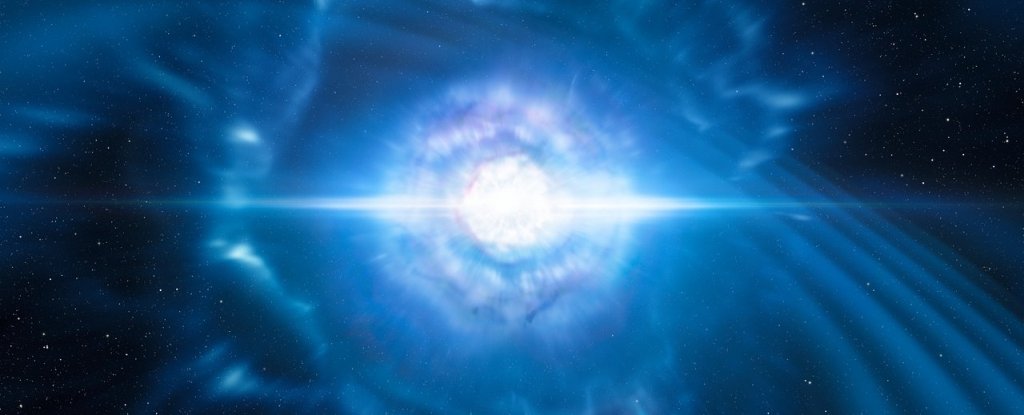

In August 2017, humanity observed a wonder. For the first time, we got to see two neutron stars colliding.

In the binary system 4U 1820-30, a neutron star is spinning so fast around its center axis that it completes a breathtaking 716 rotations per second.
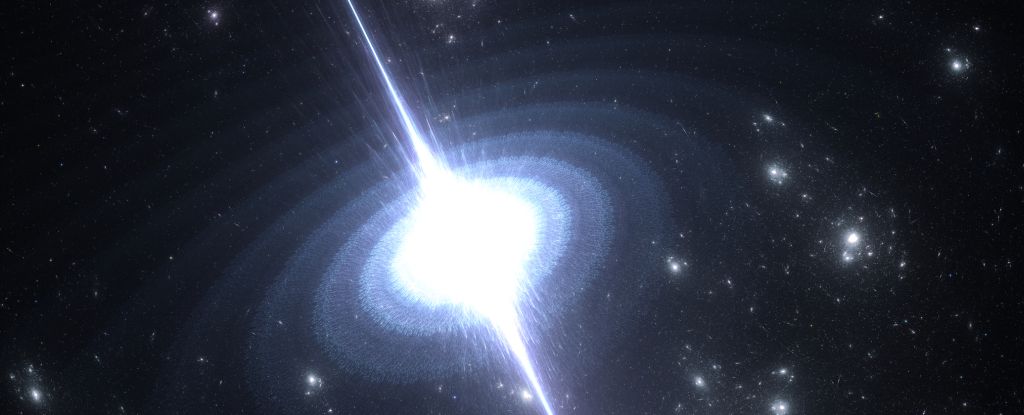

Neutron stars with a penchant for extreme spinning could be churning out one of the most sought-after particles in the Universe.
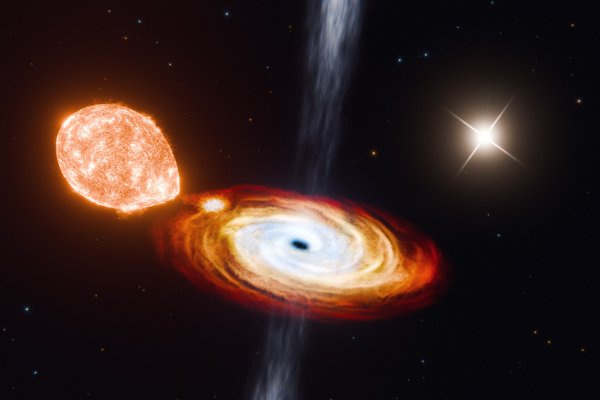
In this system, called V404 Cygni, the black hole is consuming a small star that is spiraling in very close and fast while a newfound third star circles the black hole from much farther away.
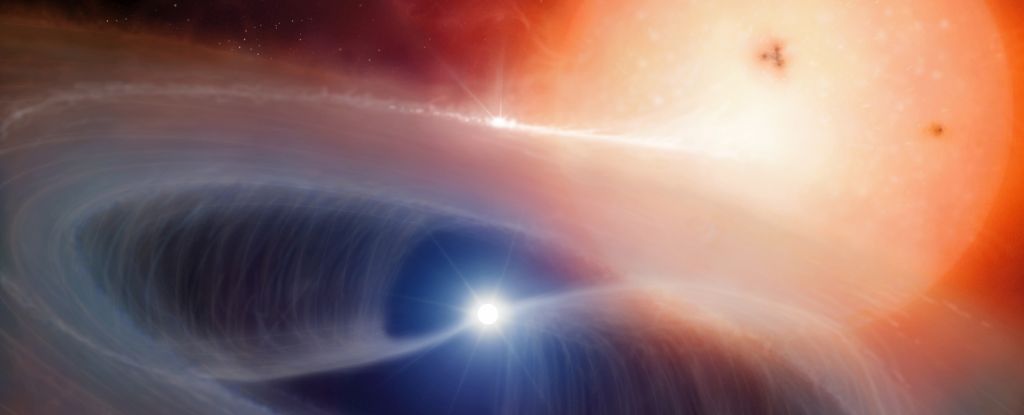

