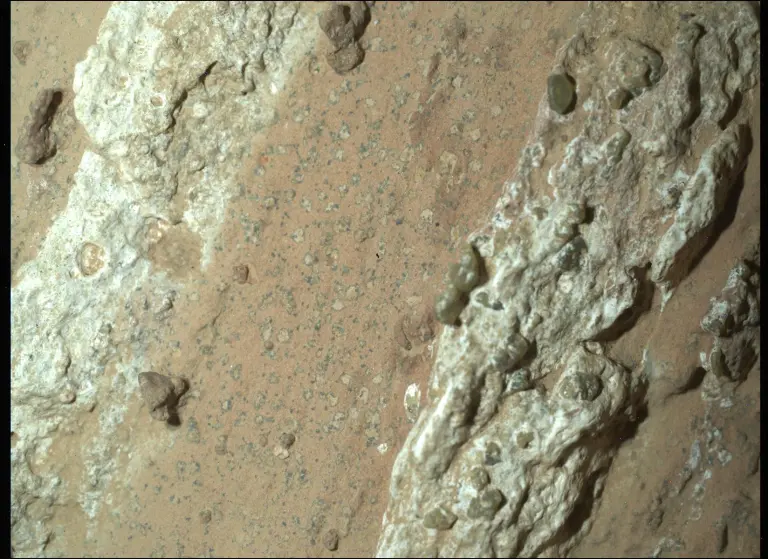

A sample collected by NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover from an ancient dry riverbed in Jezero Crater could preserve evidence of ancient microbial life.
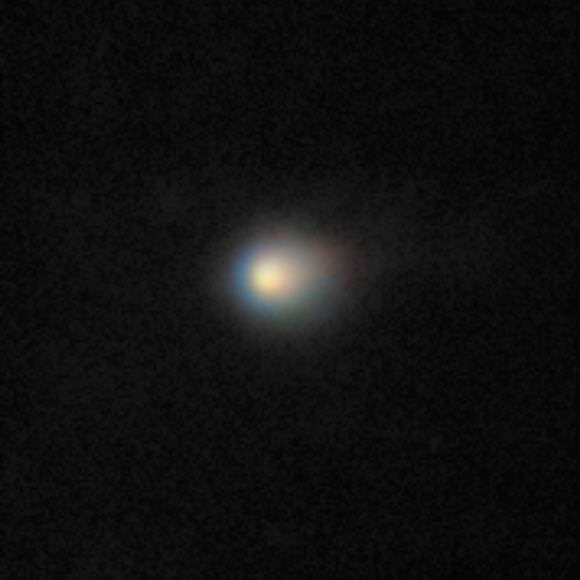

The comet is unique - not only was it made of carbon dioxide, but it had a carbon dioxide ice-to-water ice ratio that was literally out of this world, 8:1, which is among the highest ever recorded.
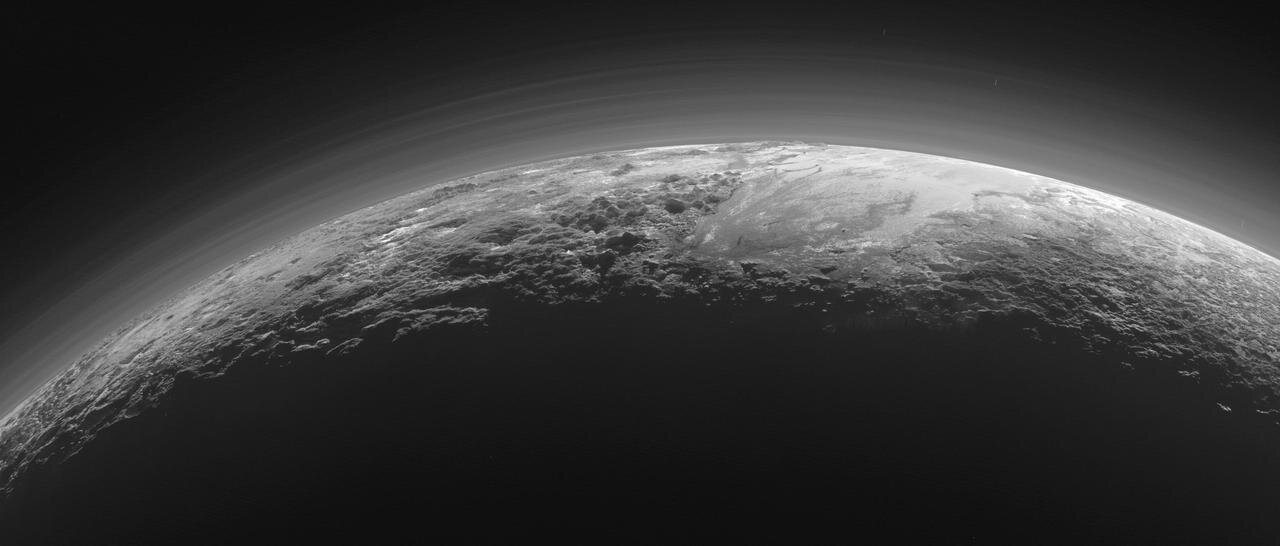

