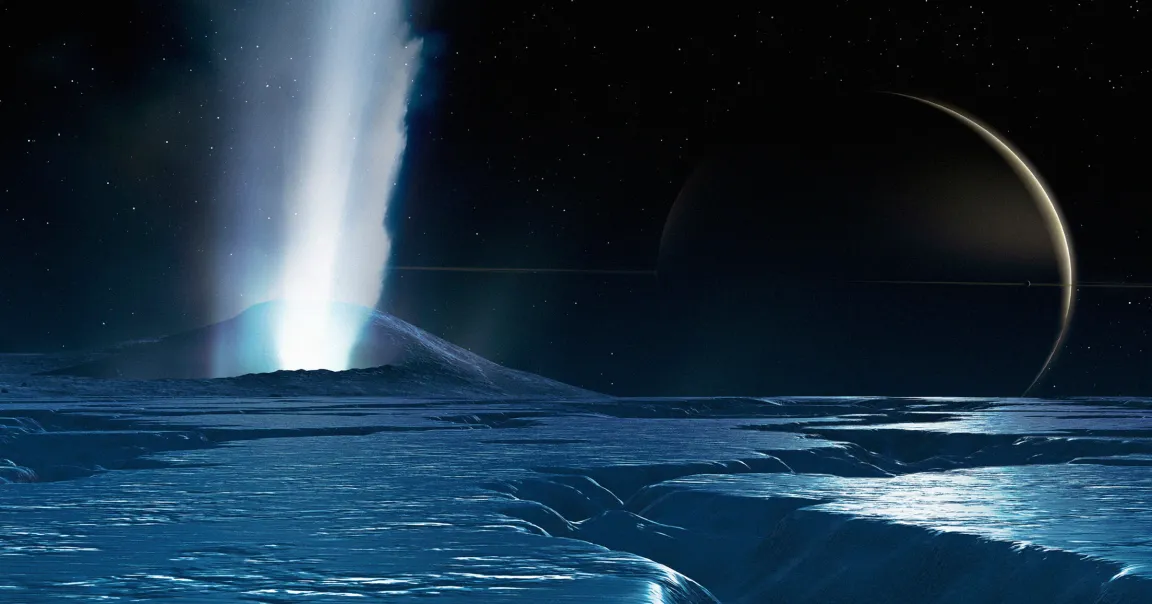

Astronomers have found that Saturn’s moon, Enceladus, is spewing out copious amounts of complex organic molecules, suggesting it’s an even more promising place to look for extraterrestrial life than previously thought.
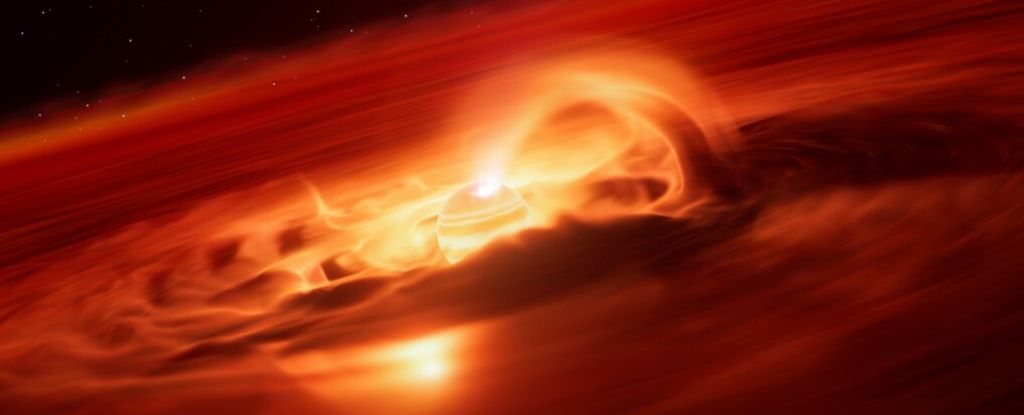

