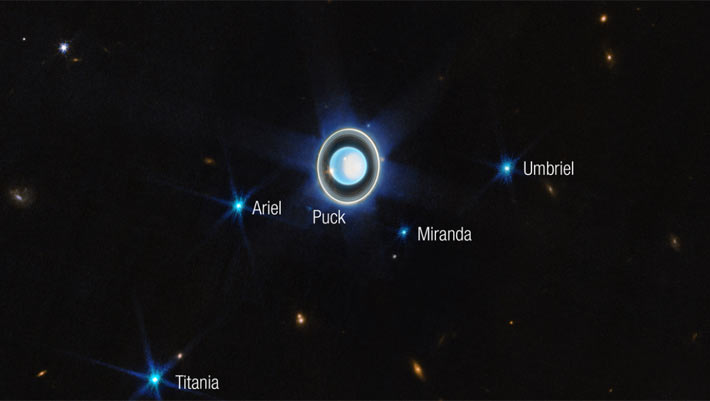
In new research, astronomers using the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope searched for signs of interactions between the magnetic environment and the surfaces of Uranus and its four largest moons: Ariel, Umbriel, Titania, and Oberon.
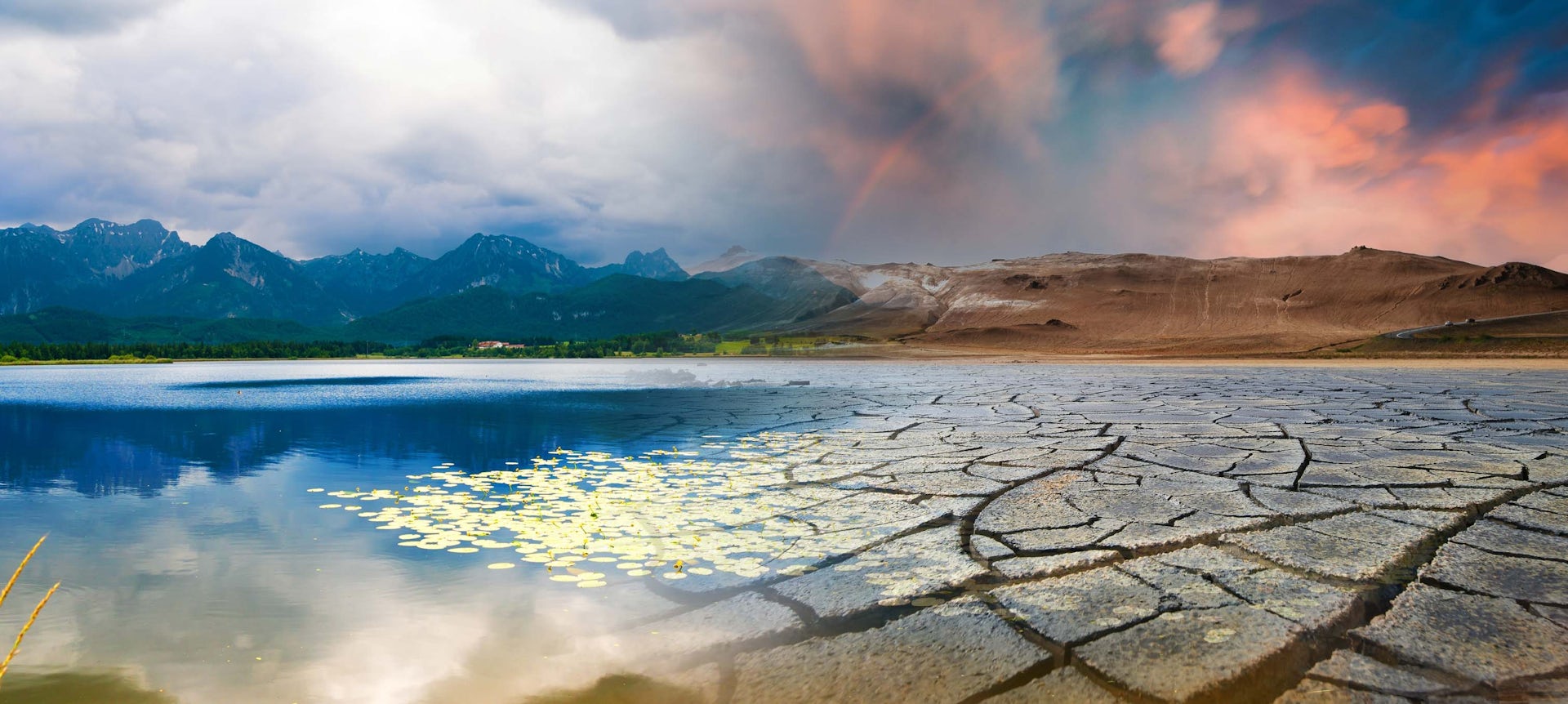

