
A US-trio appears to have discovered a distant dwarf planet with a 25,000-year orbit bringing it into the ring of icy rocks around the solar system - the Oort cloud.
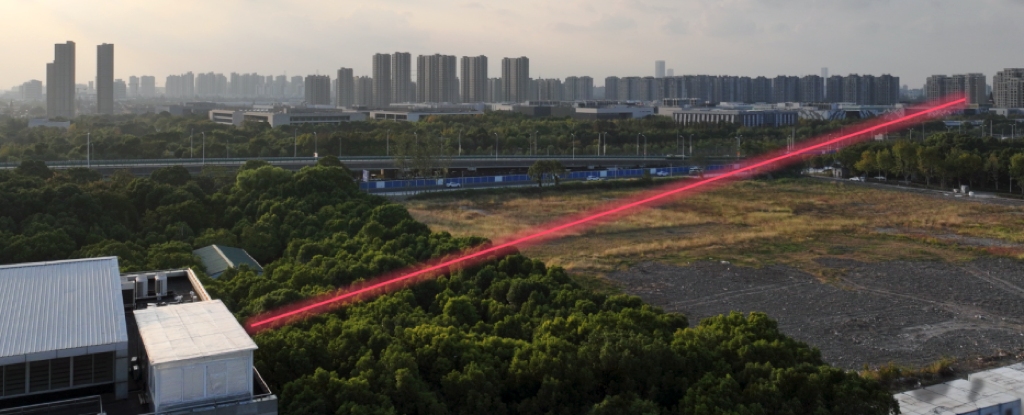

A new device recently demoed by researchers was able to scan tiny individual characters of text from a distance of 1.36 kilometers.

Curiosity triggered a thought-provoking conversation about light - ultimately, why doesn't light wear out and lose energy over time?

Dangerous rocks may co-orbit with Venus, but new research suggests only a space-based mission can prove it.

New research suggests that Jupiter used to be at least twice as big as it is today . Over time, the bloated world cooled off, contracting to the relatively humbler size it is today.
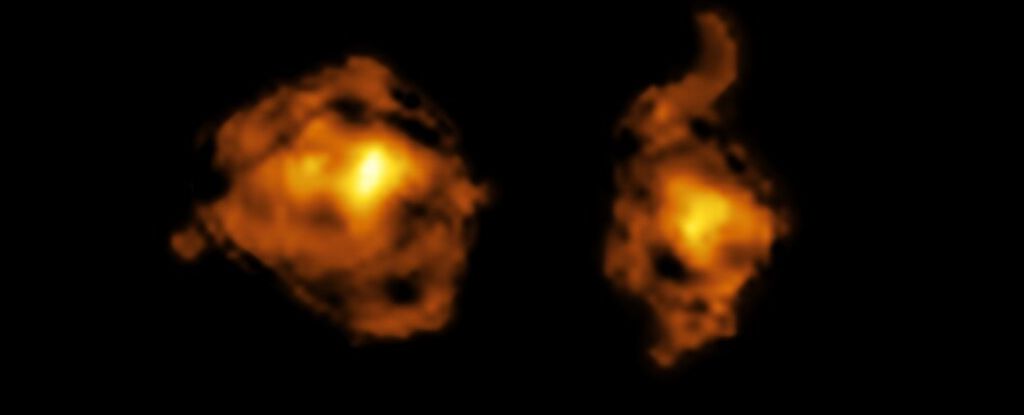
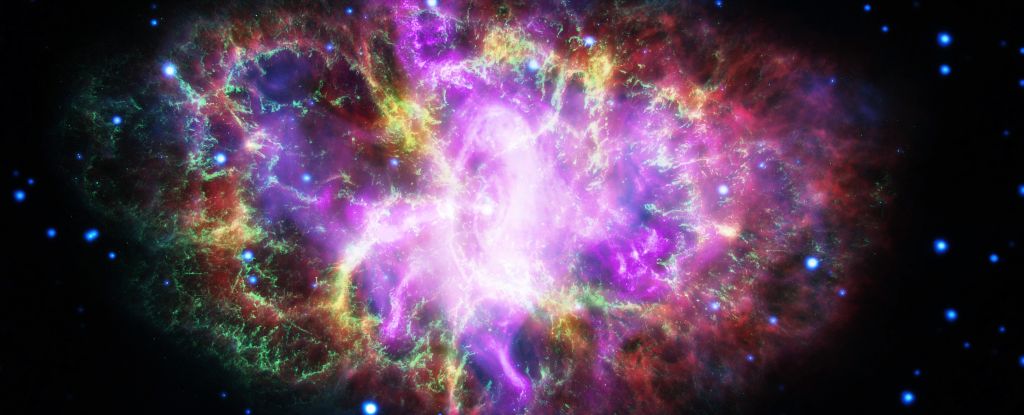
The moment one galaxy spears another with a powerful beam of radiation shooting from its central black hole has been spotted in a distant galactic collision.