One of the great mysteries of the Universe is where all the metal actually comes from.
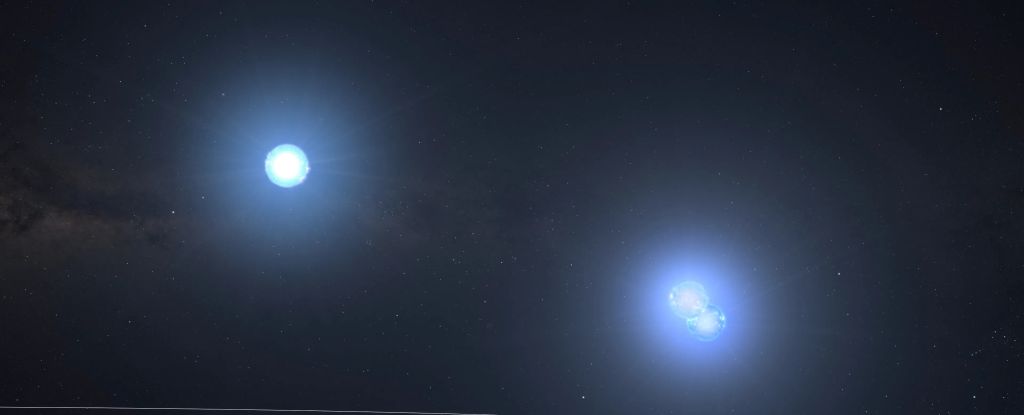

TIC 290061484 is a system of gravitationally bound stars consisting of a tightly-orbiting binary pair with a third star that circles both. Astonishingly, they're so close together the entire system would fit inside the orbit of Mercury.
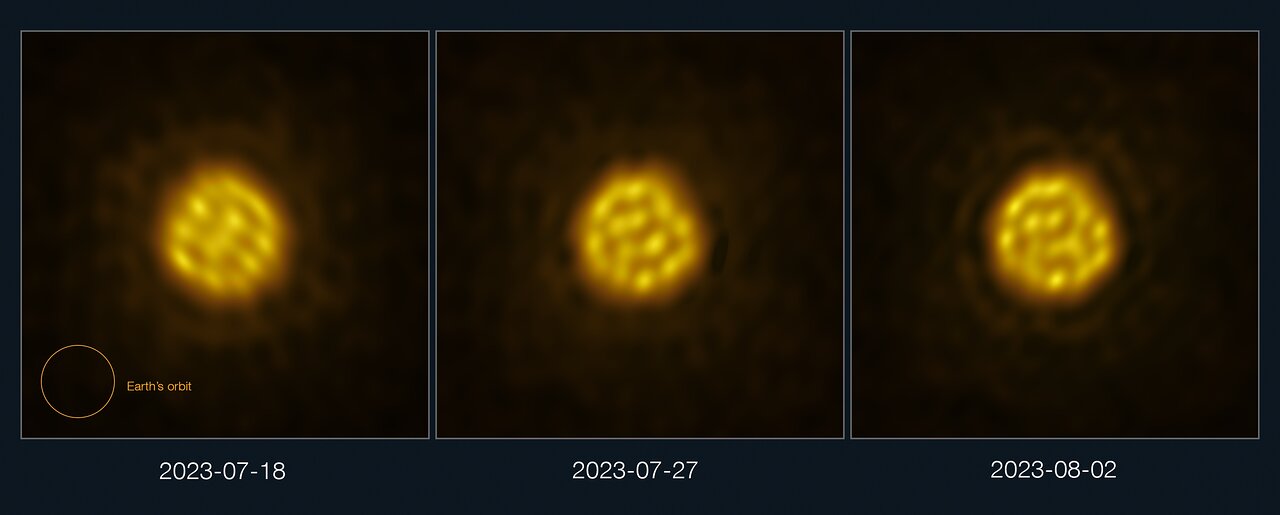