Rising “atmospheric thirst” – also known as atmospheric evaporative demand (AED) – is responsible for about 40% of the increase in drought severity over the last four decades (1981-2022).
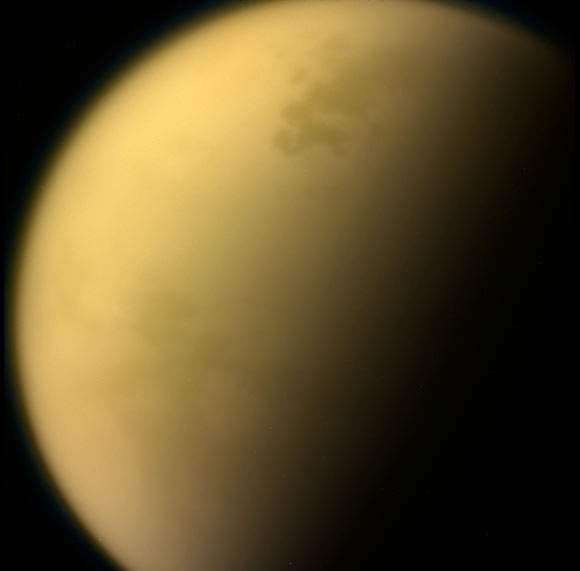

Titan is the only moon in the Solar System with a significant atmosphere, and one that has long captivated planetary scientists.
Astronomers in Hawaii detected three different stars being devoured by supermassive black holes that released more energy than 100 supernovas. These are the largest explosions since the Big Bang.
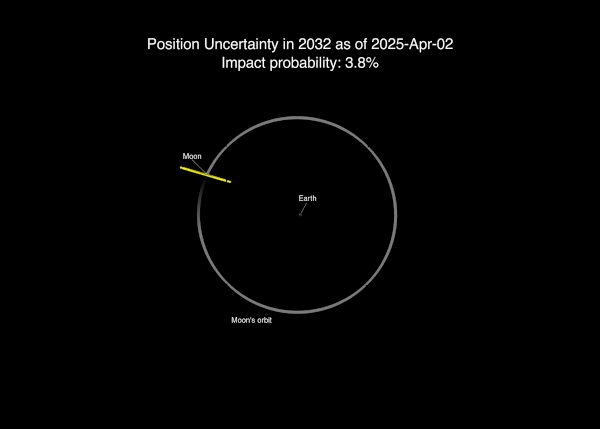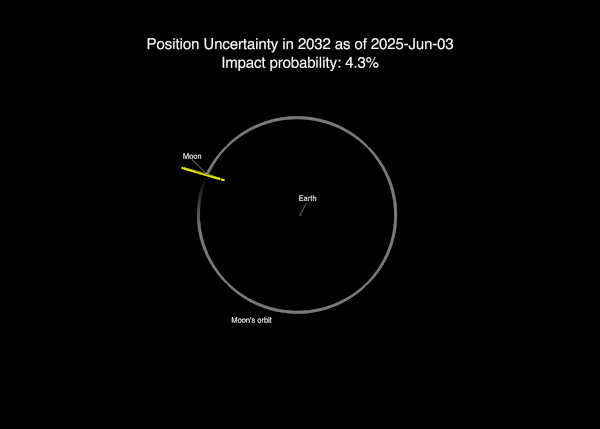
On April 2, 2025, NASA said that new data from the Webb space telescope and ground-based telescopes suggested a 3.8% chance of a moon strike.