Scientists in China have developed contact lenses that let wearers see light normally invisible to the human eye.

For the first time, scientists have caught lightning in the act of unleashing a powerful burst of gamma radiation known as a terrestrial gamma-ray flash (TGF).

A team of astronomers has identified a giant spiral galaxy so well-formed that it already has a stable galactic bar; a long, straight structure filled with stars across the galaxy's center. It was formed just 2.6 billion years after the Big Bang.
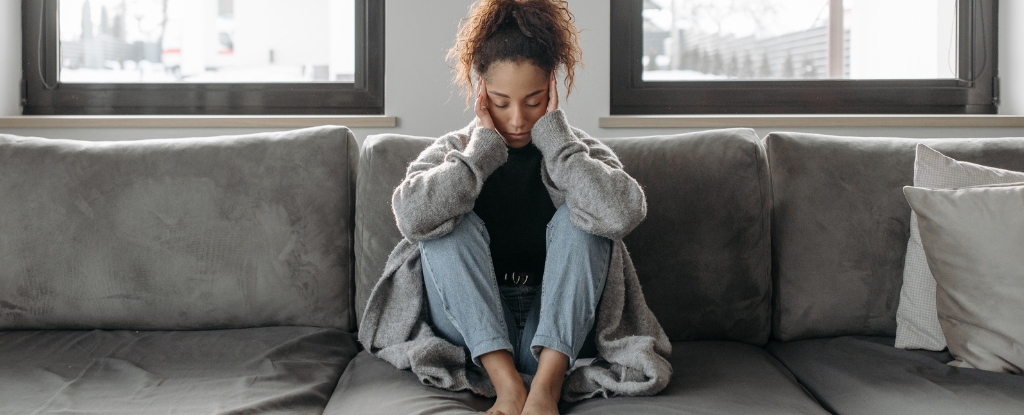

A new study of older adults suggests it can lead to brain shrinkage and cognitive issues, irrespective of how much exercise you're managing to fit in.