A young rogue planet about 620 light-years away from Earth has experienced a record-breaking "growth spurt," hoovering up some six billion tons of gas and dust each second over a couple of months.
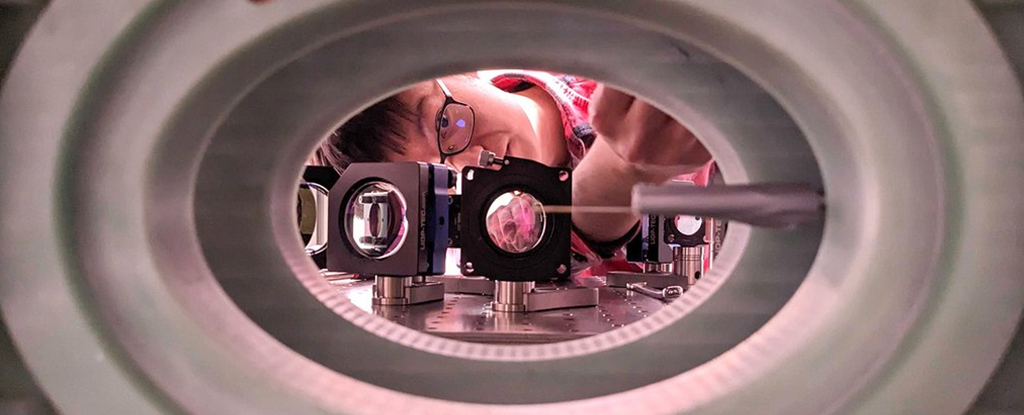

Another major quantum computing record has been broken: physicists have now built an array containing 6,100 qubits, the largest of its type and way above the thousand or so qubits previous systems contained.
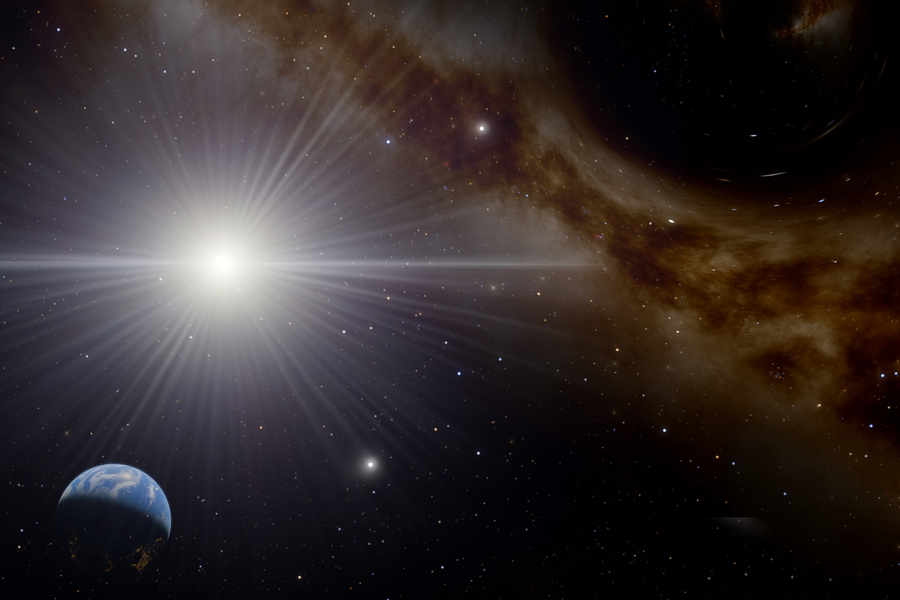

If a new proposal by MIT physicists bears out, the recent detection of a record-setting neutrino could be the first evidence of elusive Hawking radiation.

