
Since the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) began science operations, astronomers have observed galaxies that existed more than 13 billion years ago.

For a long time, scientists thought that only actively star-forming galaxies should be observed in the very early Universe. The James Webb space telescope now reveals that galaxies stopped forming stars earlier than expected.
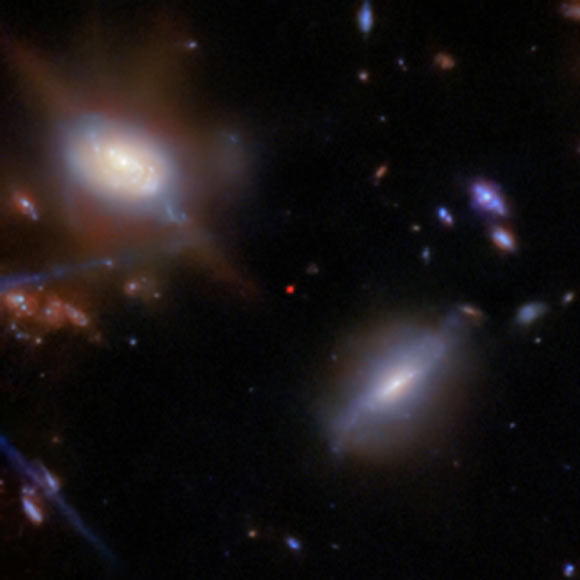

The Lyman-apha light from JADES-GS-z13-1 has taken nearly 13.47 billion years to reach us, as it dates back to just 330 million years after the Big Bang.

For the first time, NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has captured bright auroral activity on Neptune.

In 2022 NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope discovered an abundance of tiny red objects scattered across the sky in the early universe. A large fraction of them are likely galaxies with supermassive black holes growing at their centers.

When you peer out into the depths of the cosmos, a mystery lies there, waiting. In a survey of the deep sky, most of the galaxies are seen rotating in the same direction.

Astronomers using the Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) onboard the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope have captured coronagraphic images of the HR 8799 and 51 Eridani planetary systems.

In this incredible image, we can see the unrestrained energy of two young stars about 650 light-years away as their energetic jets create a distinct hourglass shape with clumps and swirls of gas and dust.

Using the James Webb Space Telescope, scientists witnessed a brilliant light show at the heart of our Milky Way galaxy.
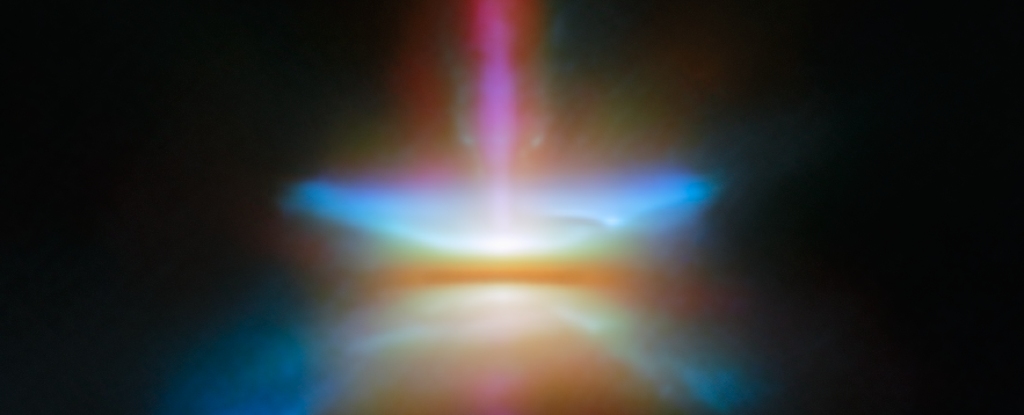