As NASA's New Horizons spacecraft traveled through the Kuiper Belt at a distance of more than 5.5 billion ml from Earth, an international team of astronomers conducted the first-ever successful demonstration of deep space stellar navigation.
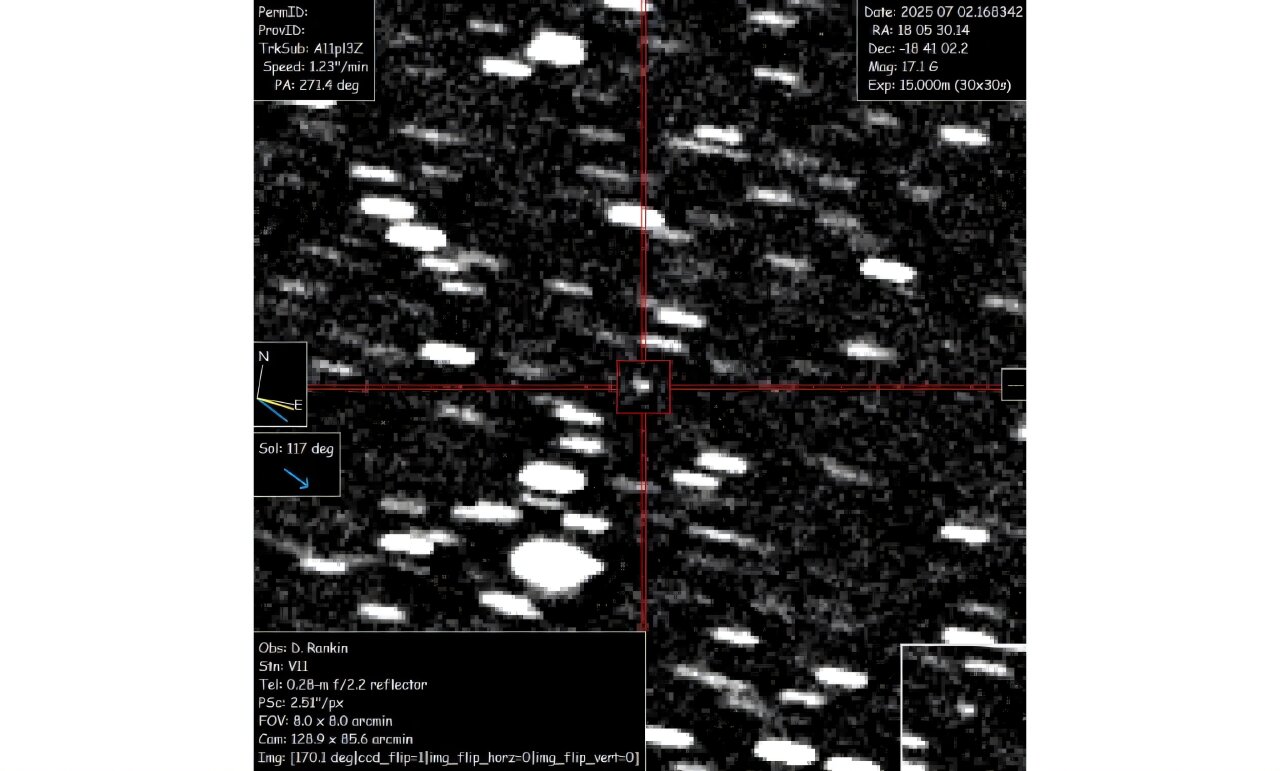
Astronomers on Wednesday confirmed the discovery of an interstellar object racing through our solar system - only the third ever spotted, though scientists suspect many more may slip past unnoticed.

