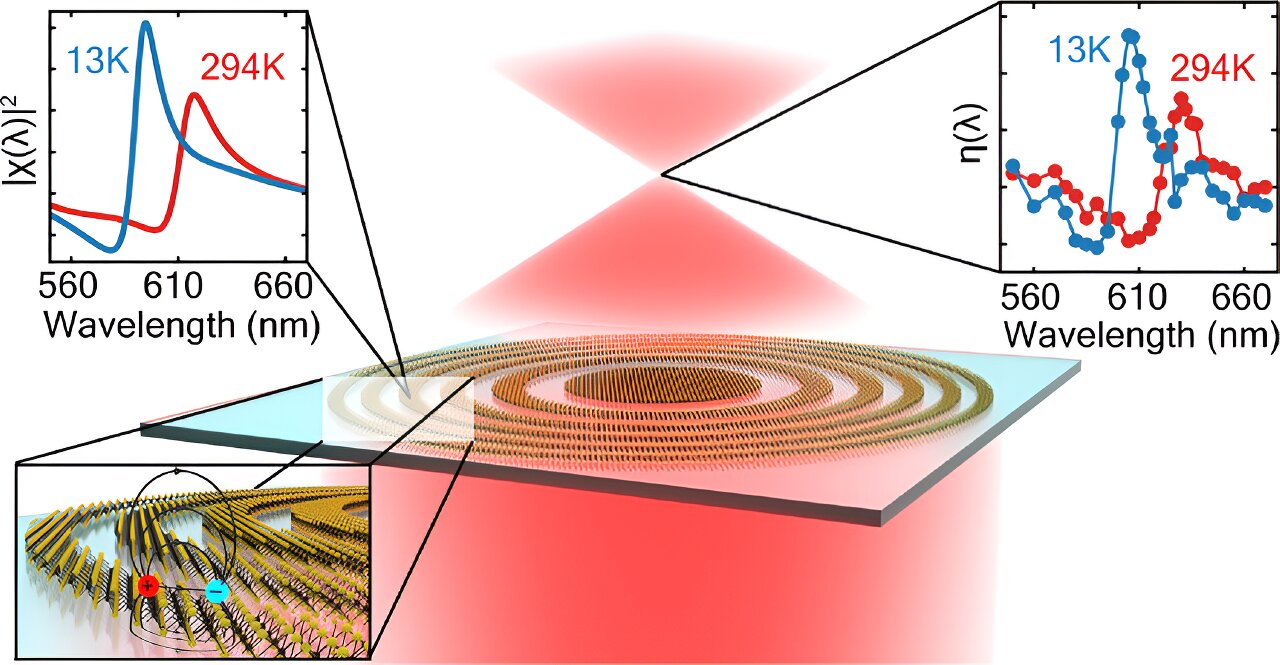
Lenses are used to bend and focus light. Normal lenses rely on their curved shape to achieve this effect, but physicists from the University of Amsterdam and Stanford University have made a flat lens of only three atoms thick that relies on quantum effects.
The Homo sapiens genome today contains a little bit of Neanderthal DNA. These genetic traces come from almost every part of the Neanderthal genome – except the Y sex chromosome, which is responsible for making males.
The human brain is said to be the most complex object in the known Universe. Its 89 billion neurons each have around 7,000 connections on average, and the physical structure of all those entities may be balanced precariously on a knife's edge.

An international scientific team has redefined our understanding of archaea, a microbial ancestor to humans from two billion years ago, by showing how they use hydrogen gas.
Geoscientists show that rocks from the Isua Supracrustal Belt in West Greenland have experienced three thermal events throughout their geological history.