The researchers suggest that LIGO and Virgo picked up the signals of a black hole collision in a different universe than ours.
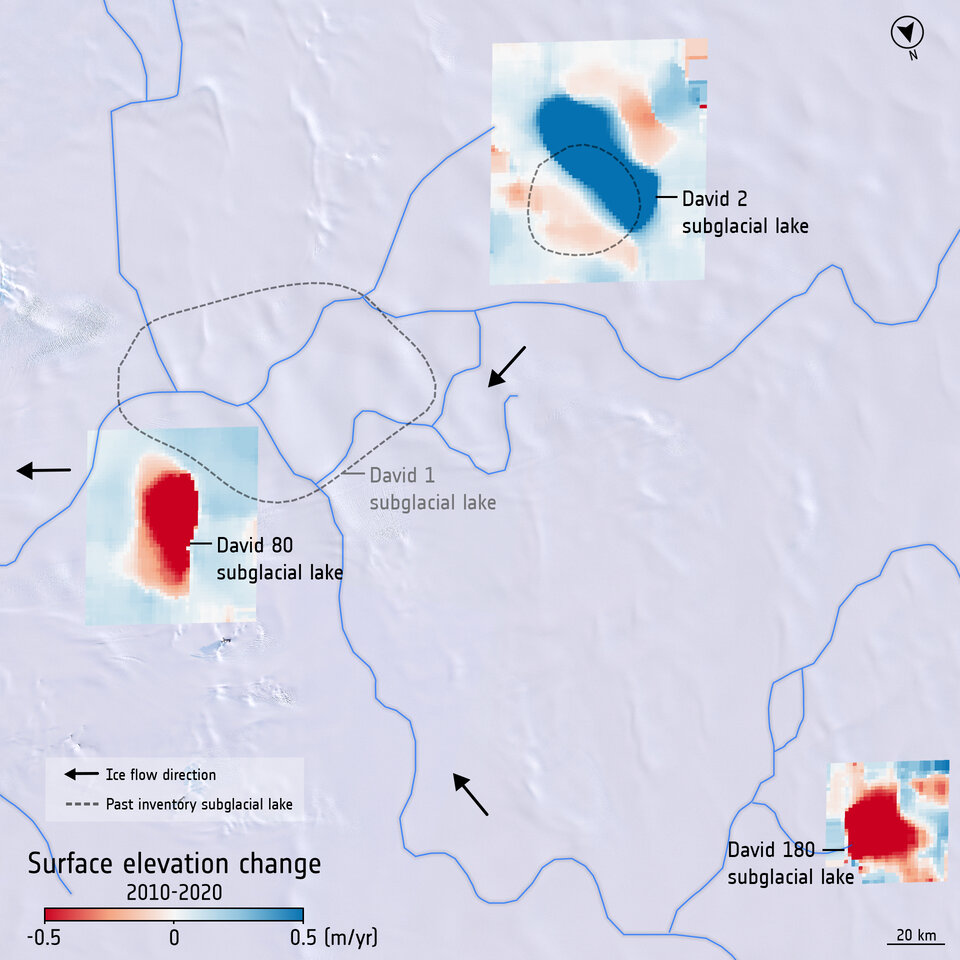
researchers have identified 85 previously unknown lakes several kilometres under the frozen surface surrounding the South Pole. This increases the number of known active subglacial lakes below Antarctica by more than half to 231.
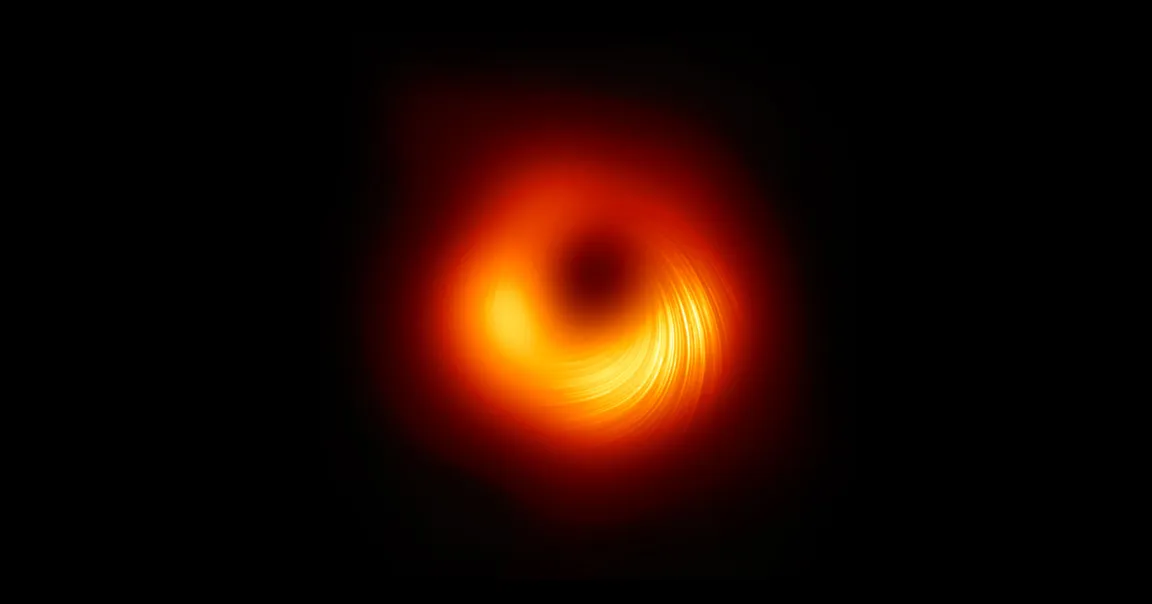

