
Climate scientists reveal that millions of today's young people will live through unprecedented lifetime exposure to heatwaves, crop failures, river floods, droughts, wildfires and tropical storms under current climate policies.

A new study from eight countries shows that premature deaths attributable to consumption of ultraprocessed foods (UPFs) increase significantly according to their share in individuals' total energy intake.

Astronomers using the James Webb Space Telescope have directly detected the faint glow of a planet that’s colder than any world whose light has been directly observed.

In a world first, Japanese researchers flew a lightning-proof drone in a thunderstorm, using it to induce and direct natural lightning strikes. The team is now working on how this flying lightning rod might capture lightning energy.

Most of the lights in the new JWST-Hubble composite image are not bright stars, but galaxies, stretching back almost as far across space-time as the beginning of the Universe.

Earth-like exoplanets might be more common throughout the Milky Way than previously believed, astronomers report in a new study.

Sophie Cohen-Bodénès and Peter Neri, neuroscientists at École Normale Supérieure, in France, report possible evidence of cuttlefish communicating by waving their 'arms' at one another.

A celestial shadow known as the Circinus West molecular cloud creeps across this image captured with fabricated Dark Energy Camera - one of the most powerful digital cameras in the world.

Spruce trees anticipated a solar eclipse by syncing their signals. Older trees responded first. Forests may behave as one living system.

Whatever caused the blackout in Spain and Portugal, it highlights the vulnerabilities in some electricity grids.
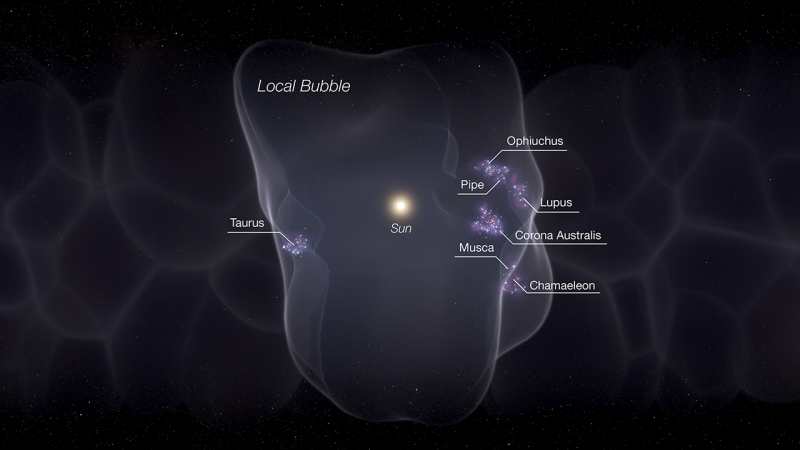
Eos is a crescent-shaped molecular cloud about 300 light-years from our solar system. It resides on the edge of the Local Bubble, a huge “cavity” in space filled with gas, which is about 1,000 light-years across.

