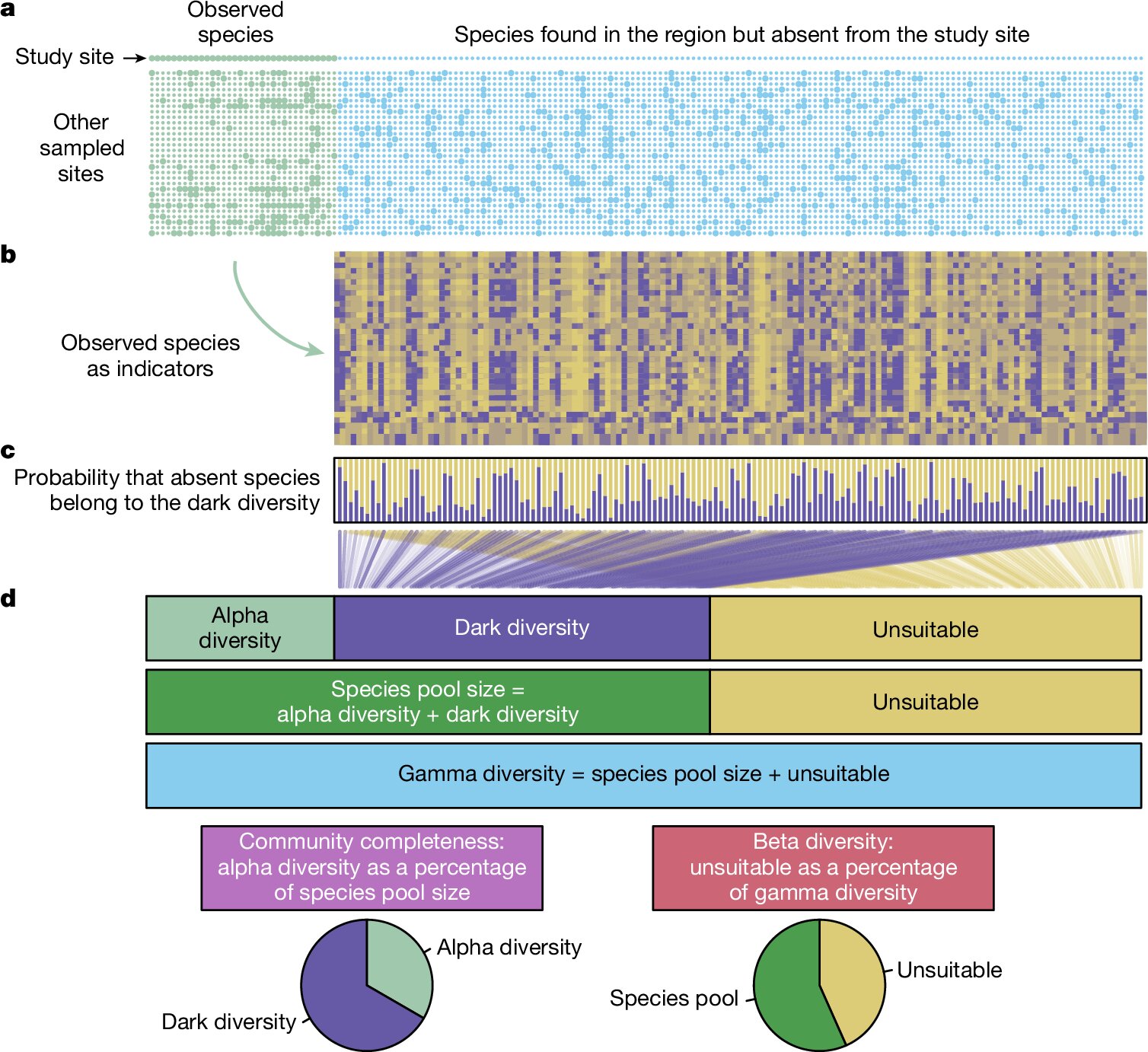
A study recently published in Nature indicates that human activities have a negative effect on the biodiversity of wildlife hundreds of kilometers away.
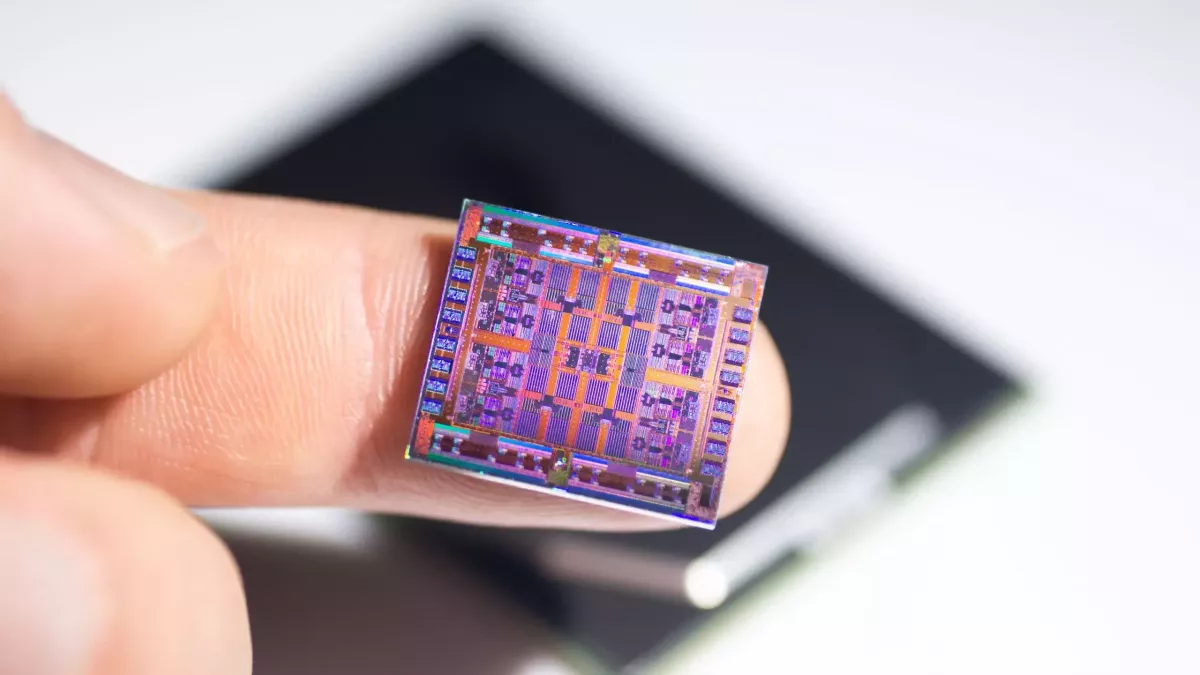
Taiwanese semiconductor leader TSMC has unveiled the world's most advanced microchip: the 2-nanometre (2nm) chip.

