
The ongoing swarm of earthquakes near Santorini continues to baffle scientists.
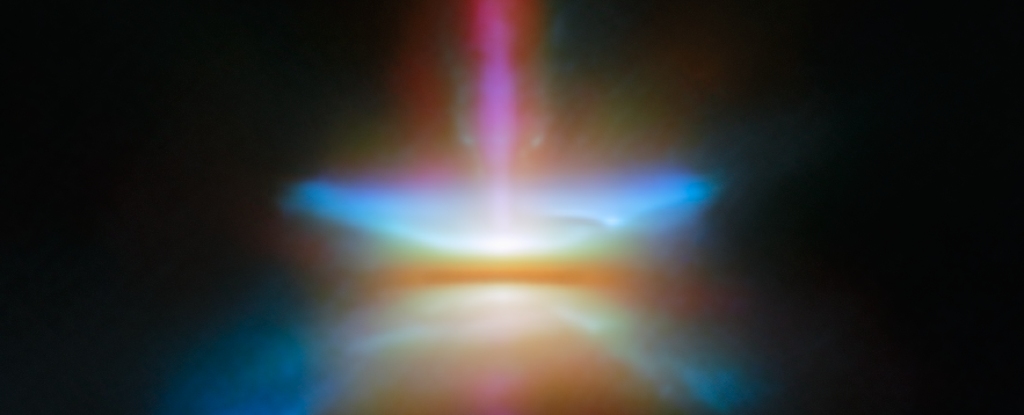

This new image of the protostar HH30 is in amazing new detail thanks to the JWST. The image shows the protoplanetary disk seen edge on, with a conical outflow of gas and dust, with a narrow jet blasting out into space.

Using the European Space Agency’s Euclid space telescope, astronomers have accidentally found a complete Einstein ring around a nearby galaxy known as NGC 6505.
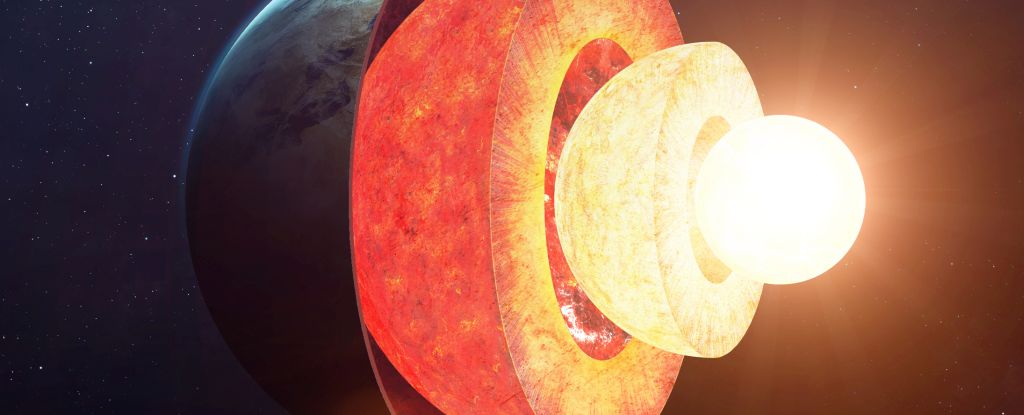
The internal, infernal machinations of our planet may be way more complex than we suspected.
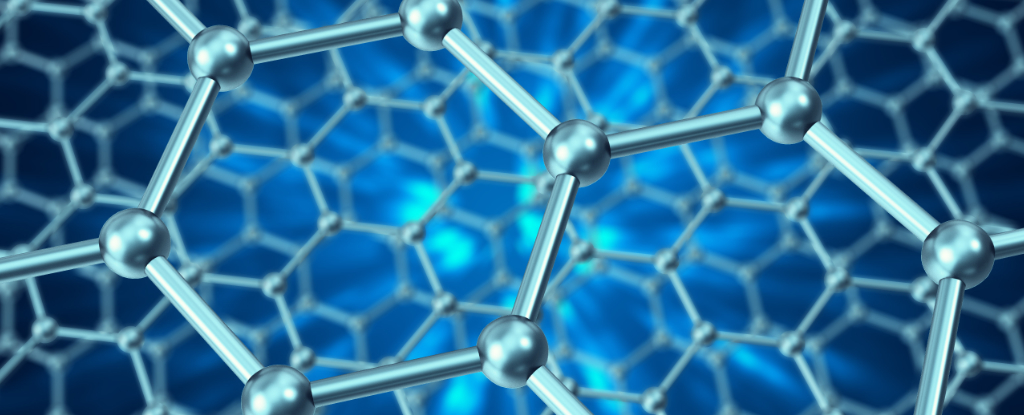
Team of international researchers have recently discovered a strange new state of matter in the dynamics of currents flowing through layers of graphene.
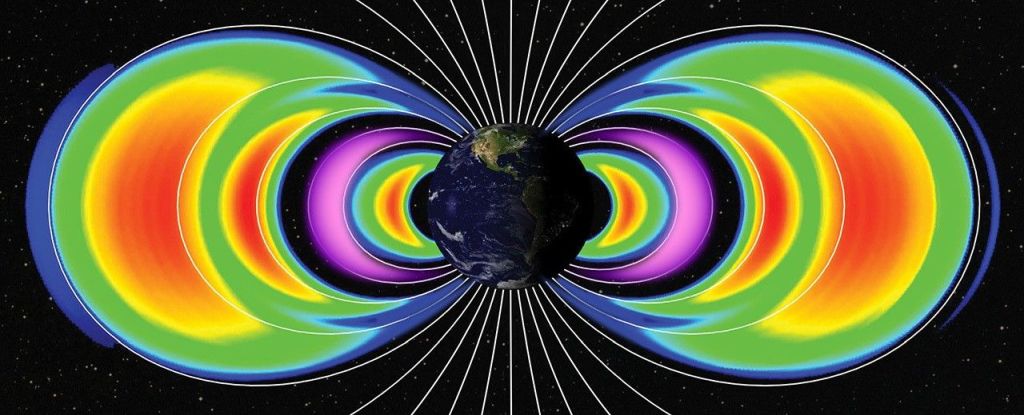