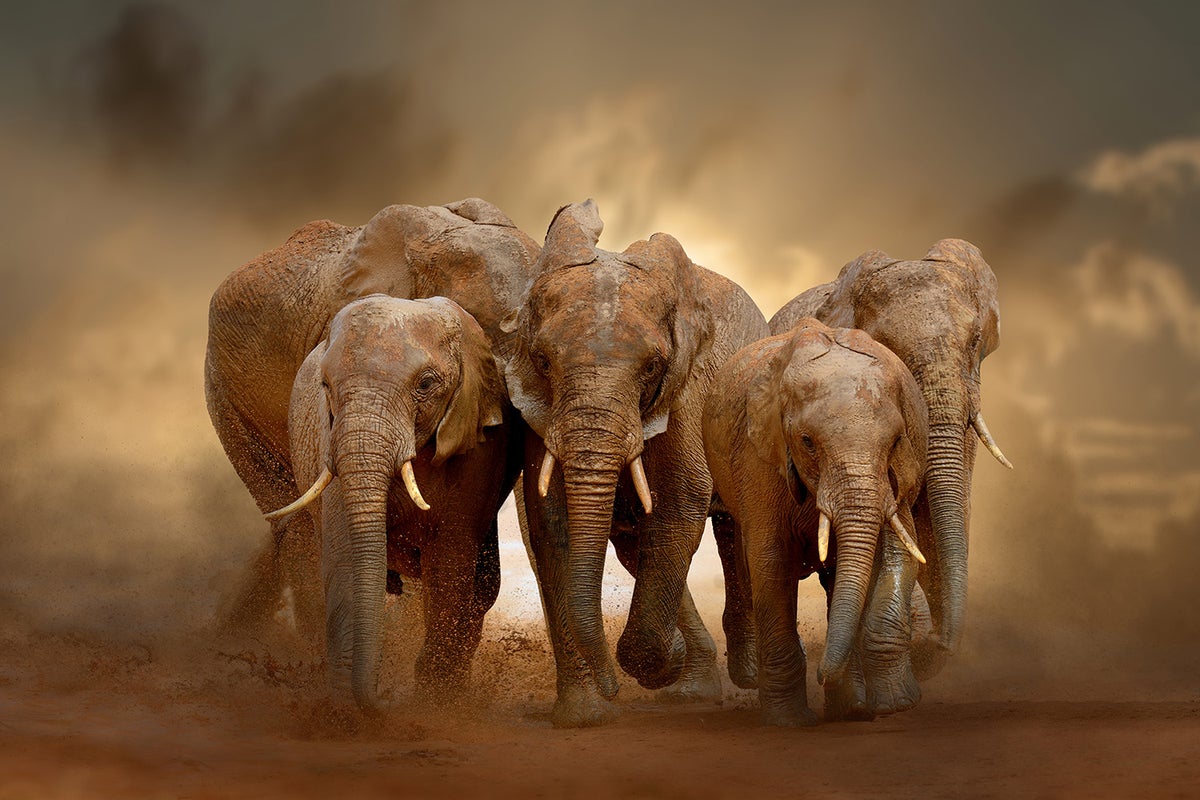

A new research suggests wild African elephants may pick their own names and use them to call and greet one another on the savanna.
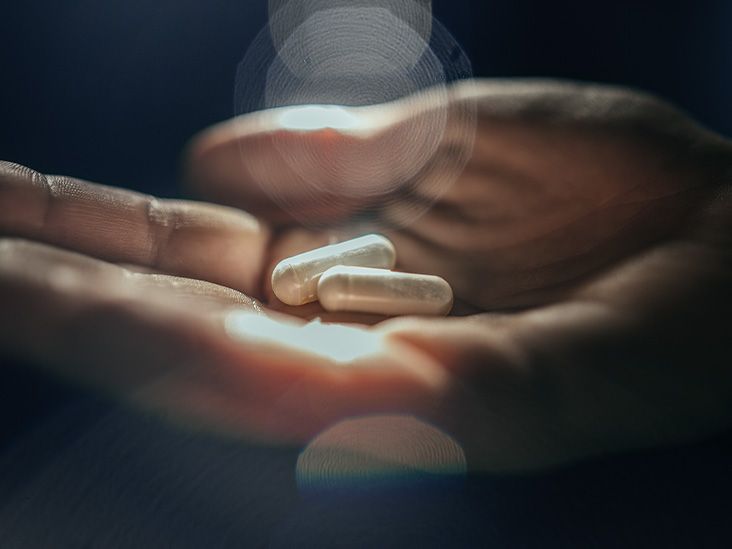

A recent study shows promise for a new antibiotic that effectively fights several bacteria while sparing the helpful bacteria that occur naturally in the gut.
