
By studying Ceres' gravity, scientists learned more about the dwarf planet's internal structure and were able to determine that the water reservoir is about 40 km deep and hundreds of km wide.

Both the Moon and Mars were volcanically active at one time and the result is lava tubes. A new study shows that lunar and Martian lava tubes might be enormous, and easily large enough to accommodate a base.

The star with the smallest orbit is known as S62. Its closest approach to the black hole has it moving more than 8% of light speed. S62 orbits our supermassive black hole Sagittarius A every ten years.

Virgin Galactic already has its commercial operating licence but it has to work through a list of "verification and validation" milestones before it can welcome passengers aboard.

Using known distances of 50 galaxies from Earth to refine calculations in Hubble's constant, astronomers estimates the age of the universe at 12.6 billion years, different to the value of 13,8 billion years.

Two American astronauts have splashed down yesterday, as the first commercial crewed mission to the International Space Station returned to Earth. Its the first crewed US water landing in 45 years.

NASA's Mars 2020 Perseverance rover mission is on its way to the Red Planet to search for signs of ancient life and collect samples to send back to Earth.

A new study identified 37 recently active volcanic structures on Venus. The study provides some of the best evidence yet that Venus is still a geologically active planet.

Direct images of exoplanets are pretty rare. This is the first direct image of multiple exoplanets orbiting a star similar to our Sun taken by The European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope (VLT).
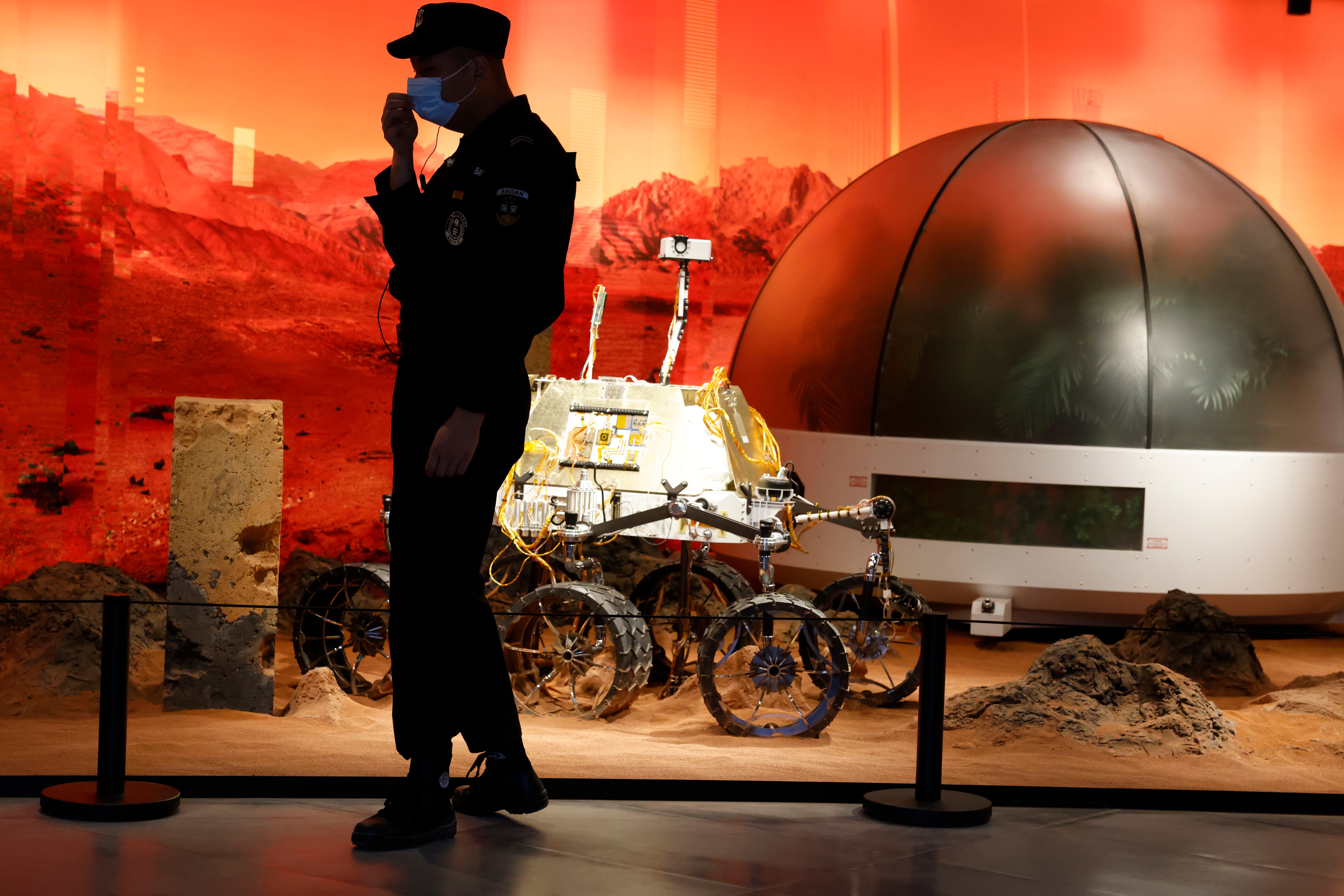