In the months following massive solar storm in May, 2024, Earth was girded by two new, temporary radiation belts of high-energy particles, trapped by the planet's magnetic field.
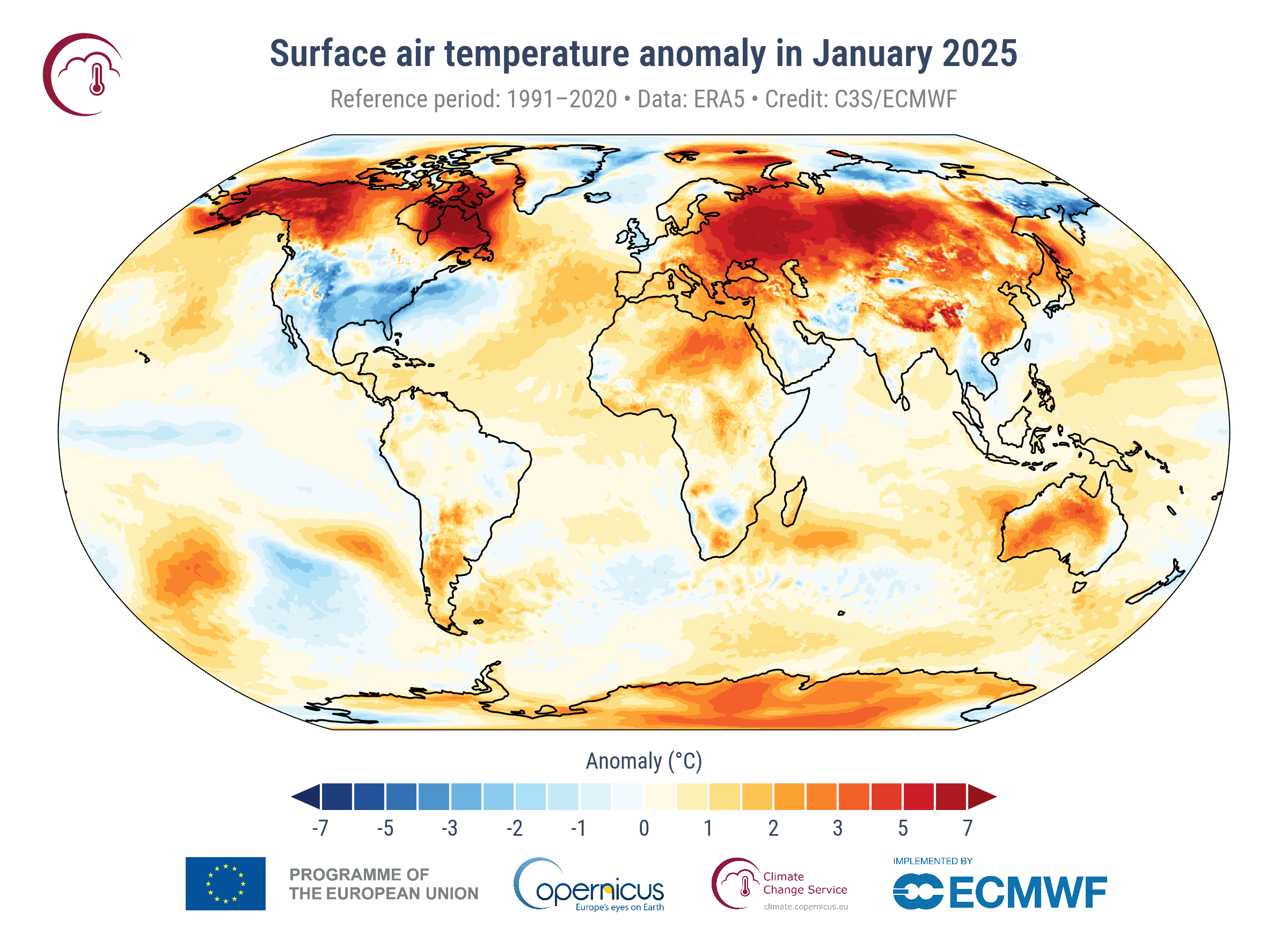
January 2025 was 1.75°C above the pre-industrial level and was the 18th month in the last nineteen months for which the global-average surface air temperature was more than 1.5°C above the pre-industrial level.
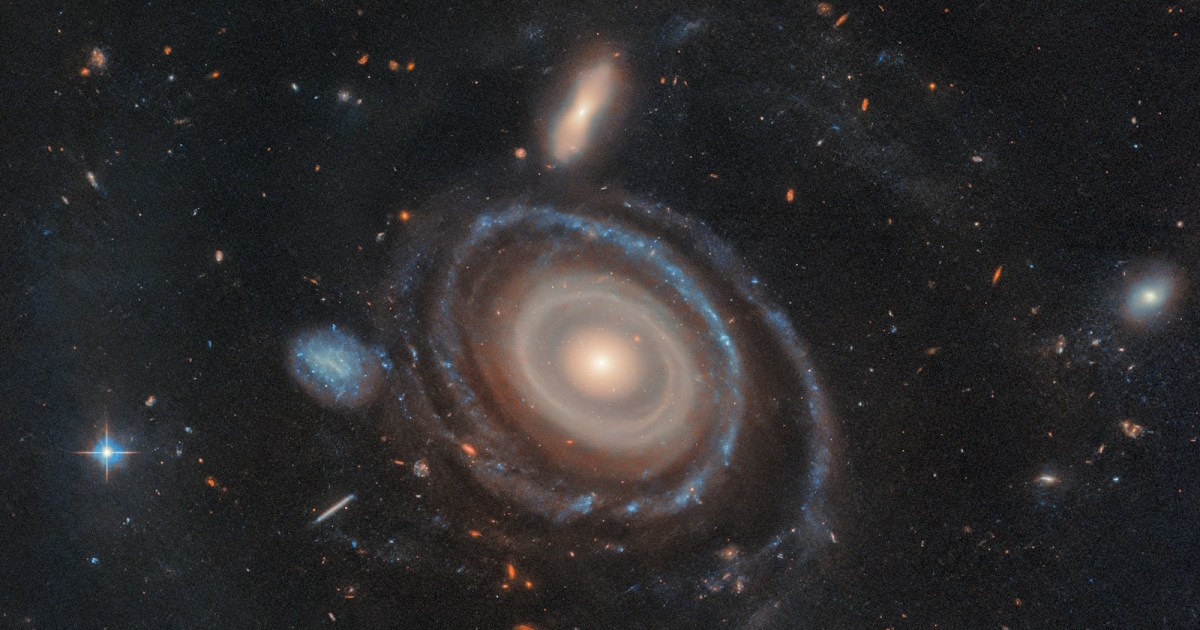