An international team of astronomers discovered a giant planet orbiting the smallest known star to host such a companion. It’s a finding that defies current theories of planet formation.
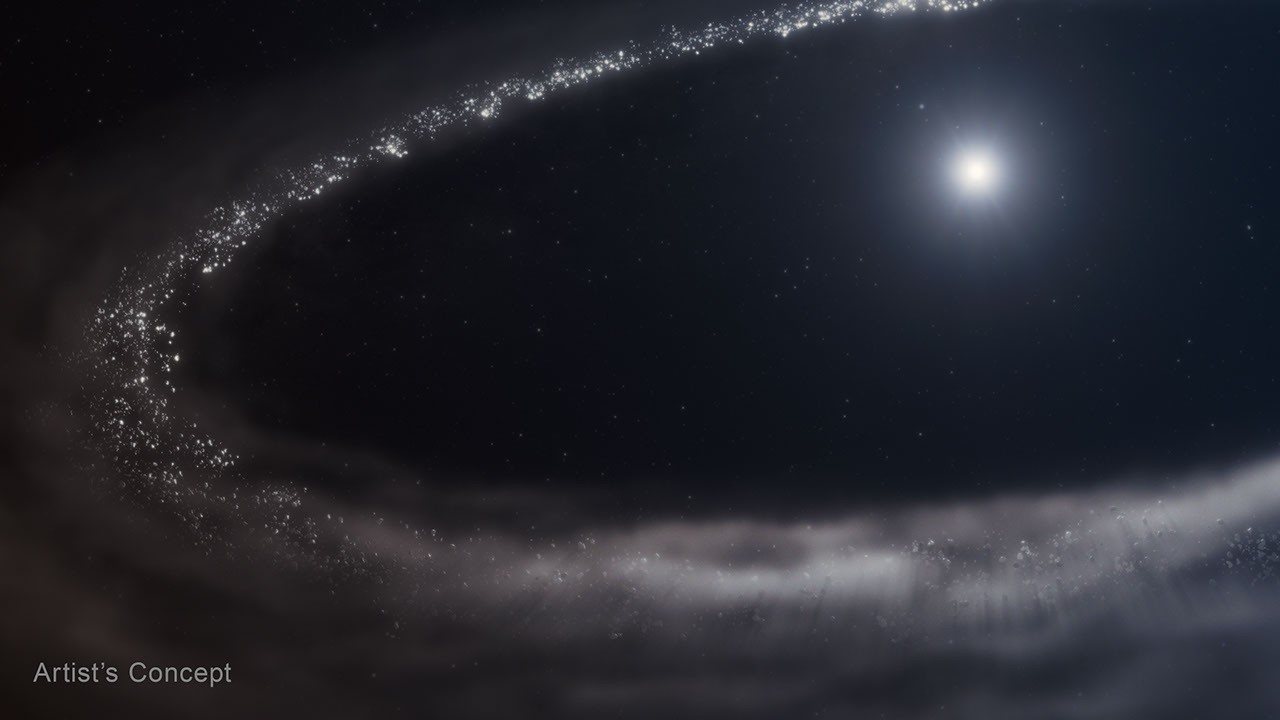