Anew study said the streaks aren’t caused by water. Instead, the study suggests, the streaks are due to wind and dust.
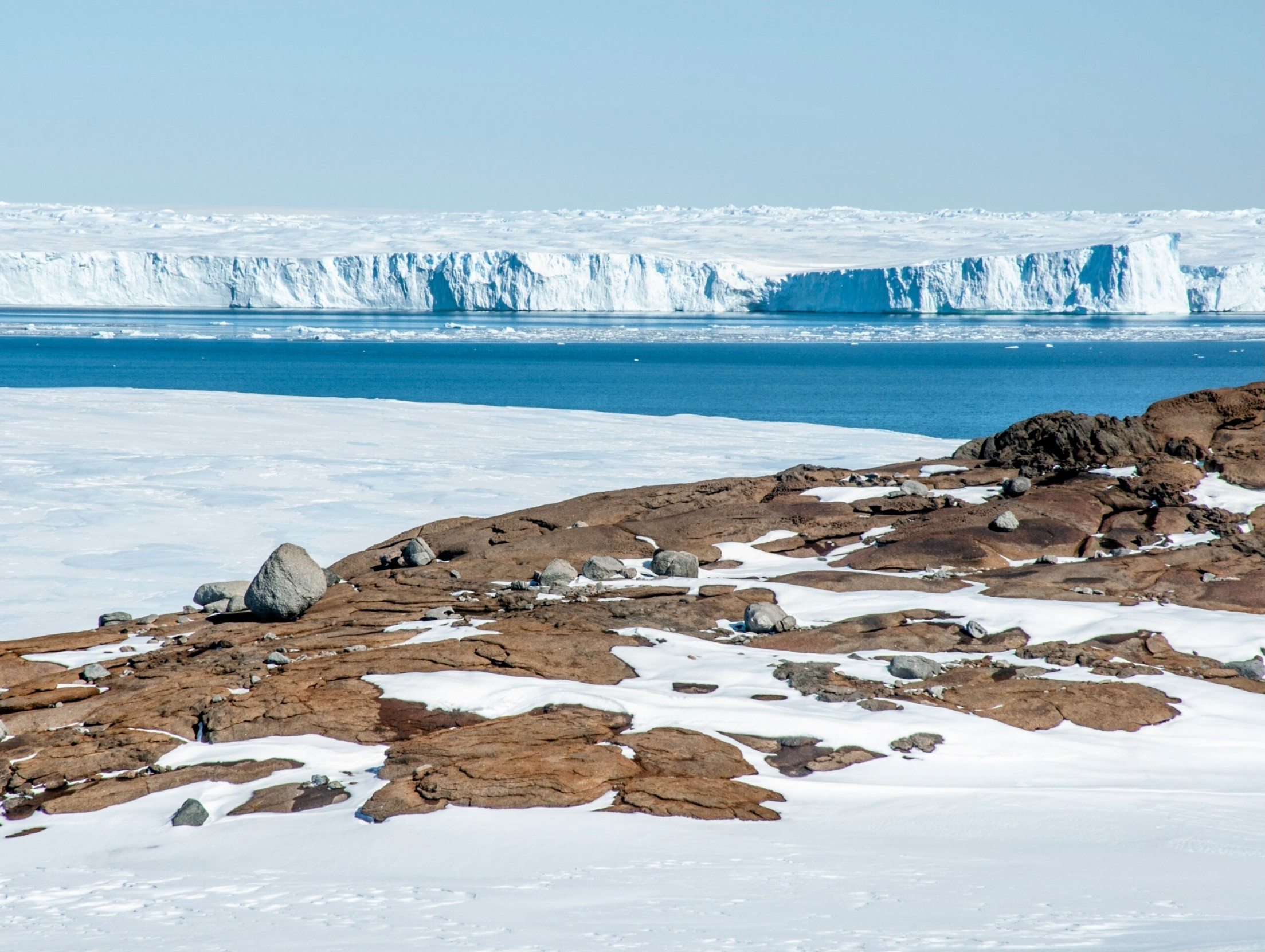

New research shows polar ice sheets may begin irreversible collapse even at 1.5 C warming - putting millions at risk.
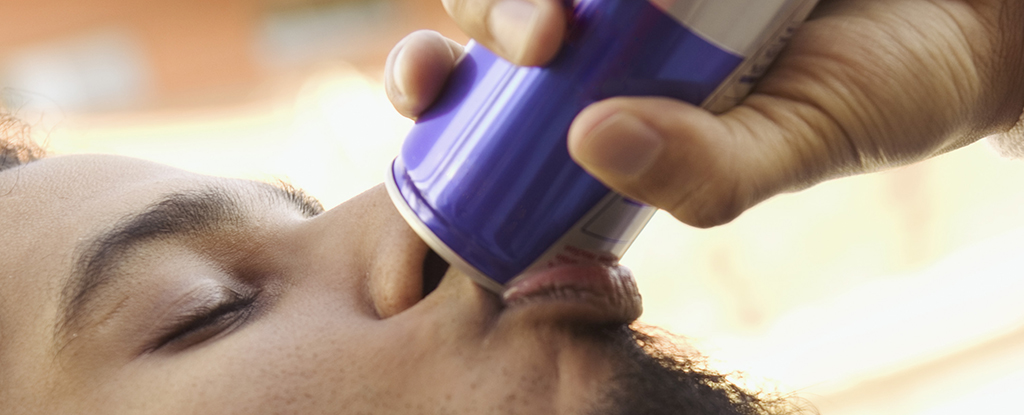