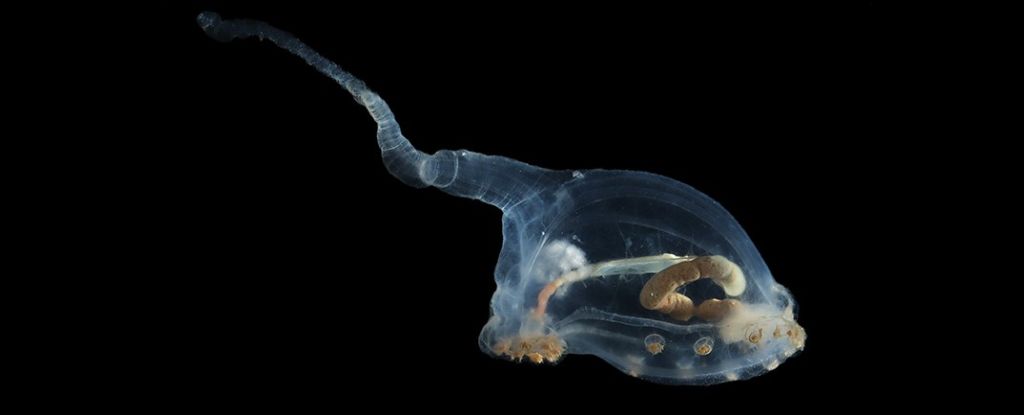

A collection of new species discovered lurking on the seafloor exemplifies exactly how alien this strange world is.
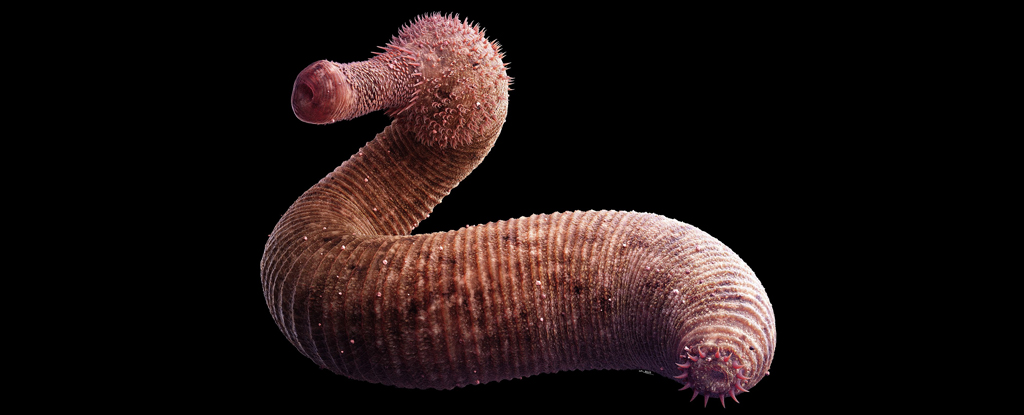
Prehistoric marine worms may have made an outsized contribution to the Great Ordovician Biodiversification Event.
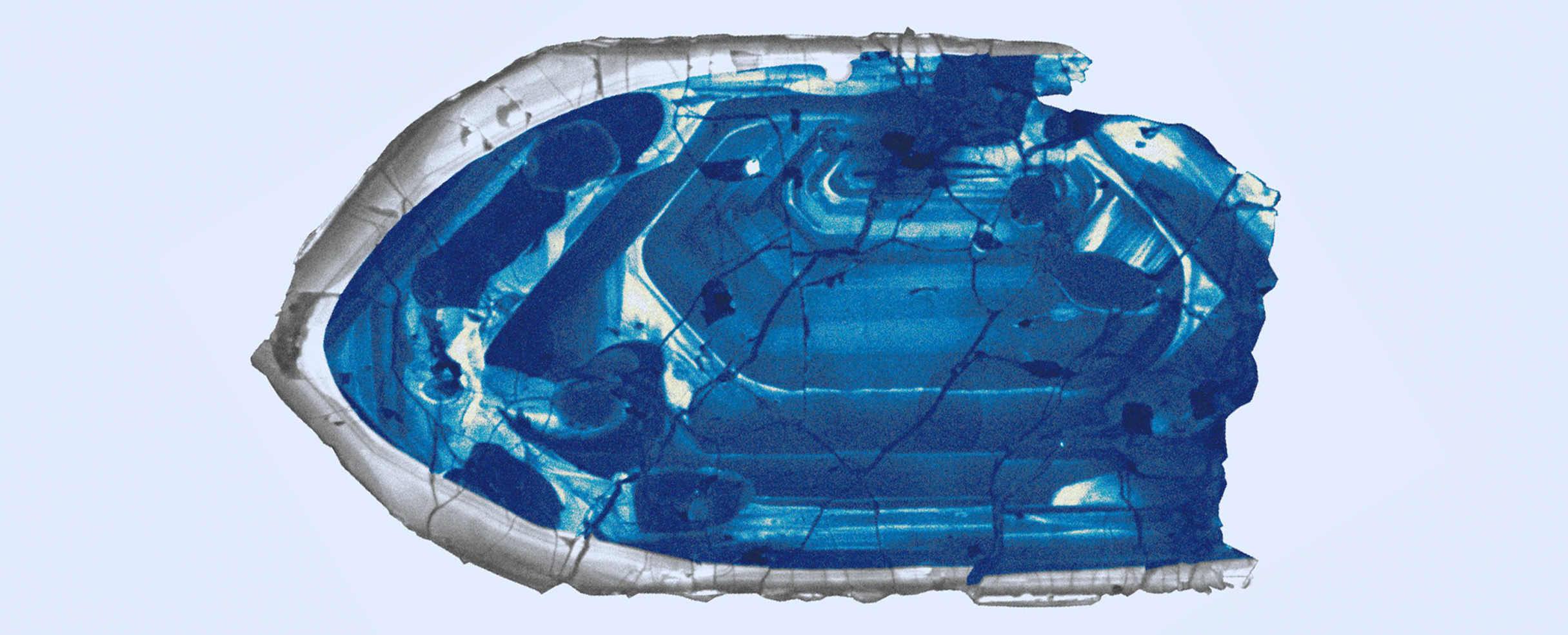
New research finds Earth's surface was first sprinkled with fresh water some 4 billion years ago, a whole 500 million years earlier than previously thought.
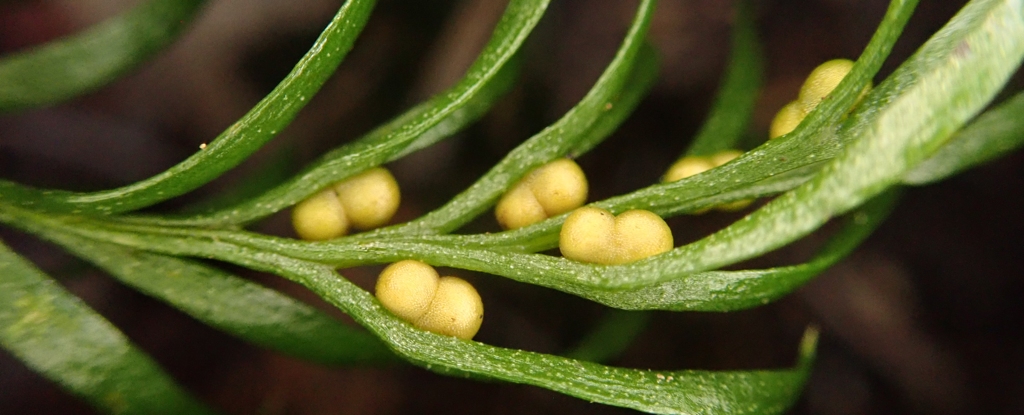

