
Cyborg cockroaches are creeping onto the scene as a surprising alternative for challenging tasks in risky locations.

The battery uses solar power generated by crystals that emit light when they absorb radiation.

A team of physicists at the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory, in Menlo Park, California, generated the highest-current, highest-peak-power electron beams ever produced.

These robots can flow around obstacles before hardening into weight-bearing tools that push, throw, twist objects like a wrench—and bear up to 150 pounds of weight.
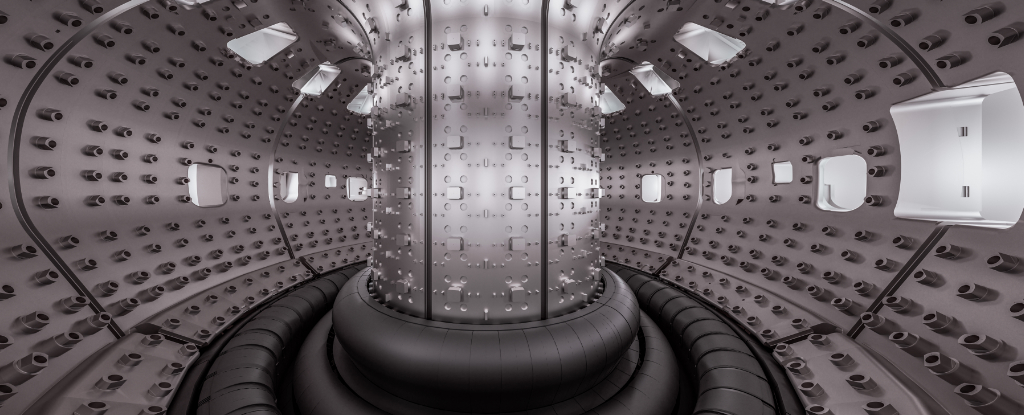
French scientists on Tuesday announced that they had reached a "crucial milestone" in the long road towards nuclear fusion by managing to maintain raging-hot plasma for a record 22 minutes.
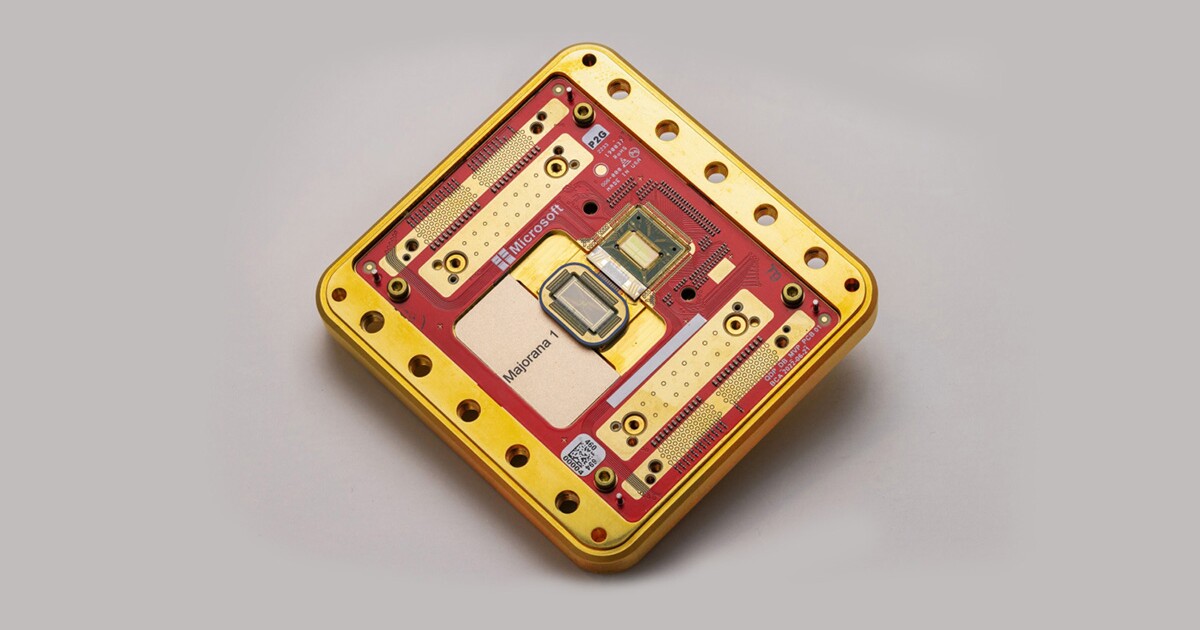
Microsoft says it's made a major breakthrough in quantum computing capabilities with the Majorana 1, its first quantum chip.