Now, by comparing observations from 2017, 2018, and 2021, scientists made a surprising discovery about how the magnetic fields near the black hole, dubbed M87*, change over time.
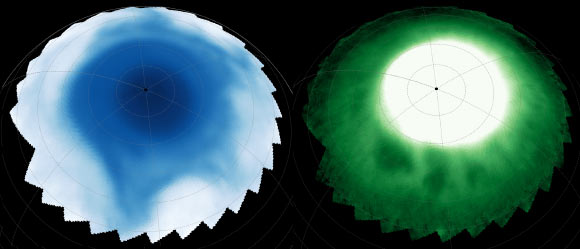
Astronomers using the NASA/ESA James Webb Space Telescope have detected a series of dark, bead-like and asymmetric star-shaped features in the ionosphere and stratosphere of Saturn.

A supermassive black hole in the center of the radio quasar RACS J032021.44-352104.1 (RACS J0320-35 for short) is growing at one of the fastest rates ever recorded.

Dark dwarfs are hypothetical dark matter-powered objects that formed from the cooling of brown dwarfs.
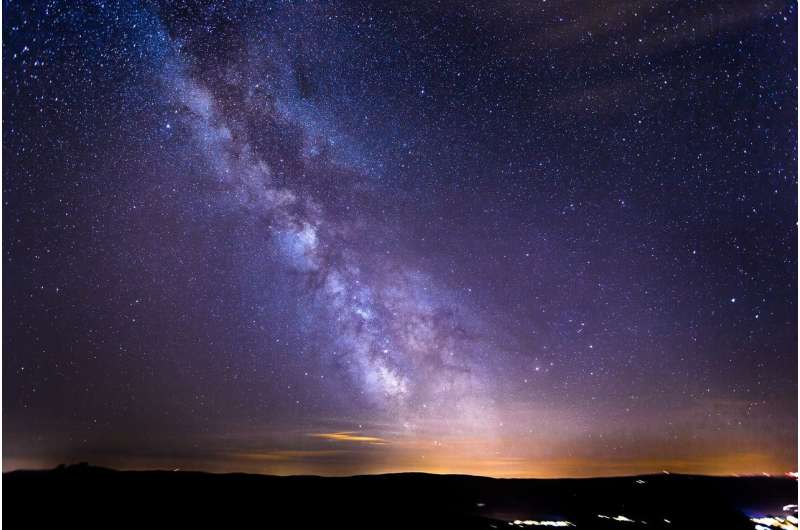