NASA's new infrared space telescope, SPHEREx, is designed to give us unprecedented insights into the evolution of the Universe.

A new study reveals some surprising discoveries about healing processes that are potentially triggered by the process of necrosis, or premature cell death.
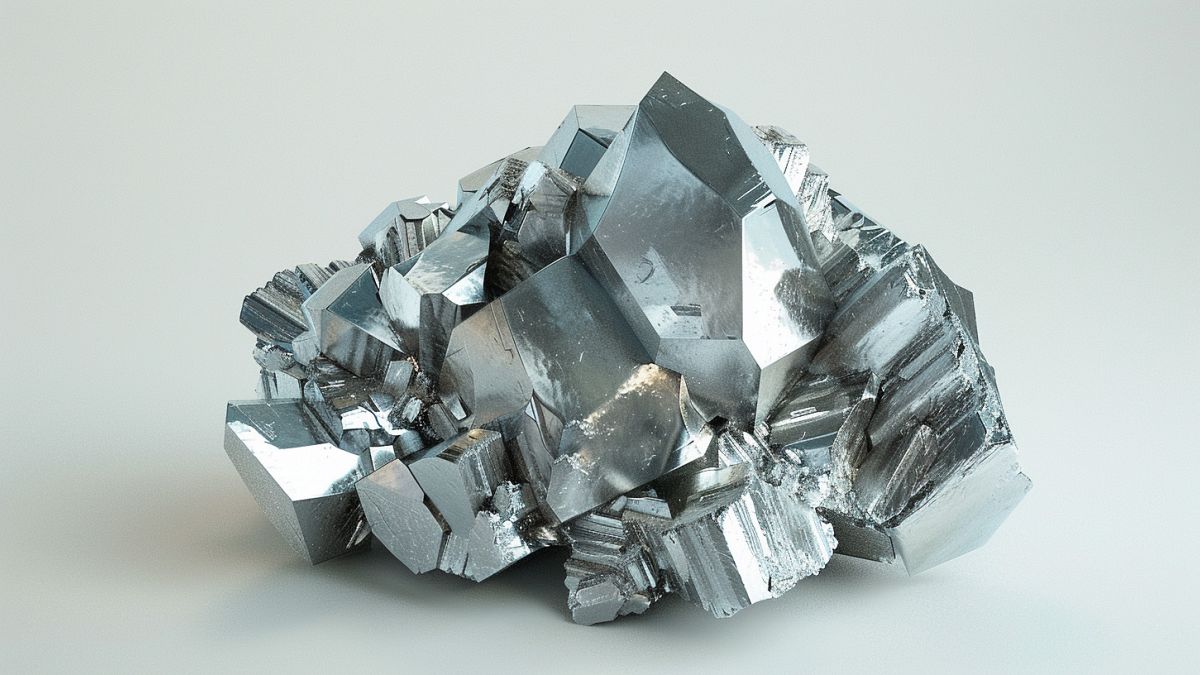

Now dubbed "New Kazakhstan," the deposit is said to have almost 1 million tonnes of cerium, lanthanum, neodymium and yttrium, elements used as components in devices such as smartphones, digital cameras and computer hard disks.