As part of NASA’s efforts to expand access to space, four private astronauts are in orbit following the successful launch of the fourth all private astronaut mission to the International Space Station.
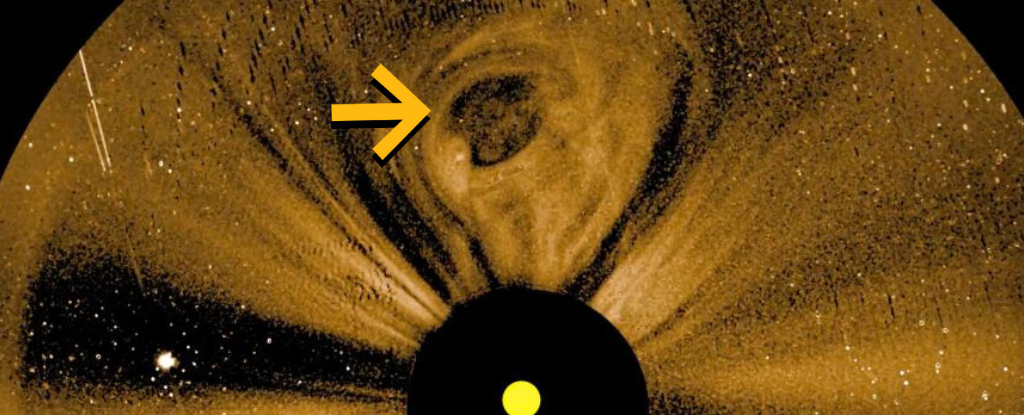
A NASA mission to observe the activity of the solar wind has returned its first images of giant coronal mass ejections (CMEs) billowing out from the Sun.
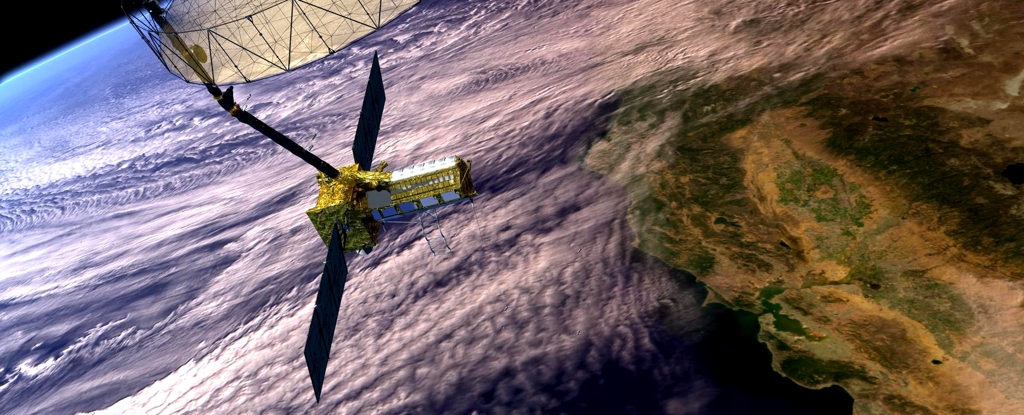

In a few days, a new satellite that can detect changes on Earth's surface down to the centimetre, in almost real time and no matter the time of day or weather conditions, is set to launch from India's Satish Dhawan Space Centre near Chennai.
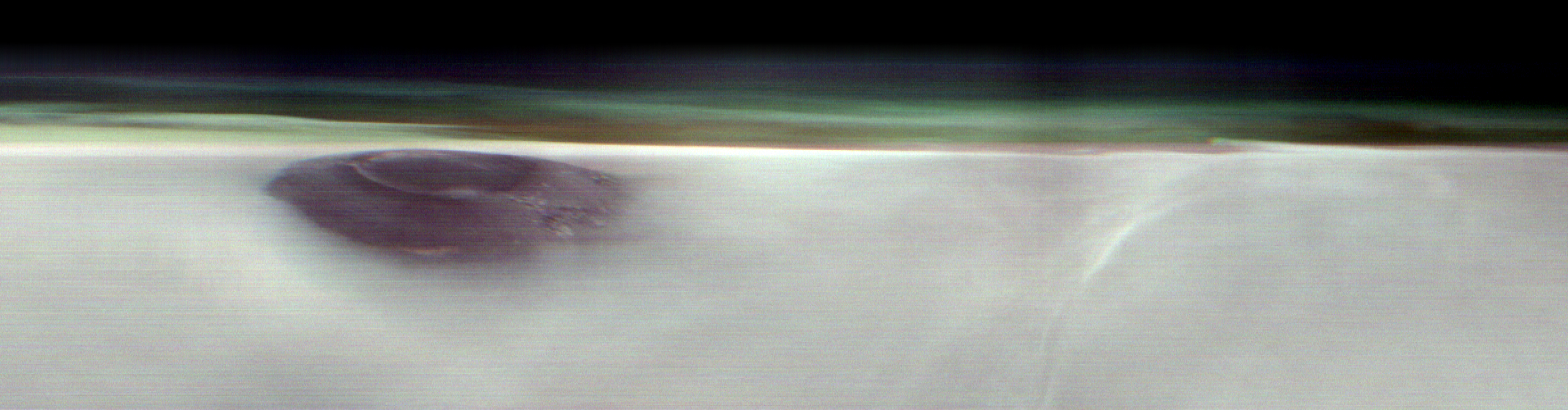
A new panorama from NASA’s 2001 Mars Odyssey orbiter shows one of the Red Planet’s biggest volcanoes, Arsia Mons, poking through a canopy of clouds just before dawn.

