
In 2022 NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope discovered an abundance of tiny red objects scattered across the sky in the early universe. A large fraction of them are likely galaxies with supermassive black holes growing at their centers.

A recent study reveals that the famous Wolf-Rayet 104 "pinwheel star" holds more mystery but is even less likely to be the potential "death star" it was once thought to be.

The discovery is one of the most significant findings in the search for evidence of past life on Mars.

Traditional models of star formation suggest there may be as few as 300 black holes in the closest region of the supermassive black hole Sagittarius A*. But a new study suggests the number of stellar-mass black holes is much higher.

When you peer out into the depths of the cosmos, a mystery lies there, waiting. In a survey of the deep sky, most of the galaxies are seen rotating in the same direction.

JADES-GS-z14-0 is rich with oxygen – which is an absolute surprise, since scientists had thought elements heavier than hydrogen and helium weren't around in significant quantities until much later in time.
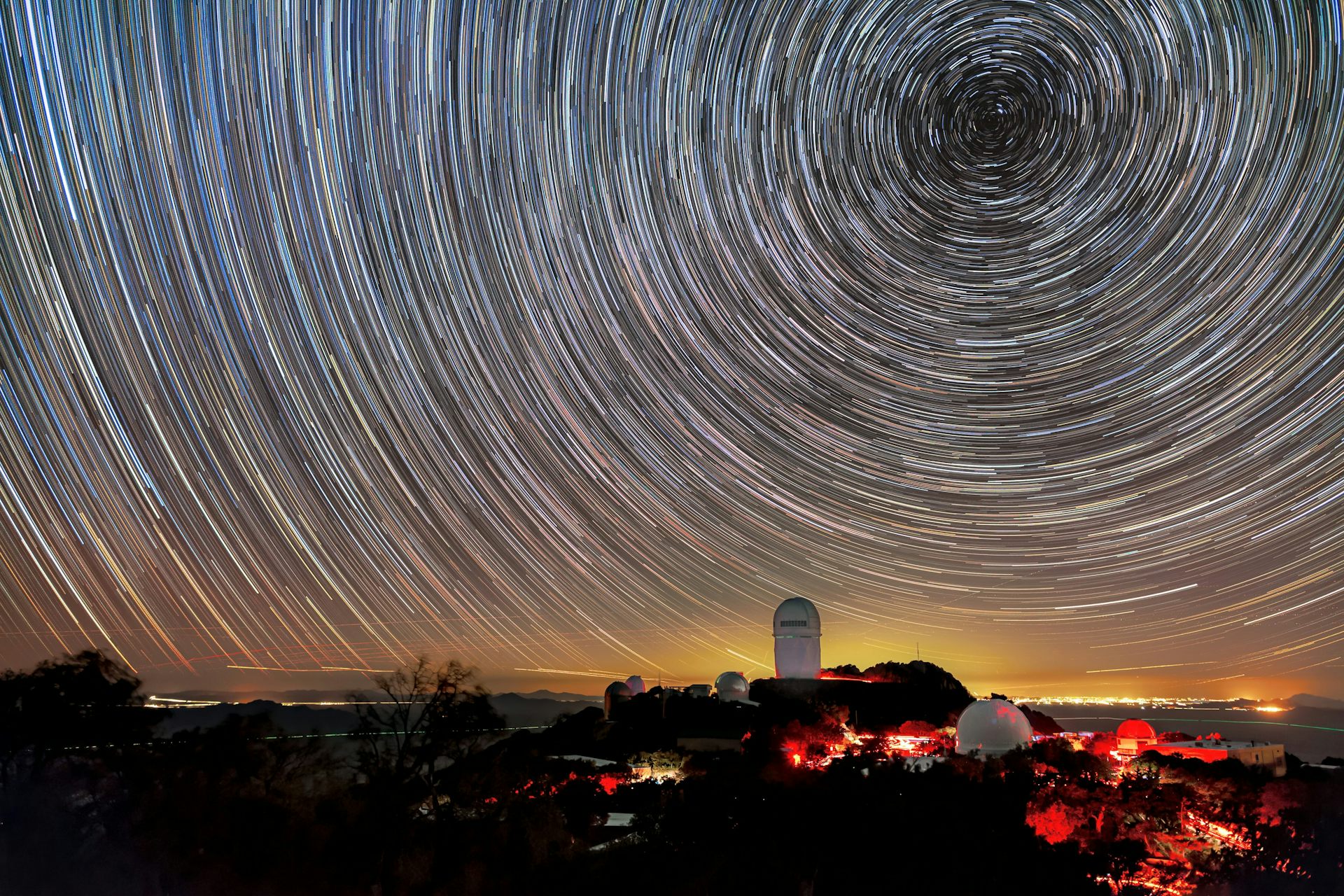

However, new results from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI), released today, suggest dark energy may be changing over time.

JWST have revealed an exceptionally large galaxy in the early universe. It’s a cosmic giant whose light has travelled over 12 billion years to reach us. We’ve dubbed it the Big Wheel.

Astronomers have detected mysterious X-ray signals coming from a nearby white dwarf star for more than 40 years. We may now know where they're coming from - the death throes of a planet being torn to shreds and raining down on the star.

A combination of cosmic processes shapes the formation of one of the most common types of planets outside of our solar system, according to a new study.

Astronomers using the Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) onboard the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope have captured coronagraphic images of the HR 8799 and 51 Eridani planetary systems.

New research suggests black holes may transition into 'white holes', ejecting matter and potentially even time back into the universe, defying our current understanding of these cosmic giants.

The mineral content of oddly pale rocks found in Jezero Crater can only have formed under very warm, very soggy conditions – suggesting that, long ago, Mars may have been a lot more peculiar than we ever suspected.

In this incredible image, we can see the unrestrained energy of two young stars about 650 light-years away as their energetic jets create a distinct hourglass shape with clumps and swirls of gas and dust.
Recent research proposes a new form of dark matter that may actually be lighter in mass than other dark matter candidates.