Researchers confirmed the presence of crystalline water ice in a dusty debris disk that orbits a Sun-like star 155 light-years away using detailed data known as spectra from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope.
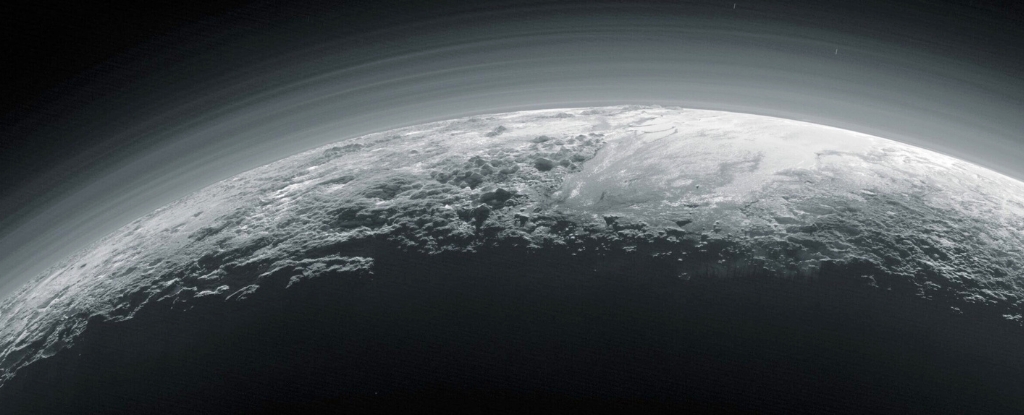

When the New Horizons spacecraft swept past Pluto and Charon in 2015, it revealed two amazingly complex worlds and an active atmosphere on Pluto.

In this blog, Professor Enrique Gaztanaga from the Institute of Cosmology and Gravitation at the University of Portsmouth, puts forward a new theory about how the Universe was created.
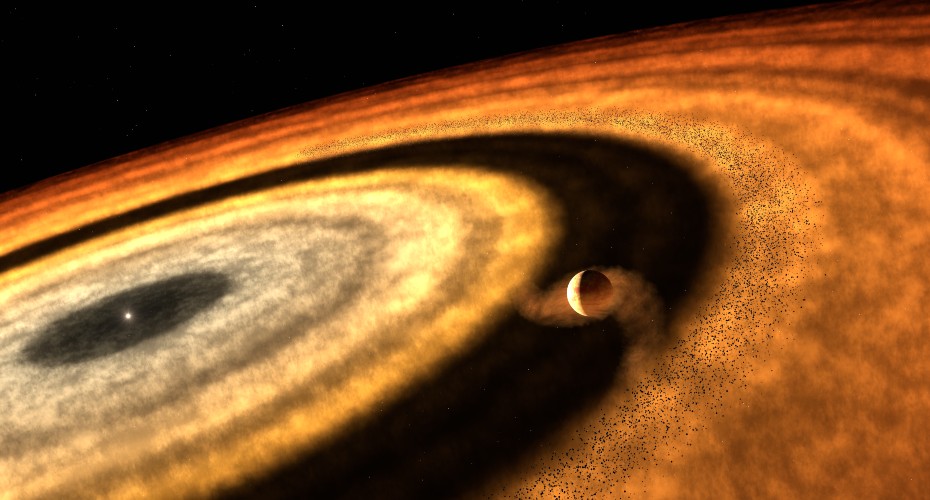
Researchers have used new clues from the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) to provide a fascinating insight into how the exoplanet WASP-121b formed.

20 years of observations have given us more knowledge about the icy giant.

The JWST shows that ice on Europa is developing at different rates in different places, such as Tara Regio, where crystalline ice (lighter colors) is found on the surface as well as below the surface.

A team at the National Solar Observatory is using AO to examine the Sun's corona in unprecedented detail.

In a new study we report the discovery of a new long-period transient – and, for the first time, one that also emits regular bursts of X-rays.

After a decade of searching, NASA's MAVEN (Mars Atmosphere Volatile Evolution) mission has, for the first time, reported a direct observation of an elusive atmospheric escape process called sputtering.