Dark matter affects how stars move within galaxies, how galaxies build up over time, and how everything in the universe is held together - but no existing tool has directly detected it. While dark matter does not reflect, absorb, or emit light, it can still be indirectly observed by telescopes.
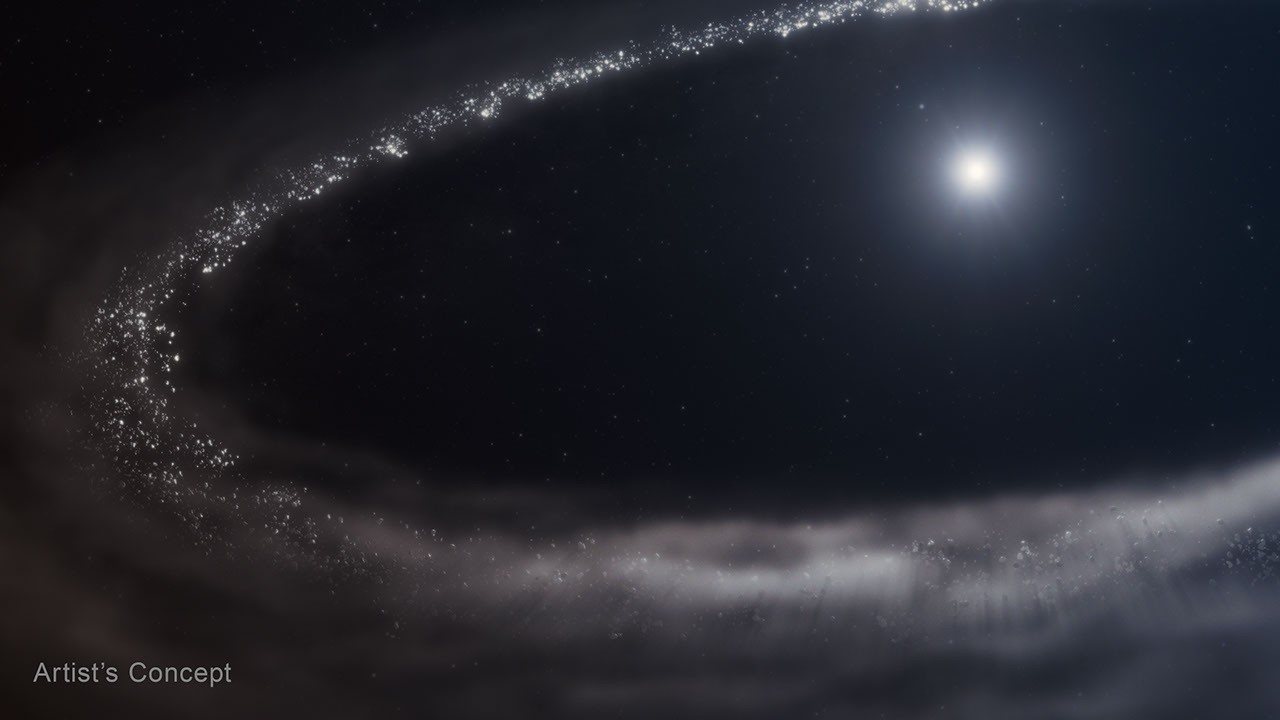

Researchers confirmed the presence of crystalline water ice in a dusty debris disk that orbits a Sun-like star 155 light-years away using detailed data known as spectra from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope.

After a decade of searching, NASA's MAVEN (Mars Atmosphere Volatile Evolution) mission has, for the first time, reported a direct observation of an elusive atmospheric escape process called sputtering.

Volcanoes often give little warning before they erupt, but now scientists have discovered an unexpected early warning sign—trees.

A green glow snapped from Mars marks the first time that an aurora has been observed from the surface of another planet.

Data from NASA's Magellan mission suggests Venus could be more geologically active than previously thought. The data shows compelling evidence for ongoing tectonic activity shaping Venus's surface features.

NASA's Chandra X-Ray Observatory helped diagnose the cause behind a large kink in a huge filament near the center of the Milky Way.