A small, seemingly unremarkable fern that only grows on a remote Pacific island was on Friday crowned the Guinness World Record holder for having the largest genome of any organism on Earth.
Batteries based on the wave-like nature of charged particles could revolutionize energy storage, potentially cramming in more power at a faster rate than conventional electrochemical cells could ever hope to manage.
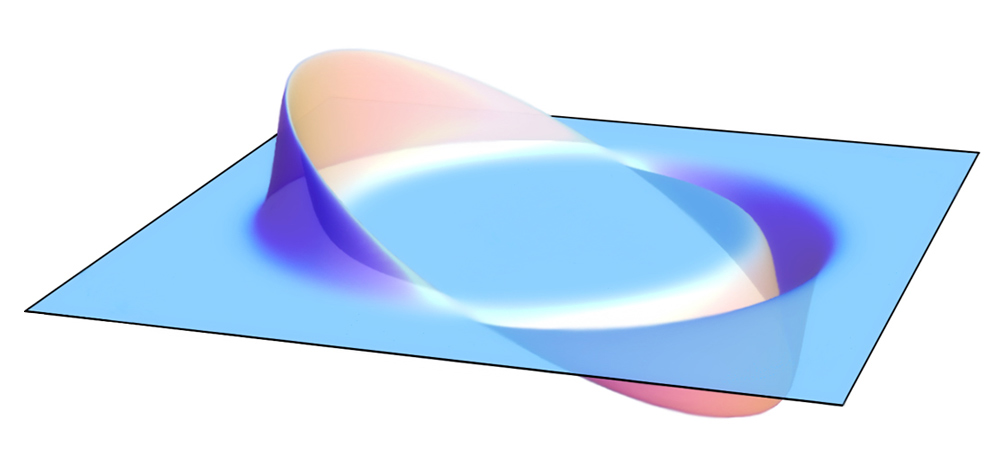
A new study suggests that a real-life warp drive might not be as far-fetched as we thought. The key, scientists say, is to look at the problem through the lens of Einstein’s theory of gravity: general relativity.
