
Since the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) began science operations, astronomers have observed galaxies that existed more than 13 billion years ago.

A team of researchers at Nagoya University has discovered evidence that the Small Magellanic Cloud is potentially being torn apart by gravitational forces from its larger companion.

A massive black hole at the heart of a galaxy in the Virgo constellation is waking up, shooting out intense X-ray flares at regular intervals that have puzzled scientists

For a long time, scientists thought that only actively star-forming galaxies should be observed in the very early Universe. The James Webb space telescope now reveals that galaxies stopped forming stars earlier than expected.

When you peer out into the depths of the cosmos, a mystery lies there, waiting. In a survey of the deep sky, most of the galaxies are seen rotating in the same direction.

JWST have revealed an exceptionally large galaxy in the early universe. It’s a cosmic giant whose light has travelled over 12 billion years to reach us. We’ve dubbed it the Big Wheel.

Located 2.5 million light-years away, the majestic Andromeda galaxy appears to the naked eye as a faint, spindle-shaped object roughly the angular size of the full Moon.

Using the European Space Agency’s Euclid space telescope, astronomers have accidentally found a complete Einstein ring around a nearby galaxy known as NGC 6505.

Ring galaxies are rare, but we think we know how they form. A new, early-stage version, the Bullseye galaxy, provides a new testing ground.
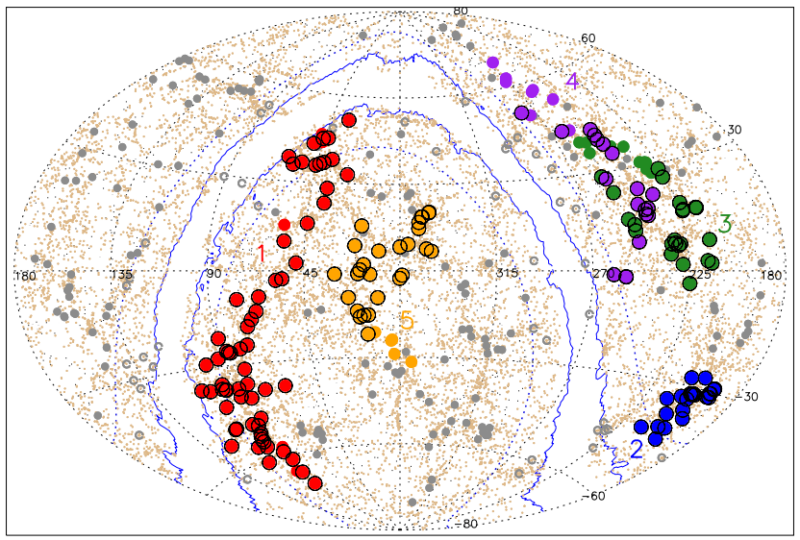
A team of astronomers have mapped the nearby universe, from about 425 million to 800 million light-years (which translates to some 130 to 250 megaparsecs), and discovered the largest-known structure residing there.
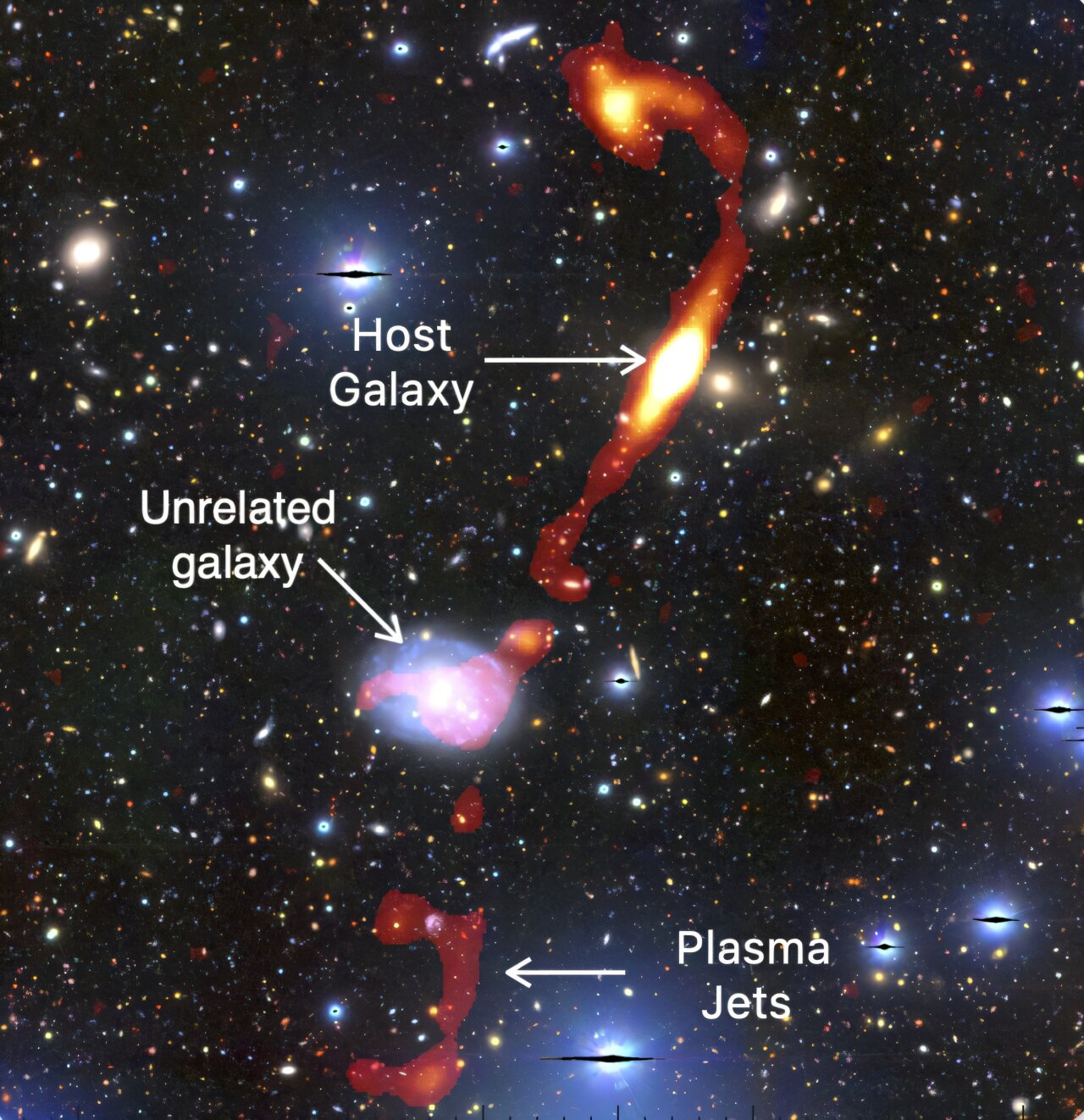
Astronomers have discovered an extraordinary new giant radio galaxy with plasma jets 32 times the size of our Milky Way.