Ring galaxies are rare, but we think we know how they form. A new, early-stage version, the Bullseye galaxy, provides a new testing ground.
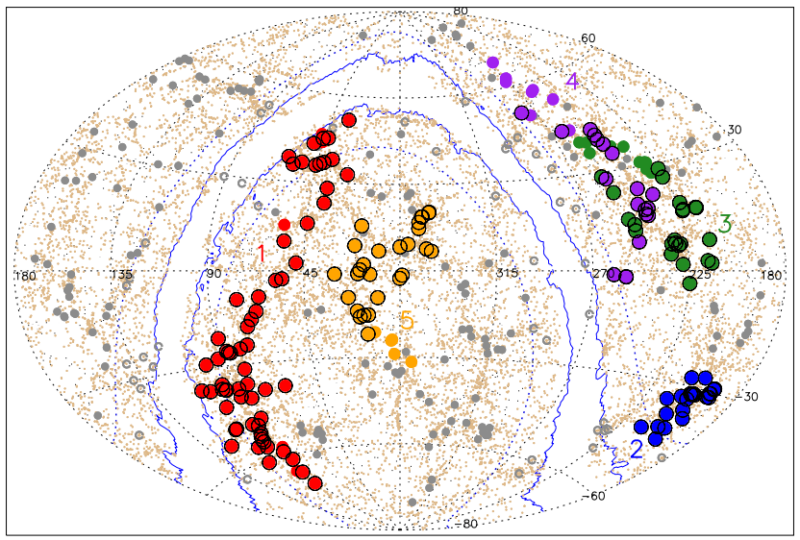
A team of astronomers have mapped the nearby universe, from about 425 million to 800 million light-years (which translates to some 130 to 250 megaparsecs), and discovered the largest-known structure residing there.

