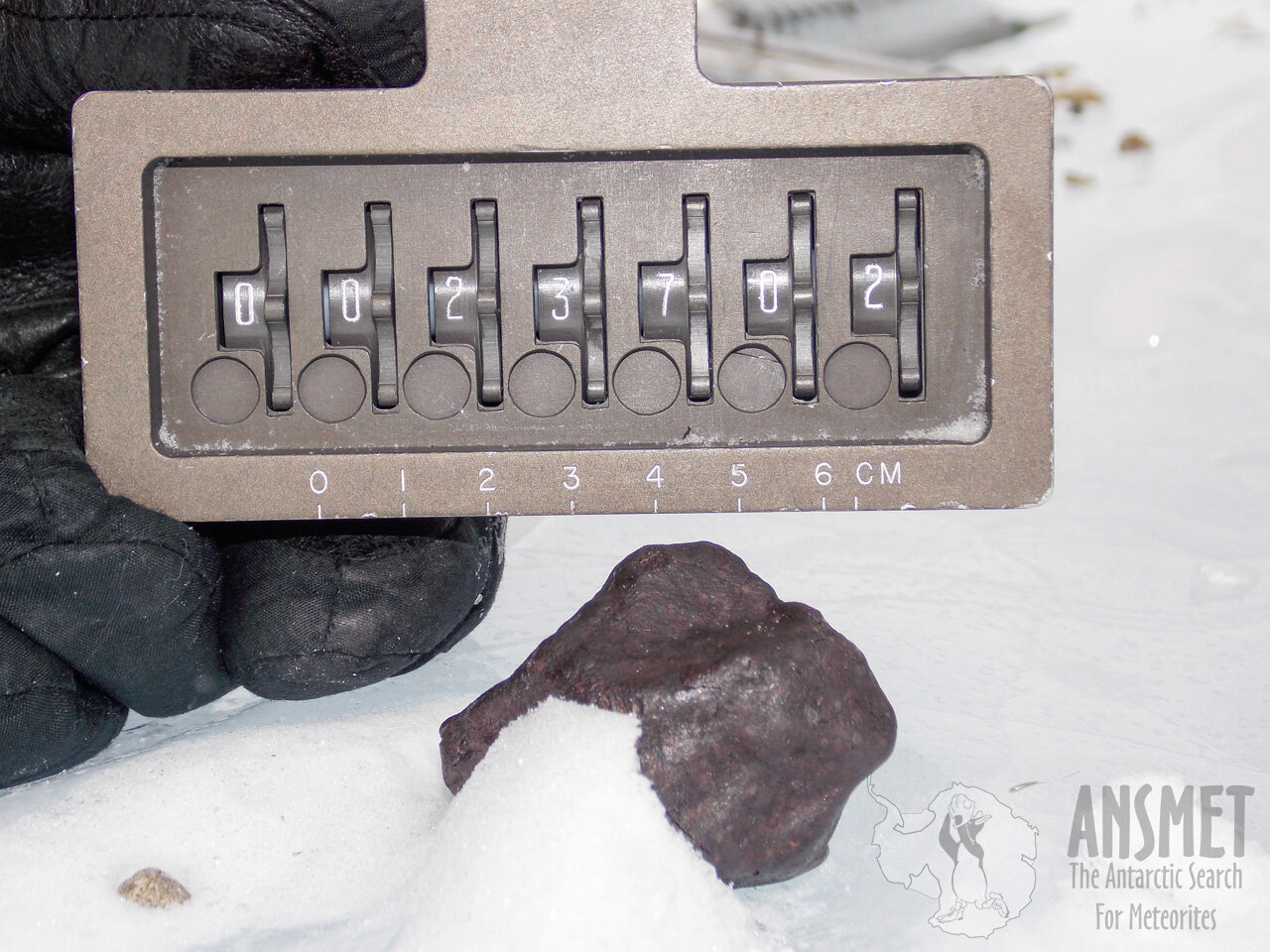

Using a rare type of meteorite, enstatite chondrite, which has a composition analogous to that of the early Earth - researchers have found a source of hydrogen which would have been critical for the formation of water molecules.