Fast radio bursts (FRBs) are puzzling phenomena because their details are so difficult to resolve. Astronomers added another piece to the puzzle with the detection of an FRB that seems to originate in a dead galaxy.

MIT astronomers observed flashes of X-rays coming from a supermassive black hole at a steadily increasing clip. The source could be the core of a dead star that's teetering at the black hole's edge.

Taking advantage of a cosmic "double lens," astronomers resolved more than 40 individual stars in a galaxy so far away its light dates back to when the universe was only half its present age.
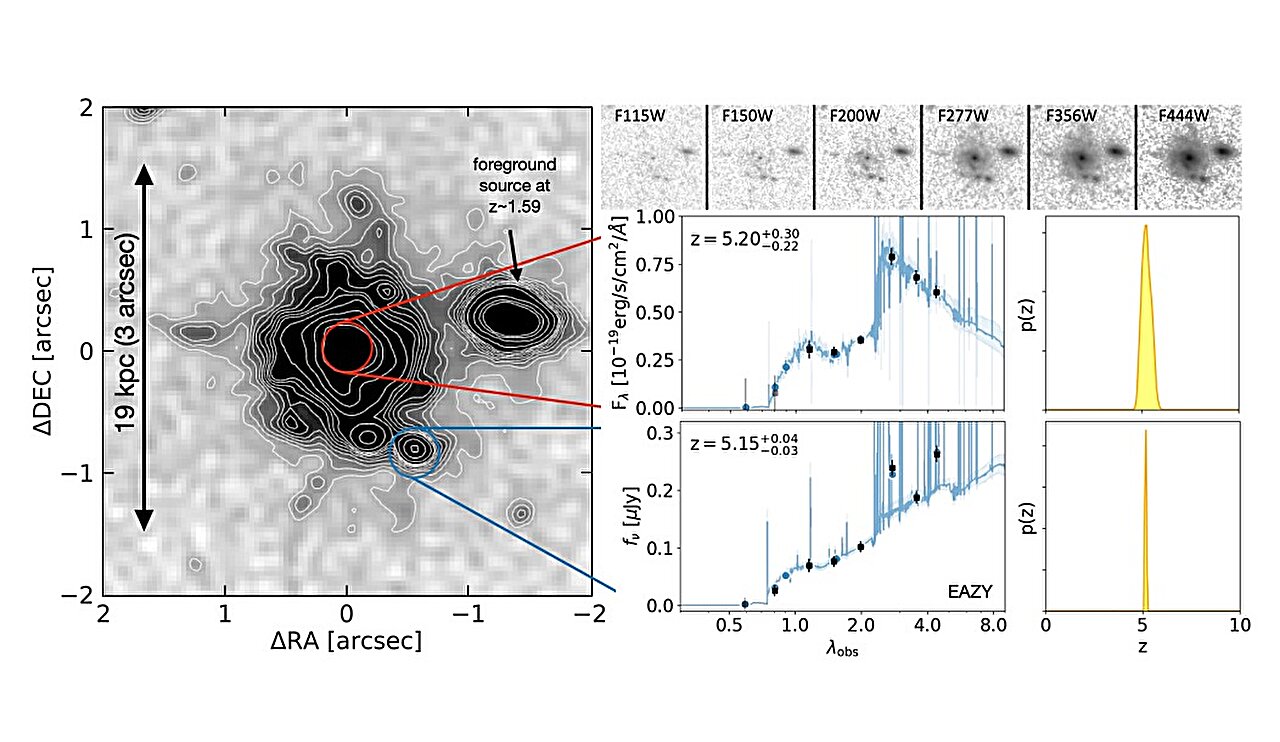
Using the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), an international team of astronomers has detected a new grand-design spiral galaxy as part of the PANORAMIC survey.