Acclaimed climate scientist Professor James Hansen and colleagues recently wrote that global temperature will not fall much below +1.5°C level, instead they will be oscillating near or above that level for the next few years.

Bennu has a 1-in-2,700 chance of colliding with Earth in 2182, causing a global winter and drought.

New research shows that when an asteroid slammed into the moon billions of years ago, it carved out a pair of grand canyons on the lunar far side.

In just five years, 930 million cubic meters of crevasses opened up in the Greenland ice sheet, equivalent to adding a crack the size of the Great Pyramid of Giza to the world's second largest ice sheet every few days.

Scientist have concluded water did not arrive as early during Earth's formation as previously thought.
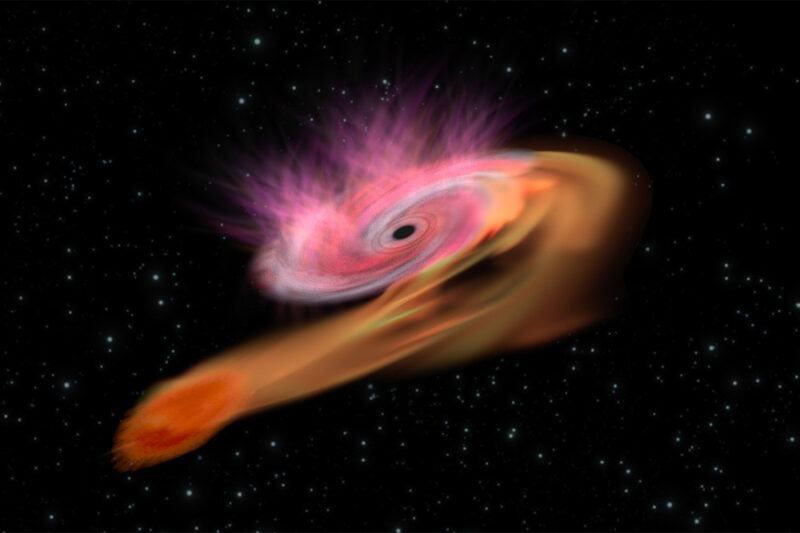

In April of 2024, astronomers spotted an unusual event that astronomers named EP240408a. While the explosion was originally thought to be a gamma-ray burst, it now appears it might represent a new class of powerful cosmic explosion.