This new image of the protostar HH30 is in amazing new detail thanks to the JWST. The image shows the protoplanetary disk seen edge on, with a conical outflow of gas and dust, with a narrow jet blasting out into space.
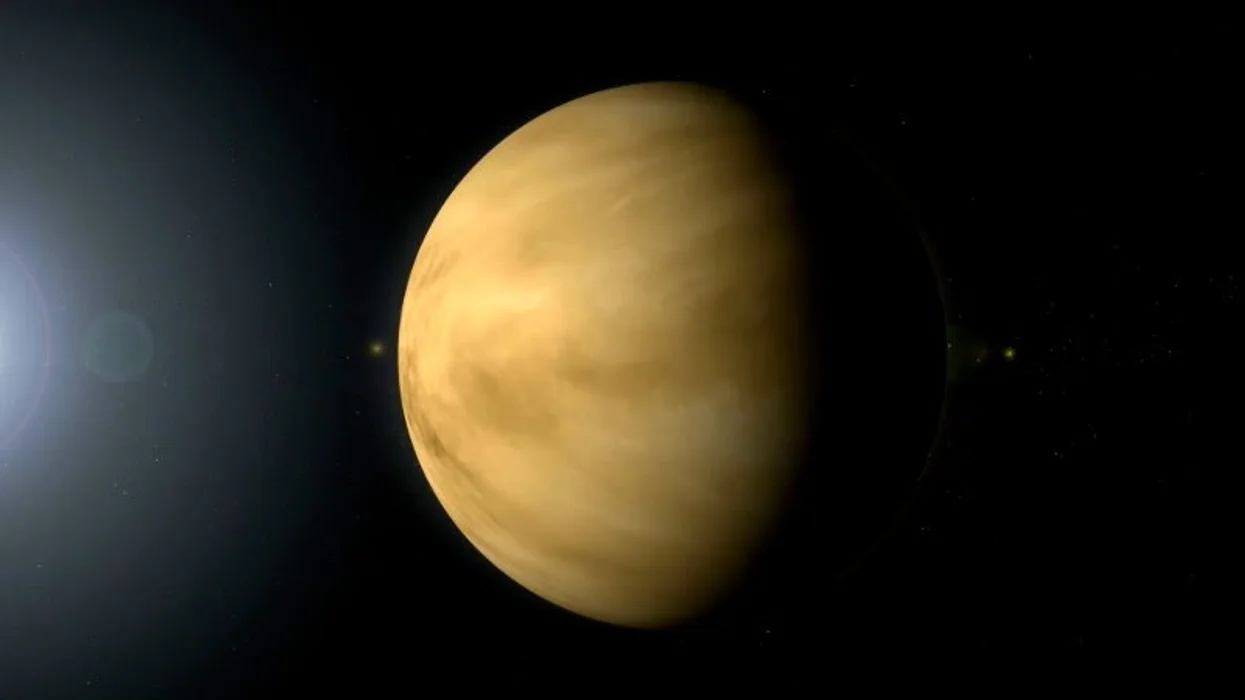

New data from James Webb Space Telescope and simulation models have confirmed a new type of planet unlike anything found in the Solar System.
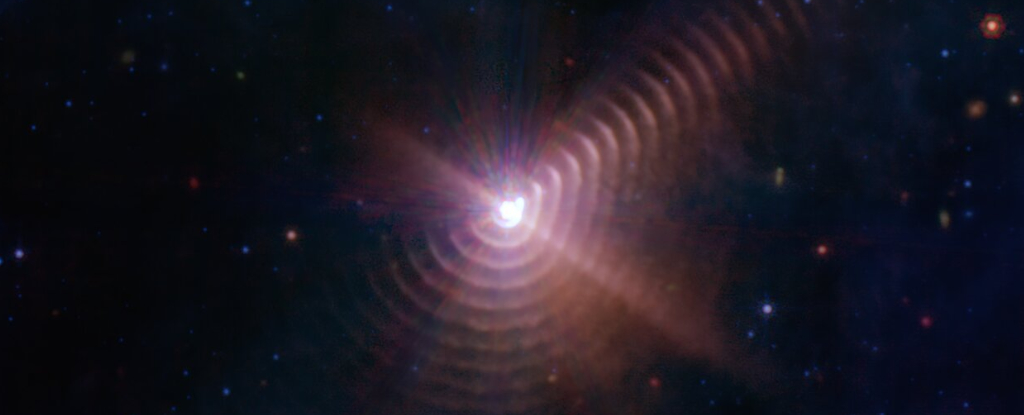