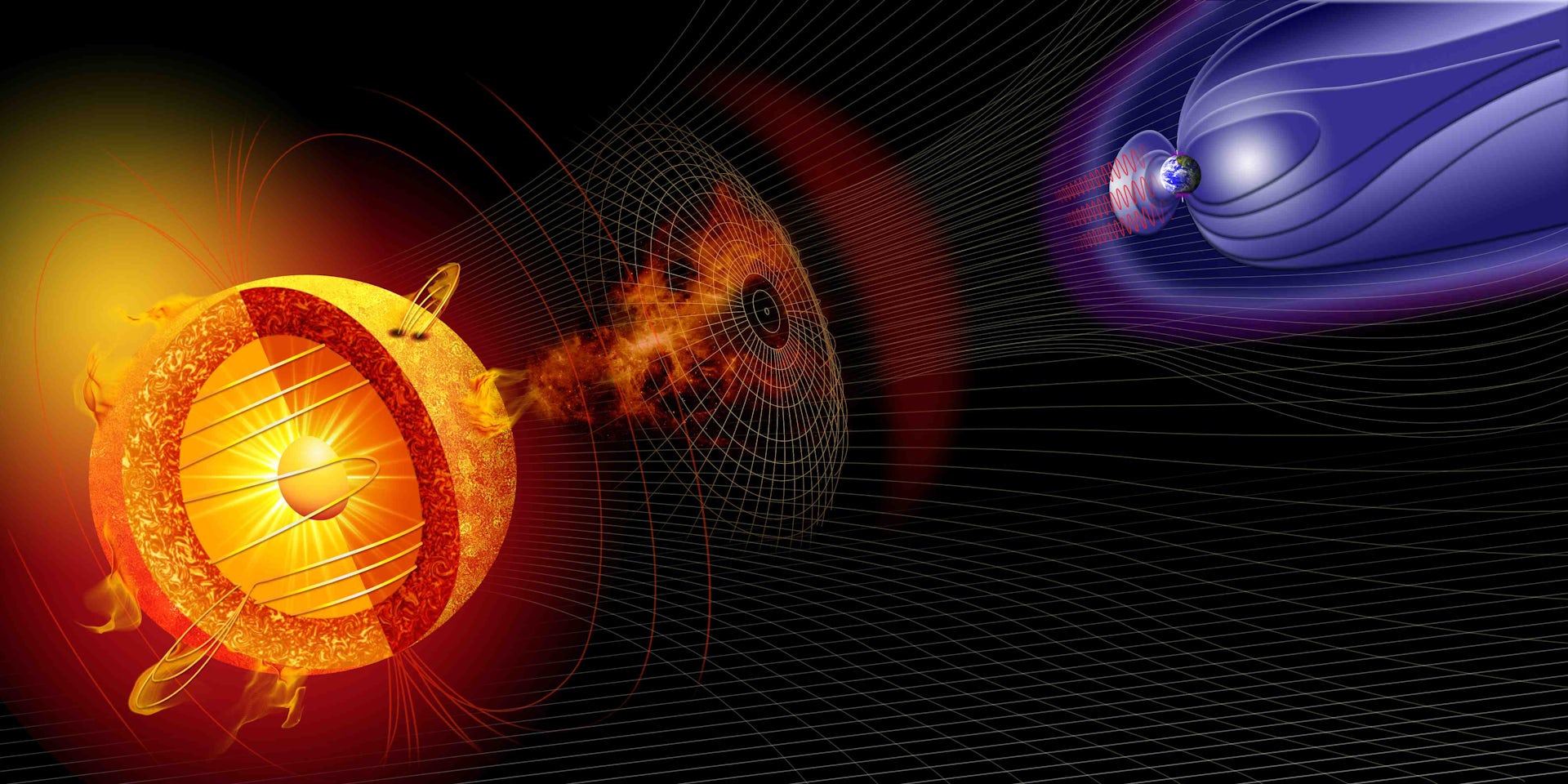
The same geomagnetic storms causing the auroras can cause havoc with our planet’s human-made infrastructure.
