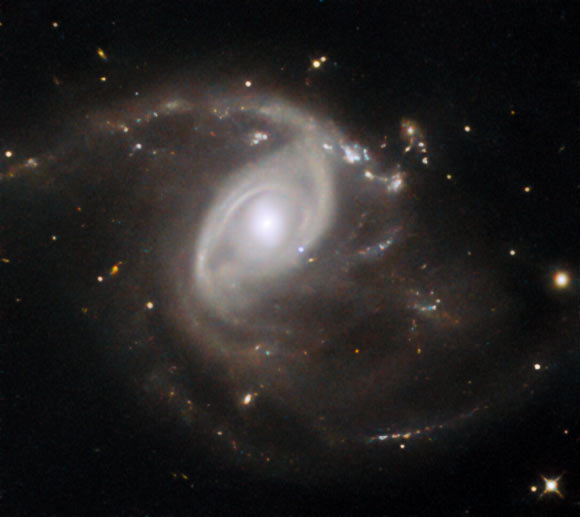

NASA has released a beautiful photo taken by the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope of the spiral galaxy LEDA 22057.

Using the Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers homed in on a quasar called 3C 273, some 2.5 billion light-years from Earth.

The James Webb Space Telescope is celebrating three years from its launch. Its discoveries have already changed our understanding of the early universe.

There's a supermassive black hole lying in the centre of galaxy NGC 5084, and astronomers have discovered that the black hole appears to be tipped over on its side.

Galaxy clusters -- the big cities of the universe -- are home to many giant elliptical galaxies that have completed their growth and are not forming stars. However, it is still unclear what has shut down star formation.

Astrophysicists find the birth sites of gigantic elliptical galaxies which they say gives new clues about how they were formed. The galaxies look like bulging footballs and how they were created remains a mystery to scientists -- until now.

The Milky Way is only one system and may not be typical of how other galaxies formed. That's why it's critical to find similar galaxies and compare them
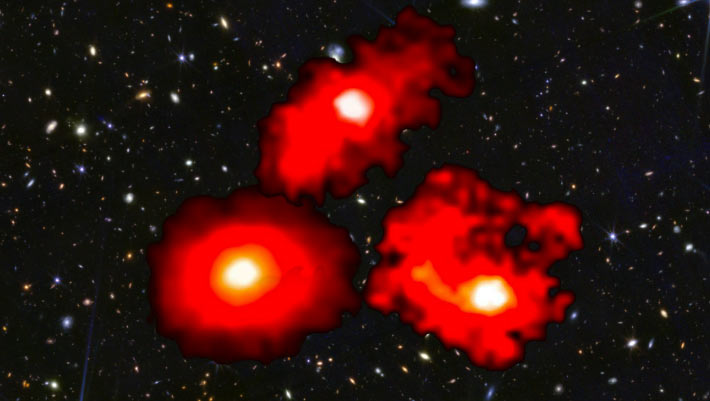

Astronomers using the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope have discovered three ultra-massive galaxies -- nearly as massive as our own Milky Way Galaxy - already in place within the first billion years after the Big Bang.

Our star resides in the Local Hot Bubble (LHB). Now a team of astronomers has mapped the bubble, revealing the presence of a mysterious tunnel pointing towards the constellation Centaurus.
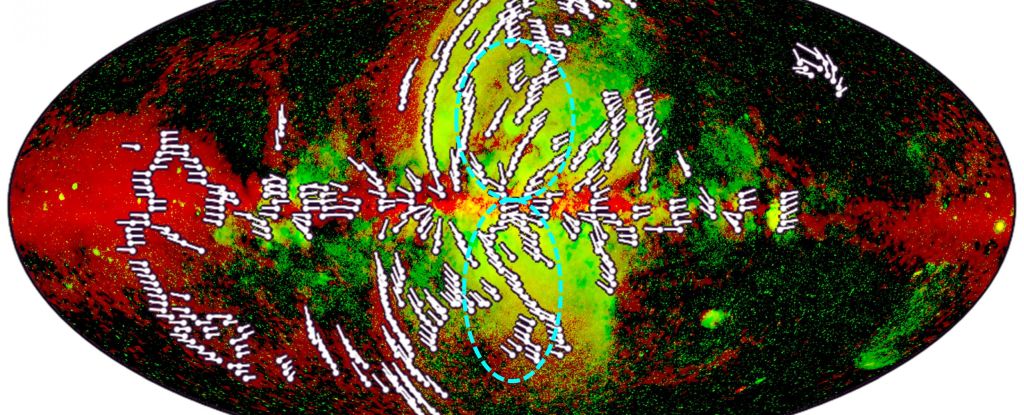
By studying hot gas glowing in circumgalactic space, astrophysicists have found evidence of enormous magnetic fields that wind through and around our galaxy's dark matter 'halo'.

A newly discovered cluster-scale strong gravitational lens, with a rare alignment of seven background lensed galaxies, provides a unique opportunity to study cosmology.

The latest discovery used the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) to spot three bright, visible light 'hot spots' deep inside a pair of colliding galaxies.

For years, astronomers thought it was the Milky Way’s destiny to collide with its near neighbor the Andromeda galaxy a few billion years from now. But a new simulation finds a 50% chance the impending crunch will end up a near-miss.

Two giant clusters of galaxies observed in the process of colliding are going so hard that their dark matter has basically detached from normal matter and flown ahead.

In a remarkable discovery, astronomers have found a disc around a young star in the Large Magellanic Cloud, a galaxy neighbouring ours. It’s the first time such a disc has ever been found outside our galaxy.