For the first time, astronomers have captured images of a star other than the Sun in enough detail to track the motion of bubbling gas on its surface.
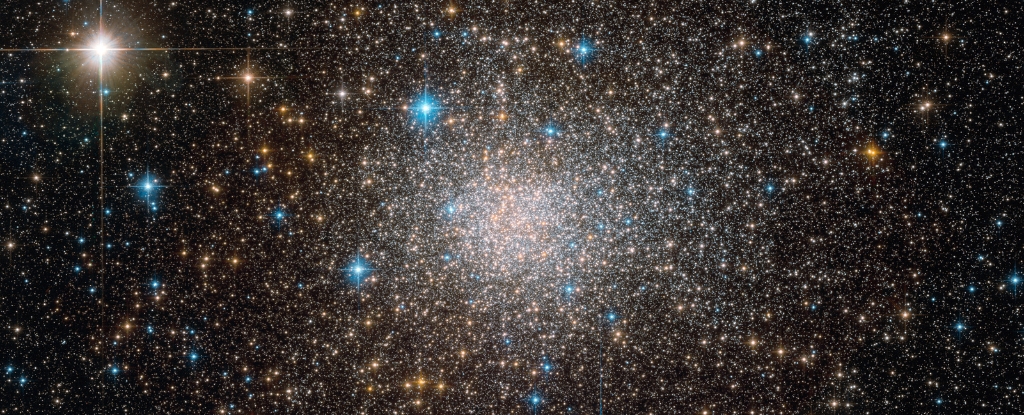

Terzan 5 star cluster is a copious producer of cosmic rays, because it contains a large population of rapidly rotating, incredibly dense and magnetised millisecond pulsars – which accelerate cosmic rays up to extremely high speeds.