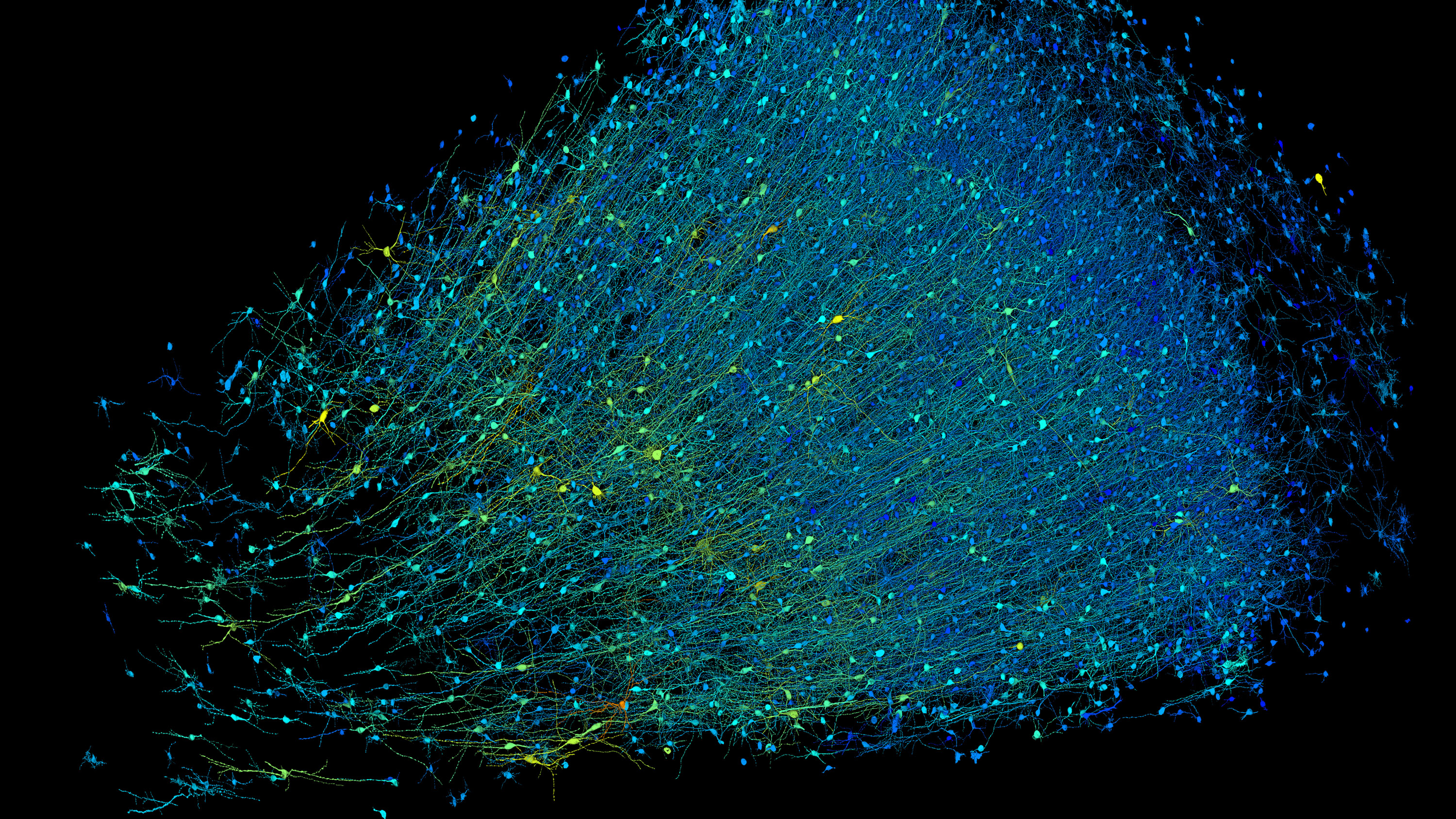
Although the map covers just a fraction of the organ—a whole brain is a million times larger—that piece contains roughly 57,000 cells, about 230 millimeters of blood vessels, and nearly 150 million synapses.