
New observations of mud cracks made by NASA's Curiosity rover show that high-frequency, wet-dry cycling occurred in early Martian surface environments.

The galaxy, called JD1, is seen as it was when the universe was only 480 million years old, or 4% of its present age.
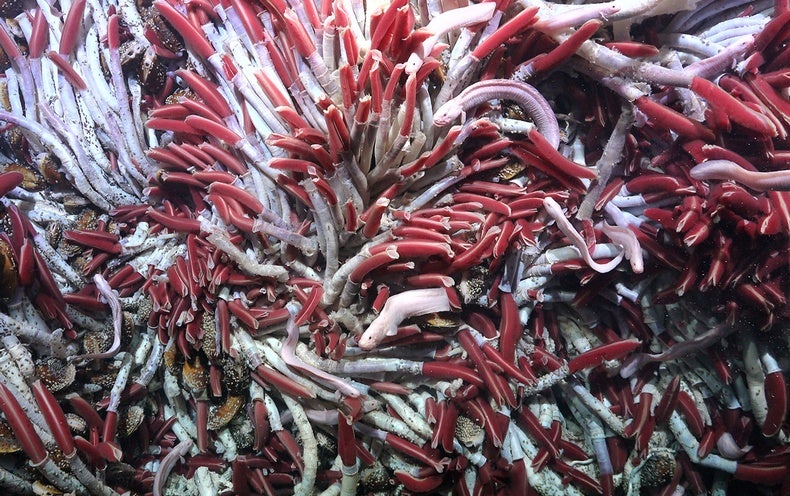

We’ve known about the vents above for a long time, but this is basically a completely new ecosystem below.

The scientists hope the breakthrough is the start of a new era. Though this experiment was performed with simple, two-atom molecules, they plan to work their way up to handling larger and more complex molecules.

Experiments have shown that microwaving plastic baby food containers can release huge numbers of plastic particles — in some cases, more than 2 billion nanoplastics and 4 million microplastics for every square centimeter of container.

Such a breakthrough could one day help curb climate change if companies can scale up the technology to a commercial level in the coming decades.

A record-breaking binary system has been found with a rotation so tight, both objects could comfortably fit inside the Sun.

The international team behind the discovery also found that this type of light, known as gamma rays, is surprisingly bright. That is, there's more of it than scientists had previously anticipated.

A newly discovered star is so large, bright, and strange that its appearance could be pointing us towards a clump of dark matter in the sky.

By using the Very Large Telescope and the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array, astronomers have identified clumps in the thick material around a star named V960 Mon that could gravitationally collapse to form the seeds of planets like Jupiter.
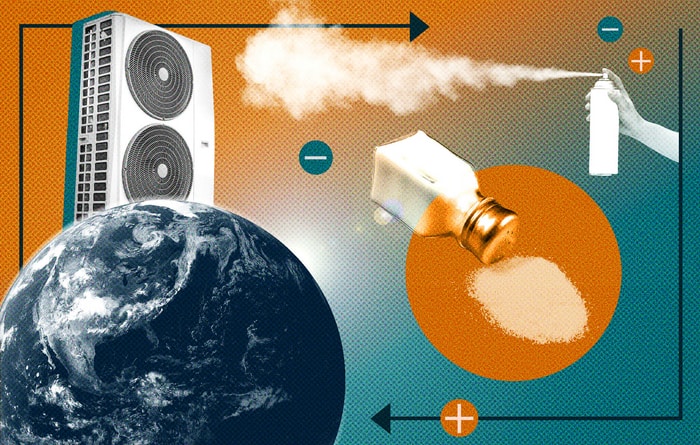
Technique could replace current systems that rely on vapour compression of powerful greenhouse gases.

July was a recording breaking month for both land and sea temperatures, according to EU climate observers Copernicus.

Deep beneath the soil of a Massachusetts forest, an international team of researchers has uncovered a multitude of mysterious, gigantic viruses of unprecedented ecological diversity.

According to an analysis of grains collected from asteroid Ryugu, at least part of the carbon-rich rock started its life much farther from the Sun before ending up in the asteroid belt and then, ultimately, at roughly Earth's distance from the Sun.

This hypothetical planet is provisionally known as Planet 9. Computer simulations show it must be a very large planet, consisting of between four and eight times the mass of the Earth and at least ten times the distance of Pluto.