Planetary scientists research the complex asteroid Vesta which may possess the same fundamental architecture as Earth such as the crust.
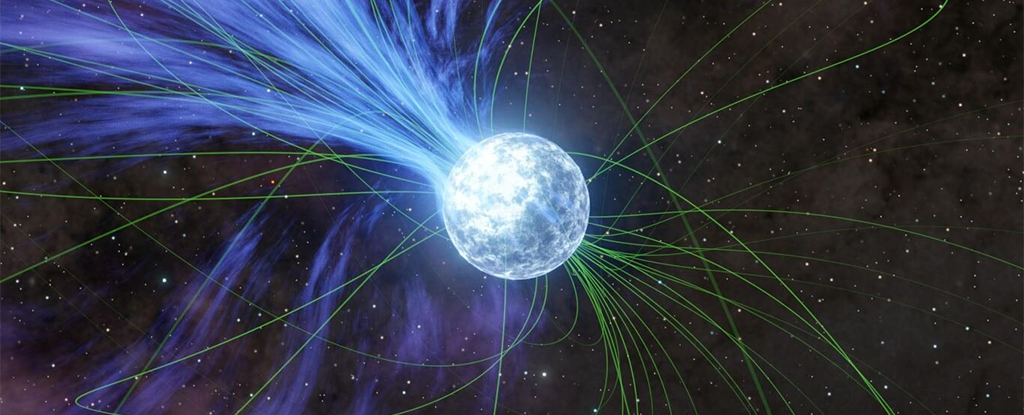
Scientists have long been trying to determine how elements heavier than iron, including gold and platinum, were first created and scattered through the Universe, and new research may give us another part of the answer: magnetars.
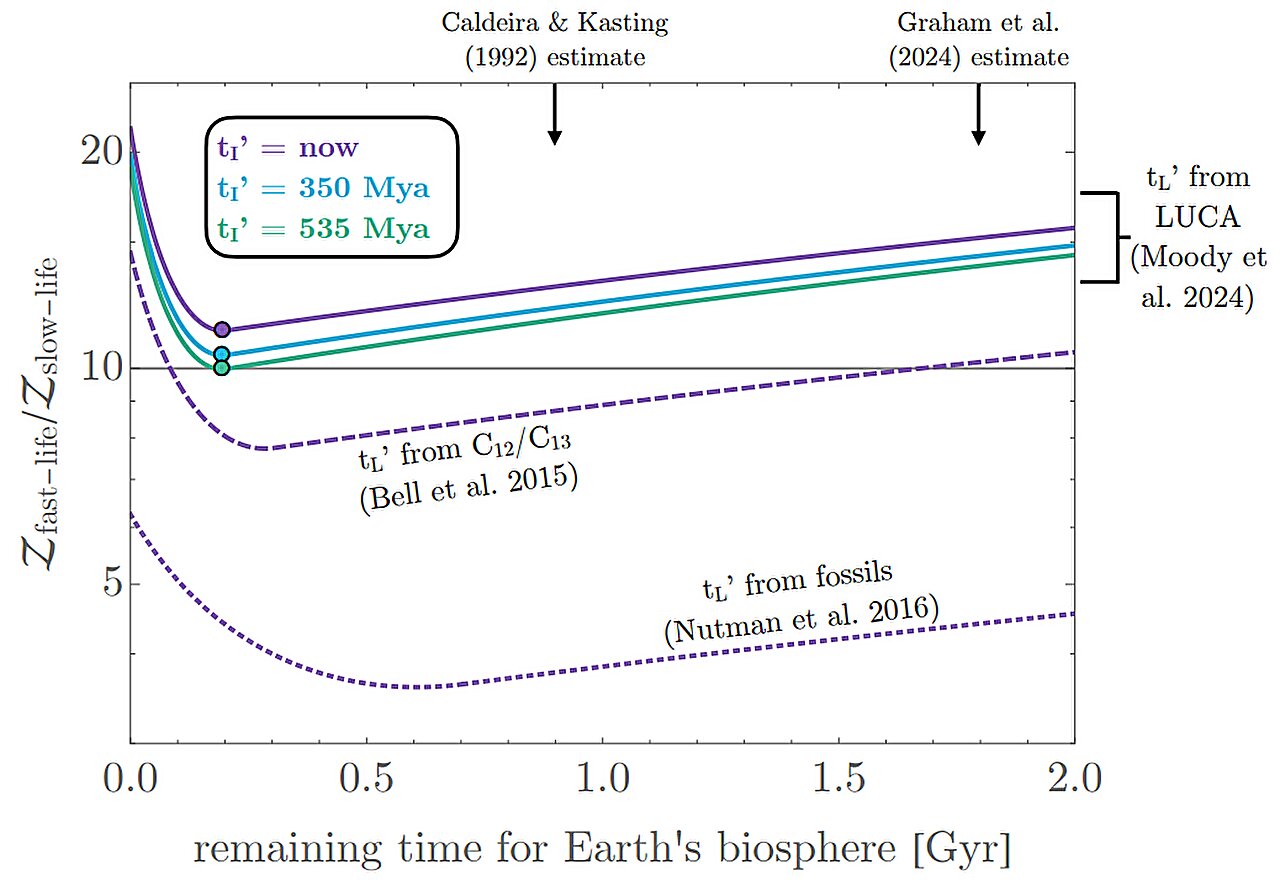
An astronomer at Columbia University is suggesting that because life emerged so soon on Earth after its formation, it may emerge rapidly on Earth-like planets after the right conditions arise in general.

Lengthening days are linked to the oxygenation of Earth's atmosphere, according to a study from 2021.