Carbon-rich cosmic dust comes from different sources and spreads out into space, where it's necessary for life and for the formation of rocky planets like ours.
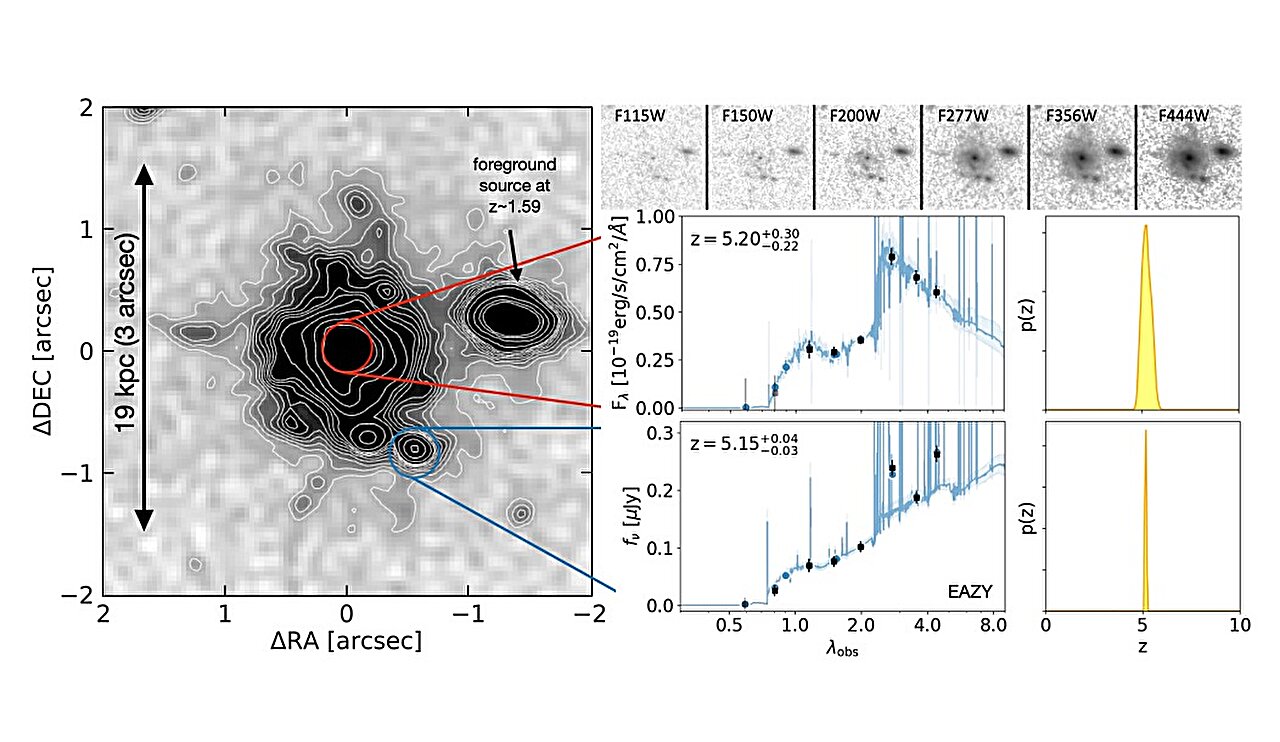
Using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), an international team of astronomers has detected a new grand-design spiral galaxy as part of the PANORAMIC survey.

The James Webb Space Telescope is celebrating three years from its launch. Its discoveries have already changed our understanding of the early universe.
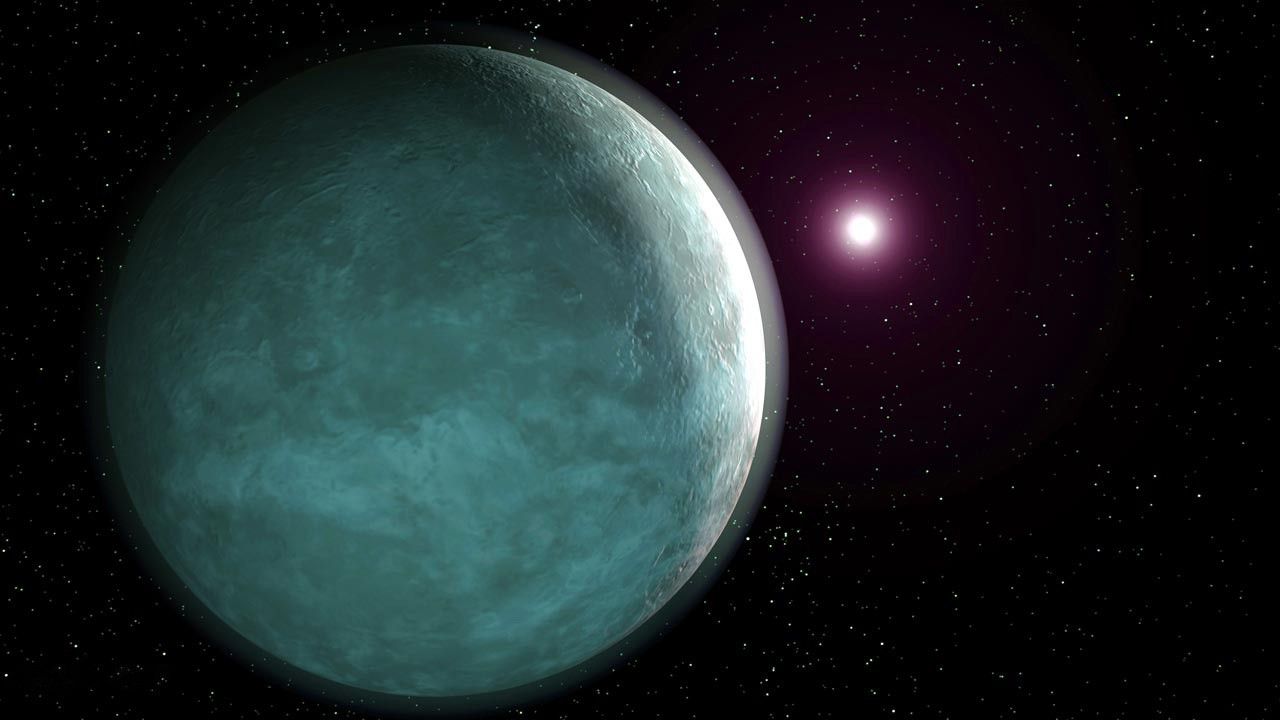

An unusual planetary system with three known ultra-low density "super-puff" planets has at least one more planet.