
The world's first commercial hybrid of silicon circuitry and human brain cells will soon be available for rent.
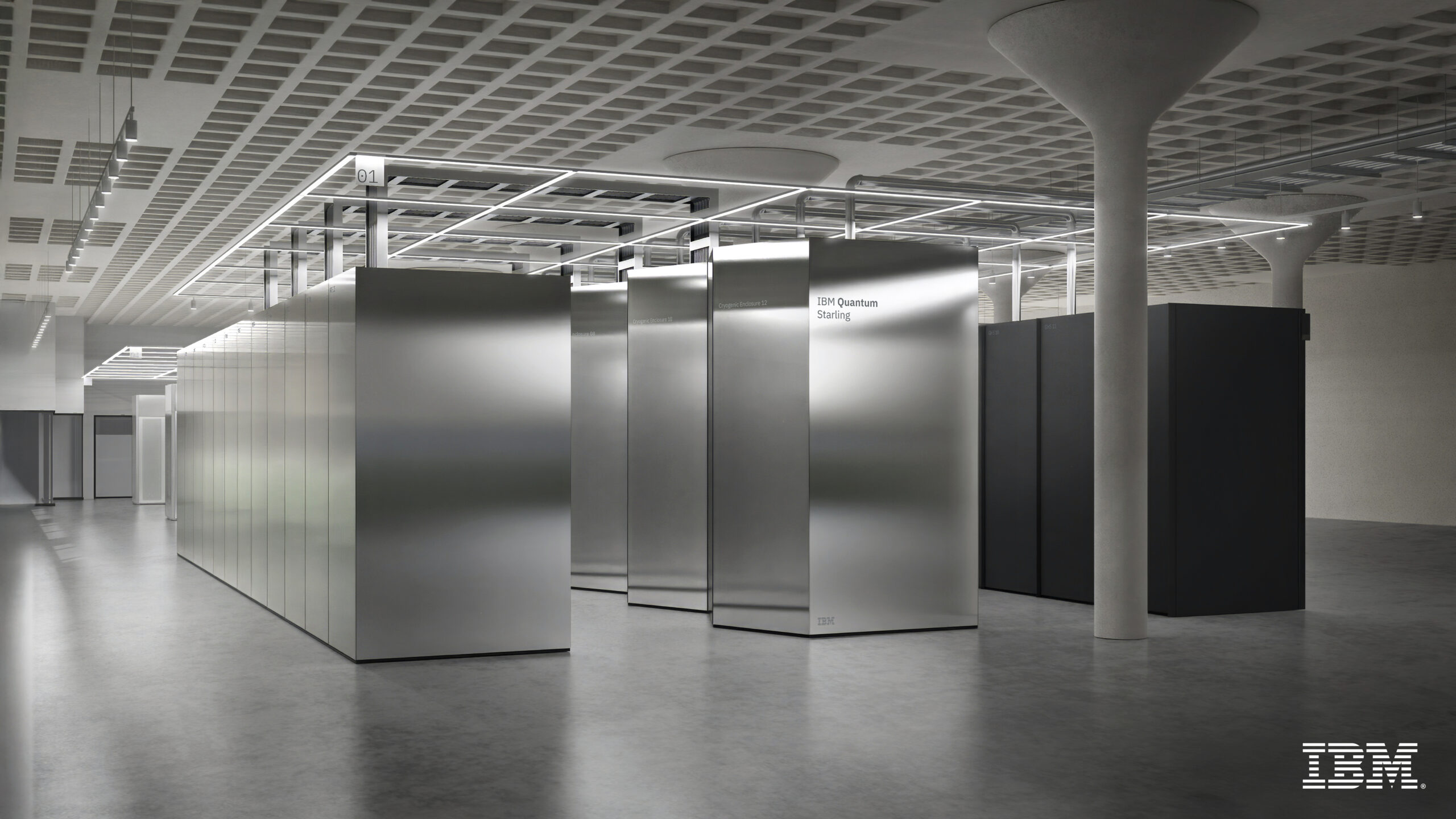

IBM released its plans for building a system that should push quantum computing into entirely new territory: a system that can both perform useful calculations while catching and fixing errors.