Taurine is an amino acid occurring naturally in the body, and found in energy drinks as well as foods like fish and meat – but a new study suggests it's also an important fuel source for driving cancers such as leukemia.
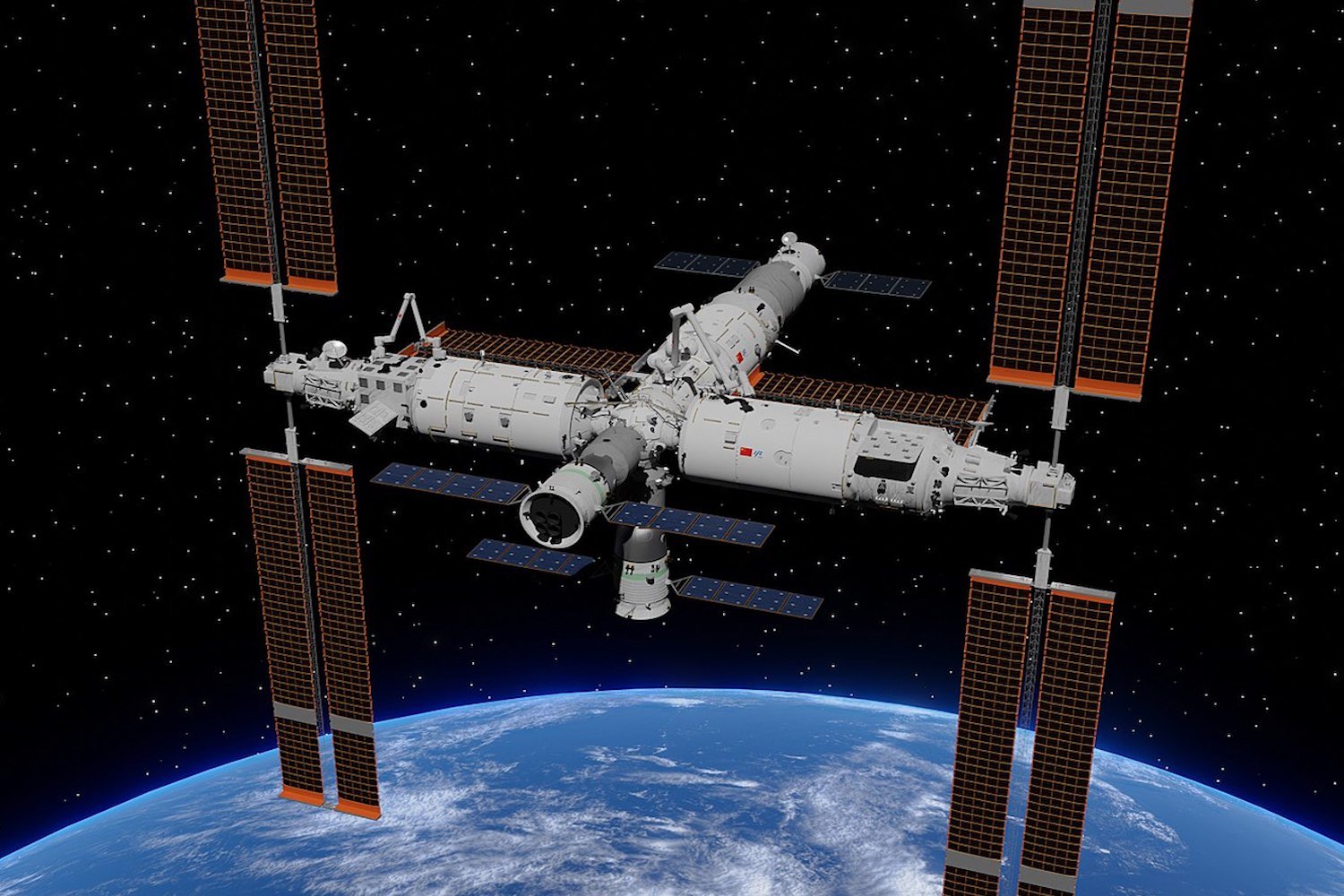

The microbes could potentially pose a threat to the health of astronauts on board Tiangong.

Researchers said on May 20, 2025, that there could be abundant water on the seven worlds.