In a remarkable discovery, astronomers have found a disc around a young star in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a galaxy neighbouring ours. It’s the first time such a disc has ever been found outside our galaxy.
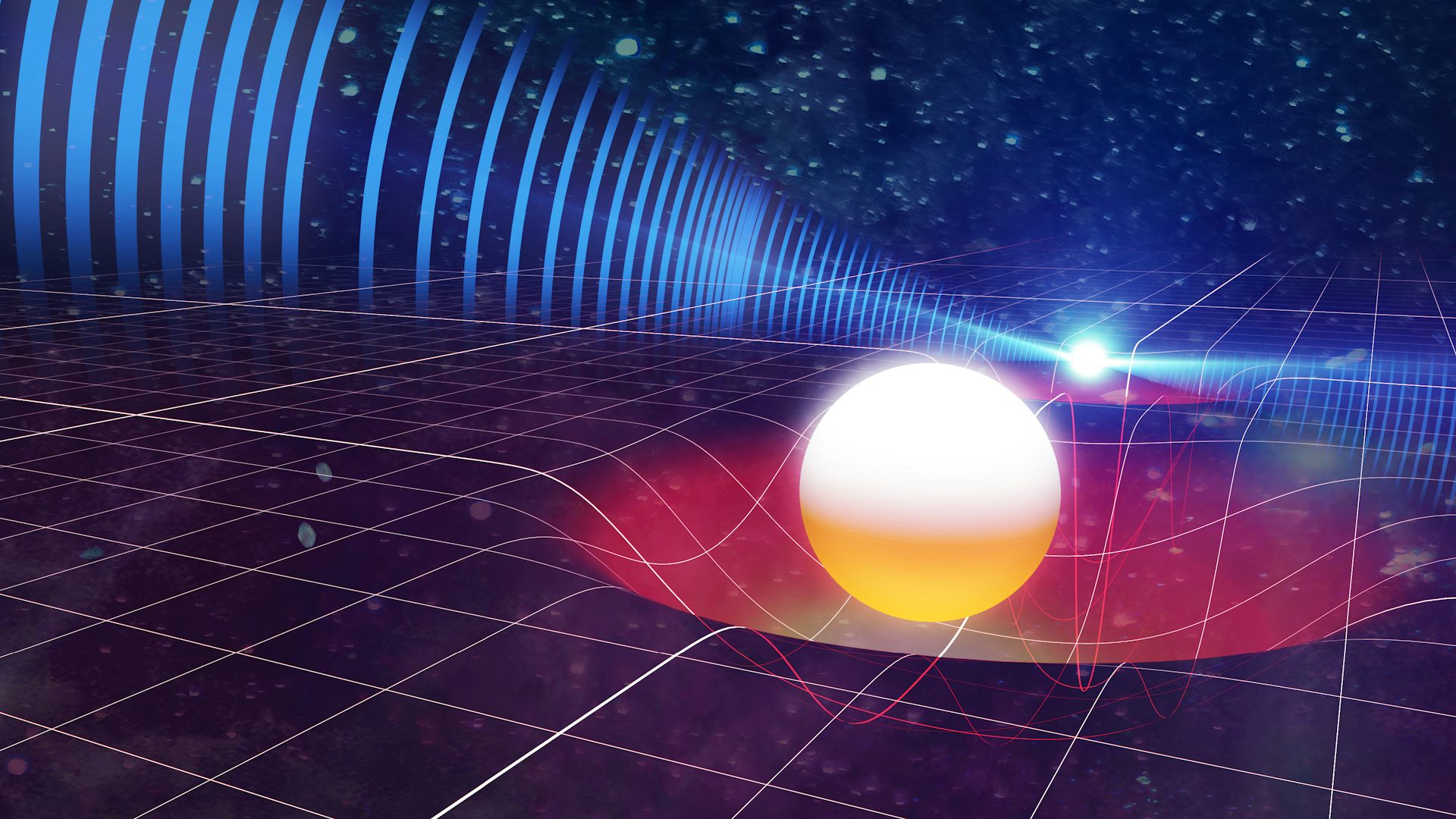
Neutron stars are some of the most extreme objects in the universe. Formed from the collapsed cores of supergiant stars, they weigh more than our Sun and yet are compressed into a sphere the size of a city.
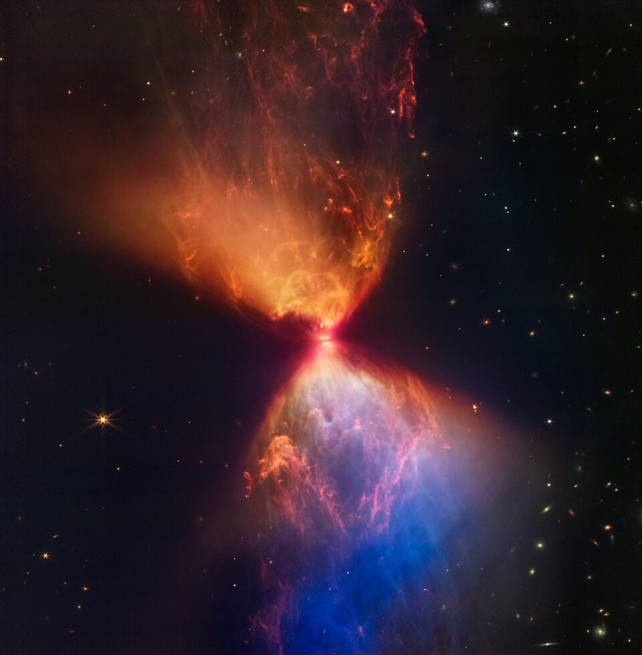

james Webb Space Telescope continues to revolutionise astronomy - it now shows the birth of a star. The star is named L1527, and at this young age, it's still ensconced in the molecular cloud that spawned it.

Strange thing about our galaxy's nucleus, according to new research: stars that stay young indefinitely by feeding off dark matter particles.