Brain-inspired computers could boost AI efficiency—a tantalizing prospect as the industry's energy bills mount.

A team of international researchers has used the unpredictable nature of quantum mechanics to create a device capable of generating truly random numbers.
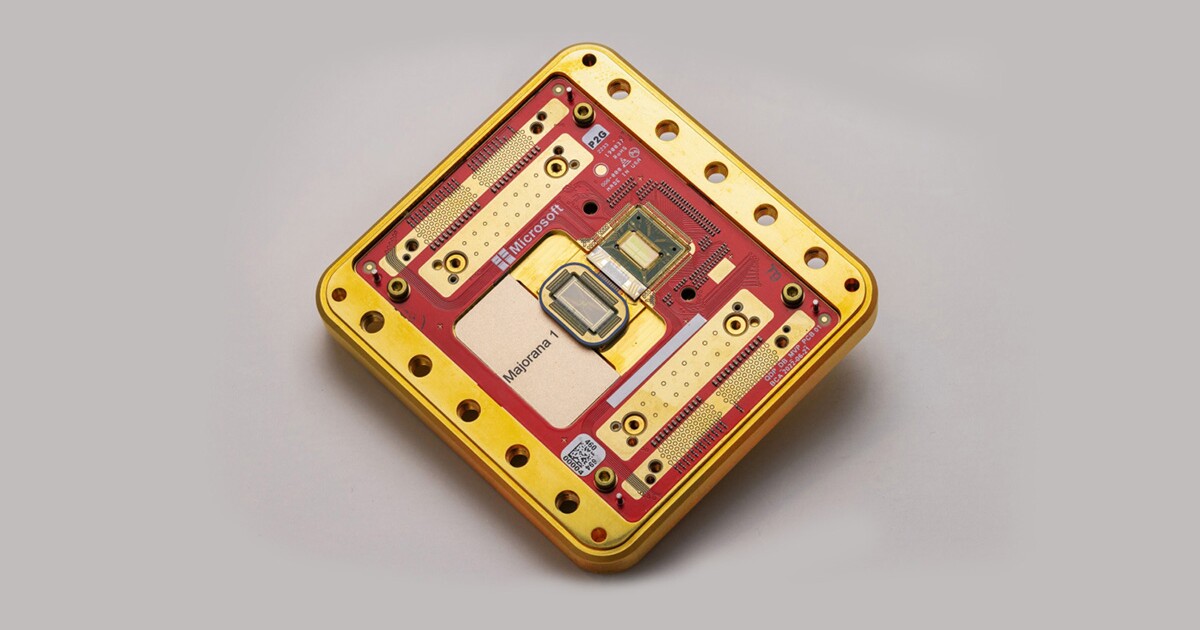
Microsoft says it's made a major breakthrough in quantum computing capabilities with the Majorana 1, its first quantum chip.

In a groundbreaking use of teleportation, critical units of a quantum processor have been successfully spread across multiple computers.
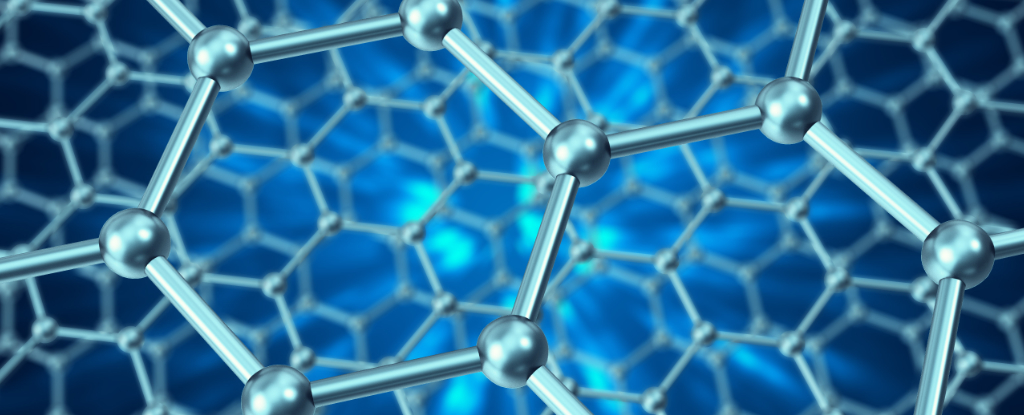
Team of international researchers have recently discovered a strange new state of matter in the dynamics of currents flowing through layers of graphene.