An unmanned spacecraft blasted off Thursday on a yearlong journey to Mars. The Tianwen-1, which translates into “Questions to Heaven,” is expected to reach the Red Planet by February.
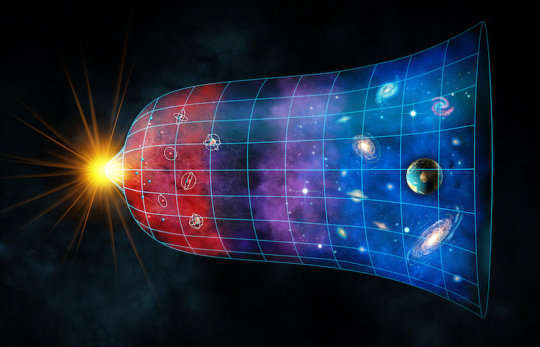
Recently scientists suggested that have suggested the universe may be hundreds of millions of years younger. However a new observations suggest the universe is still about 13.8 billion years old.
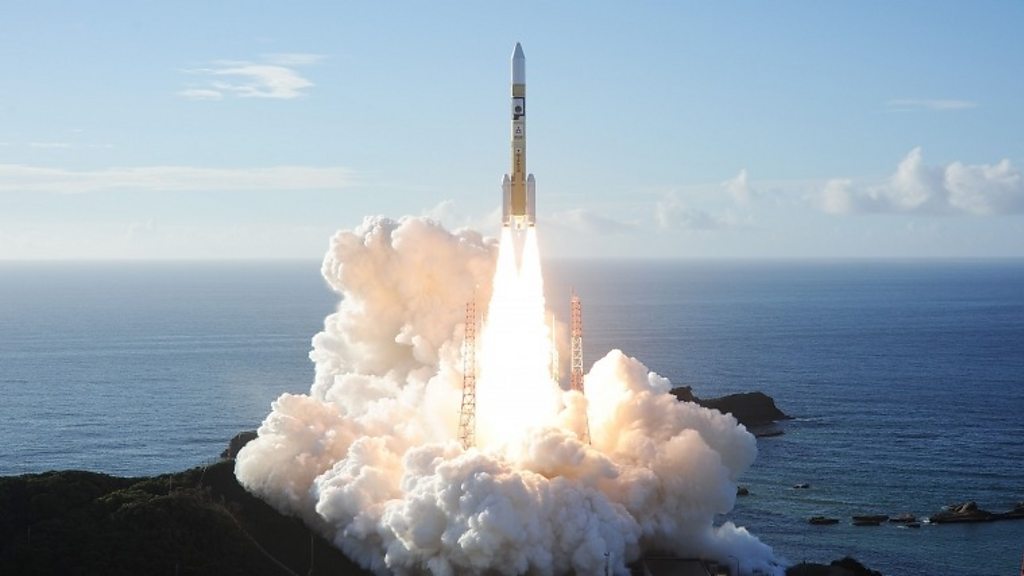

The Hope orbiter will arrive in February 2021 to begin a two-year survey of the weather on the red planet. For Emirati scientists the mission represents a new chapter in the history of scientific discovery.

Hundreds of scientists from about 30 institutions worldwide have published the largest-ever 3D map of the Universe, the result of an analysis of more than 4 million galaxies and ultra-bright, energy-packed quasars.

Four of these strange objects have been detected and an international team of astronomers has nicknamed them ORCs - short for "Odd Radio Circles". All four are only visible in radio wavelengths.

The black hole’s mass is about 8,000 times bigger than the black hole in the centre of the Milky Way. If the Milky Way’s black hole wanted to grow that fat, it would have to swallow two thirds of all the stars in our galaxy.