New research has uncovered a striking link between the structure of our galaxy and the evolution of Earth's crust, showing its development was shaped by the impact of meteorites during its journey through the Milky Way.
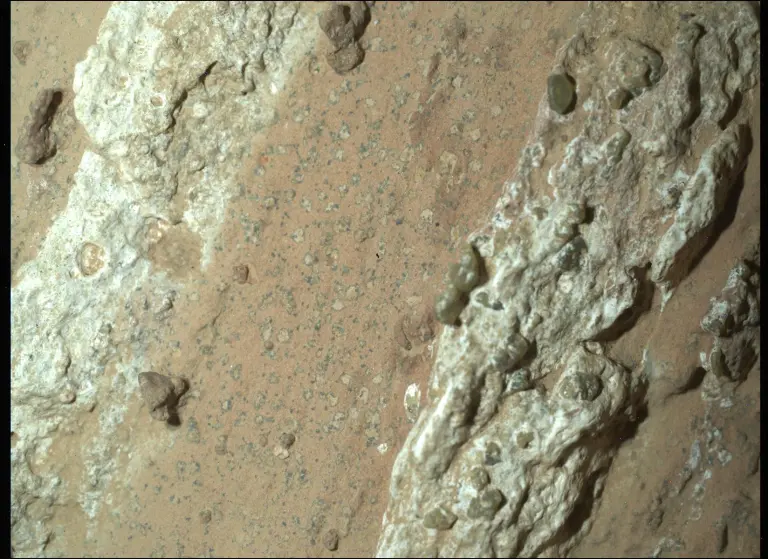

A sample collected by NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover from an ancient dry riverbed in Jezero Crater could preserve evidence of ancient microbial life.

78 million years ago, a 1.6 km asteroid slammed into what is now Finland, creating a crater 23 km (14 mi) wide and 750 m deep. The catastrophic impact created a fractured hydrothermal system in the shattered bedrock under the crater.

The gamma-ray burst (GRB) recorded on 2 July 2025 is the longest of its kind ever observed, lasting about a day. By comparison, GRBs normally last on the scale of milliseconds to minutes at most.
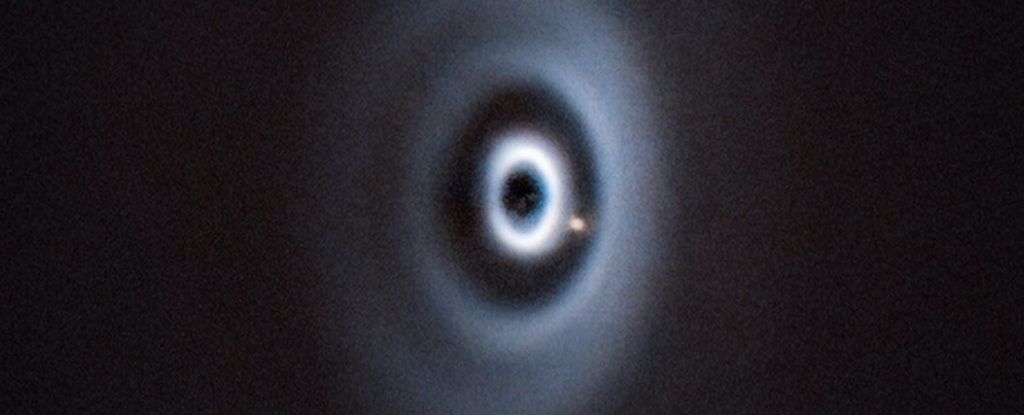
For the first time, astronomers have actually found a baby planet responsible for carving out gaps in the dusty disk surrounding a newborn star.