Google’s latest quantum computer chip, which the team dubbed Willow, has ignited a heated debate in the scientific community over the existence of parallel universes.
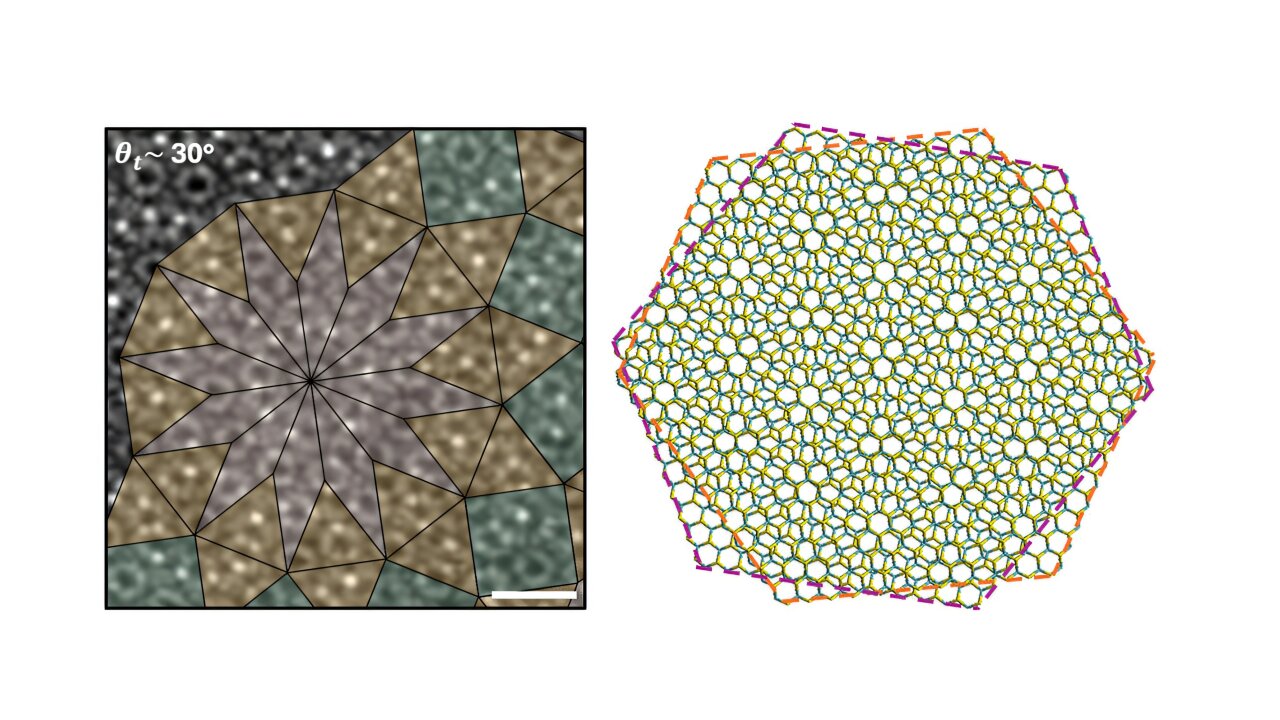
A new vortex electric field with the potential to enhance future electronic, magnetic and optical devices has been observed by researchers from City University of Hong Kong and local partners.
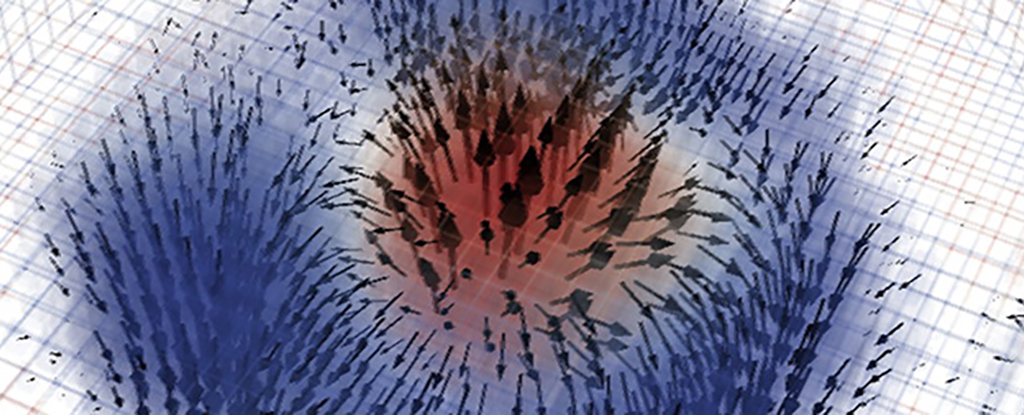