In a groundbreaking use of teleportation, critical units of a quantum processor have been successfully spread across multiple computers.
Team of international researchers have recently discovered a strange new state of matter in the dynamics of currents flowing through layers of graphene.
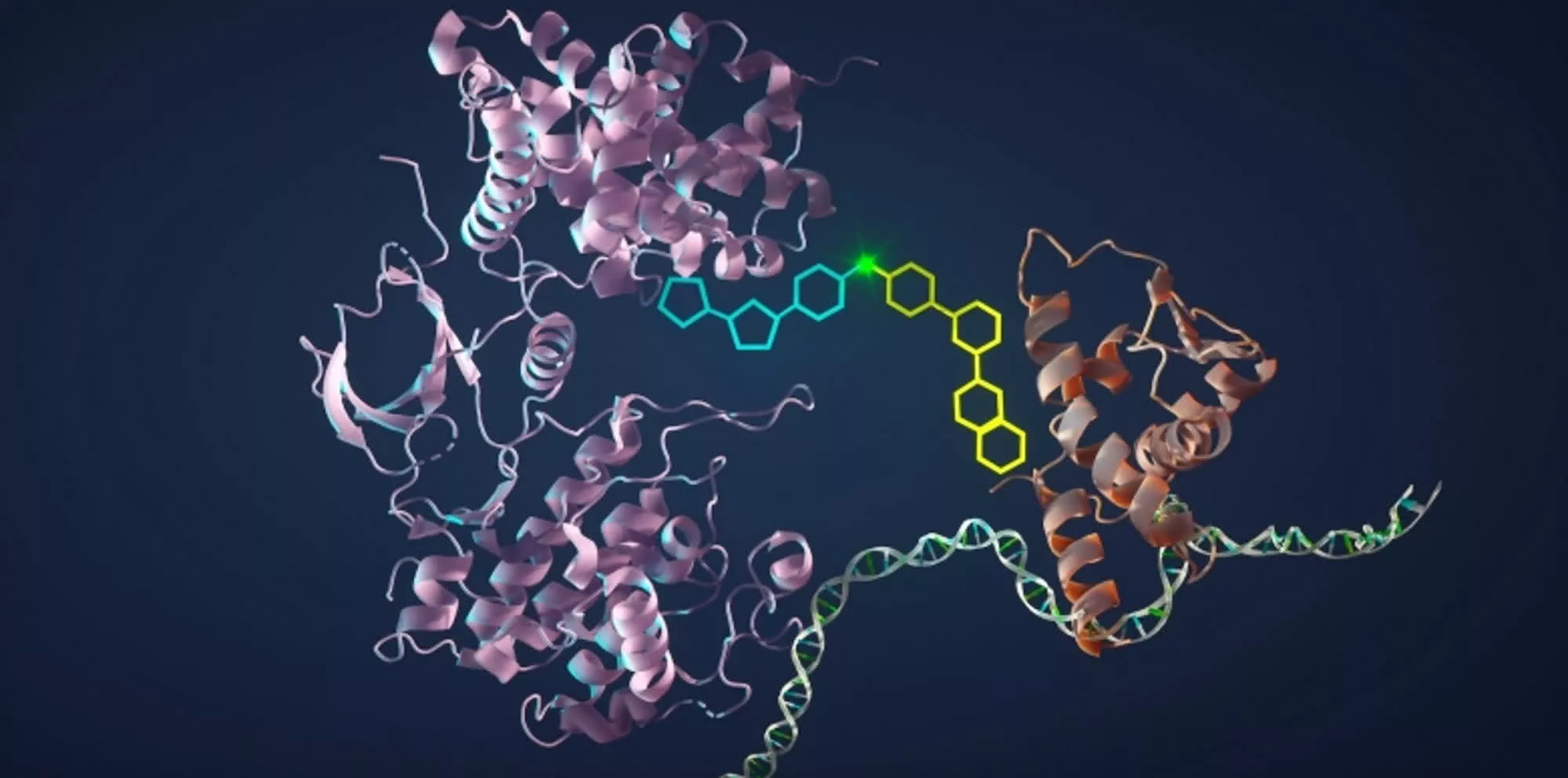
A team of AI researchers, biologists and evolutionary specialists have designed and built an AI model capable of generating the code to synthesize novel proteins.

The computer science behind translating speech from 100 source languages.

Our digital legacies don’t just preserve memories; they can continue to influence the world, long after we’re gone.
Interacting with AI chatbots like ChatGPT can be fun and sometimes useful, but the next level of everyday AI goes beyond answering questions: AI agents carry out tasks for you.

Even highly realistic androids can cause unease when their facial expressions lack emotional consistency.

Quantum teleportation over a busy internet cable opens the door for quantum applications without requiring specialized infrastructure.

China is now home to the world's most powerful centrifuge capable of creating artificial gravity. This facility will enable a wide range of experiments to help make sense of scientific phenomena, simulate geological events, and test new materials.