The "music" of starquakes - enormous vibrations caused by bursting bubbles of gas that ripple throughout the bodies of many stars - can reveal far more information about the stars.
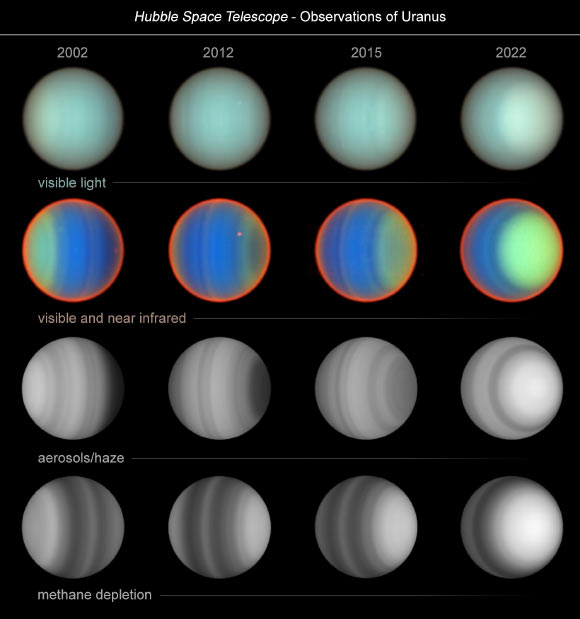
A 20-year Hubble study of Uranus provide valuable data for understanding the atmospheric dynamics of this distant ice giant, which can serve as a proxy for studying exoplanets of similar size and composition.

Scientists in Japan have developed a new type of plastic that's just as stable in everyday use but dissolves quickly in saltwater, leaving behind safe compounds.

Scientists have uncovered a surprising role for calcium in shaping the building blocks of life.

For a long time, scientists thought that only actively star-forming galaxies should be observed in the very early Universe. The James Webb space telescope now reveals that galaxies stopped forming stars earlier than expected.
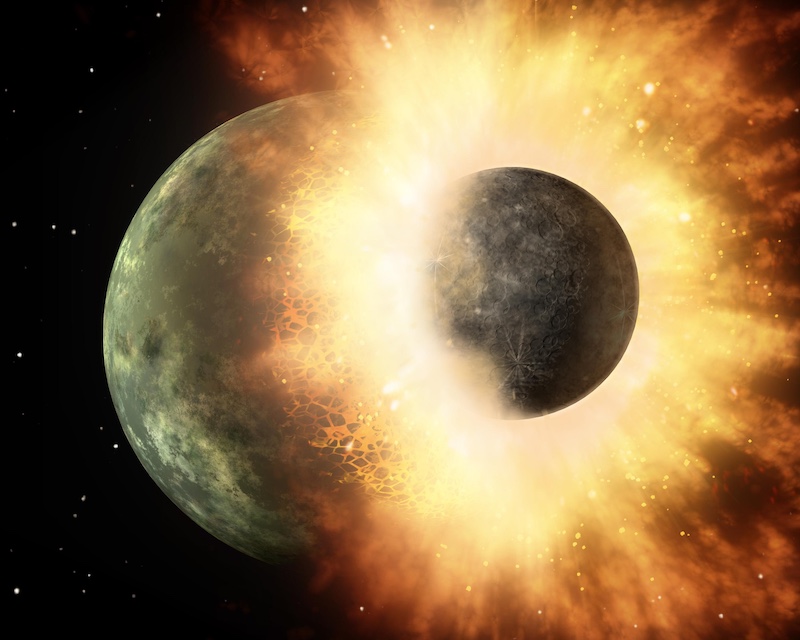

A grazing giant collision between two similar-sized rocky bodies likely created Mercury a few billion years ago.
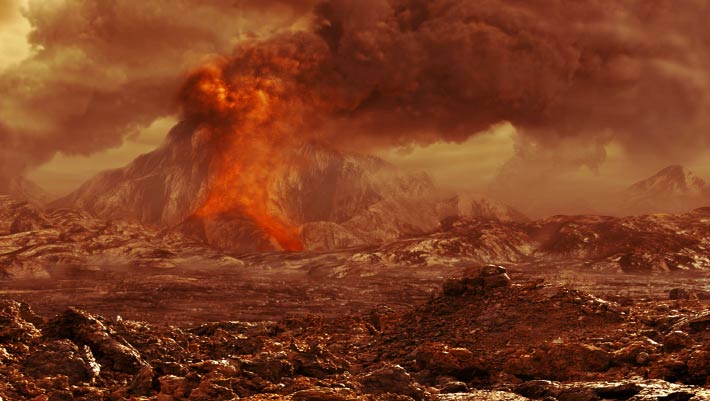

An unexpected phenomenon called convection could help explain many of the volcanoes and other features of the Venusian landscape.

Researchers have discovered that the underside of the North American continent is dripping away in blobs of rock—and that the remnants of a tectonic plate sinking in Earth's mantle may be the reason why.

The damage climate change will inflict on the world’s economy is likely to have been massively underestimated.

"Half ice, half fire" is notable not only because it has never been observed before, but also because it is able to drive extremely sharp switching between phases in the material at a reasonable, finite temperature.