For the first time, we've got a three-dimensional picture of a magnetic skyrmion. This tiny, spiraling flaw in the magnetic properties of some materials could find uses in next-gen electronics storage devices and quantum computers.

A full DNA computer is a step closer, thanks to a new technology that could store petabytes of data in DNA for thousands or even millions of years. The system can also process data, as demonstrated by solving sudoku puzzles.

Researchers say that time crystals could one day become a core component in the construction of quantum computers.
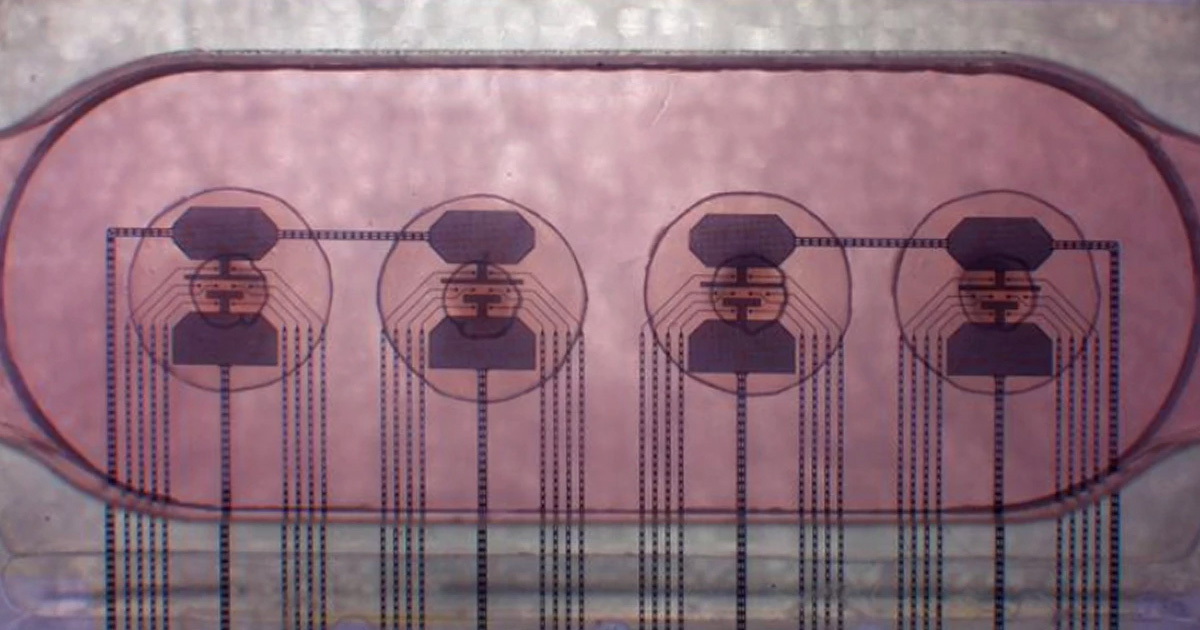
A startup in Switzerland has built a unique computer processor made from 16 tiny brains made from human tissue, basically a living computer.

The potential of quantum computing is immense, but the distances over which entangled particles can reliably carry information remains a massive hurdle.

For decades, the pursuit of quantum computing has struggled with the need for extremely low temperatures, mere fractions of a degree above absolute zero.