Scientists have clocked the speed of Cepheid stars -- 'standard candles' that help us measure the size of the universe -- with unprecedented precision, offering exciting new insights about them.

A neutron star labeled ASKAP J1935+2148 defies rules for neutron stars, emitting radio signals on a comparatively leisurely interval of 53.8 minutes.
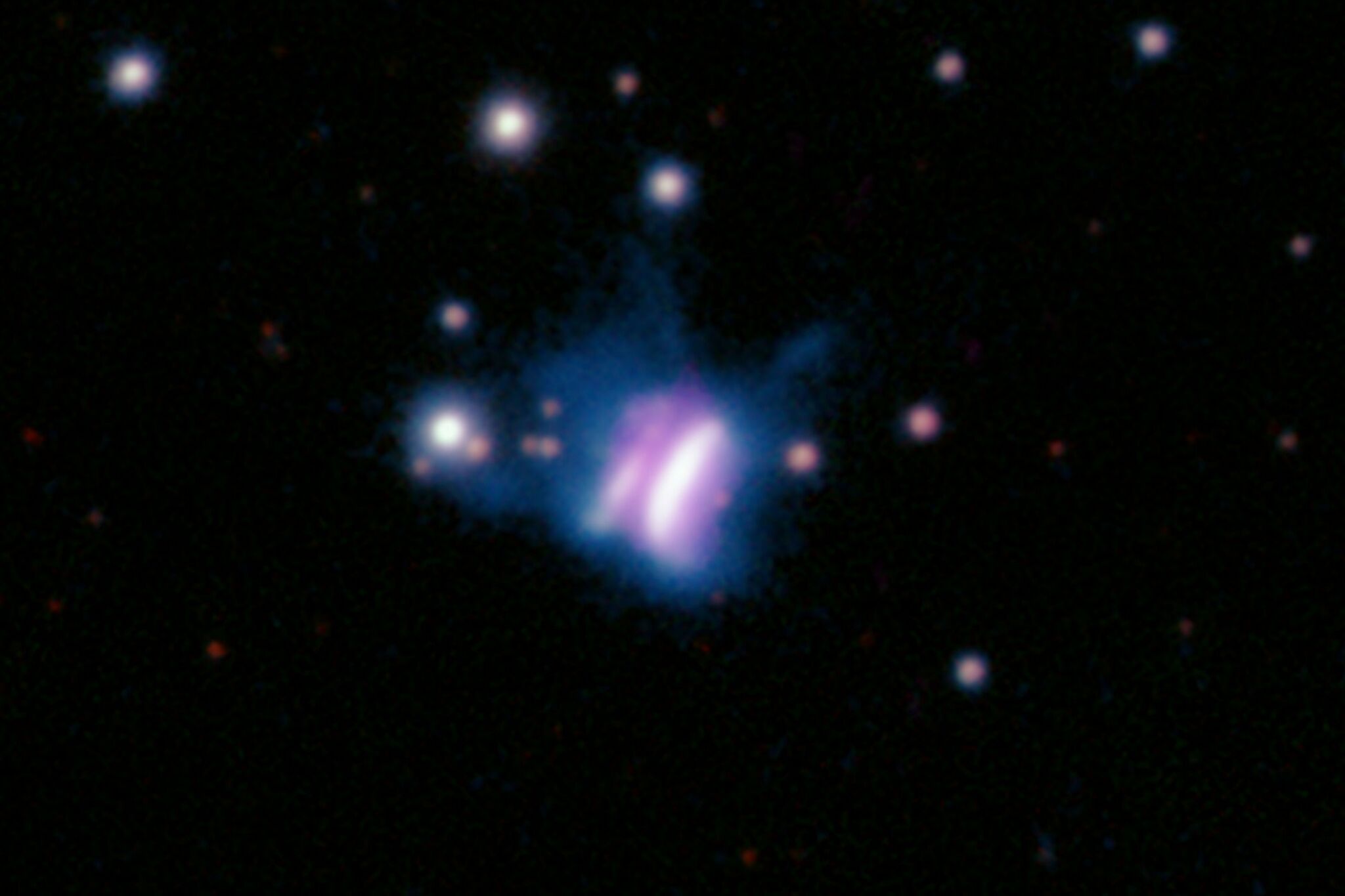

Astronomers discover the biggest planet-forming disk ever and it resembles a butterfly.