
Over the past three decades, there has been a startling increase in the prevalence of obesity across the U.S., at least doubling in adult men and women since 1990.

Knowing how high-potency cannabis alters gene activity may bring us closer to understanding why some users develop psychosis.
Approximately one-third of children and teens worldwide are nearsighted — a figure that's more than three times higher than it was in 1990, according to a UK study.

A study of more than 700 counties across multiple U.S. states found a link between childhood leukemia and levels of decaying radon gas, including those lower than the federal guideline for mitigation.

The study sheds light on the widespread human exposure to food contact chemicals that could be detected in human samples, such as urine, blood, and breast milk.

A new study has found more than 1,000 human infant deaths resulted from the loss of bats in North America – which led to increased pesticide use, a grim reminder of how vital this much-maligned mammal is to our wellbeing.

A research team discovered that obesity causes chronic changes in the brain which affects sperm count.

The consumption of ultra-processed foods (UPFs) may be associated with insomnia experienced by an estimated one third of adults, a report has revealed.
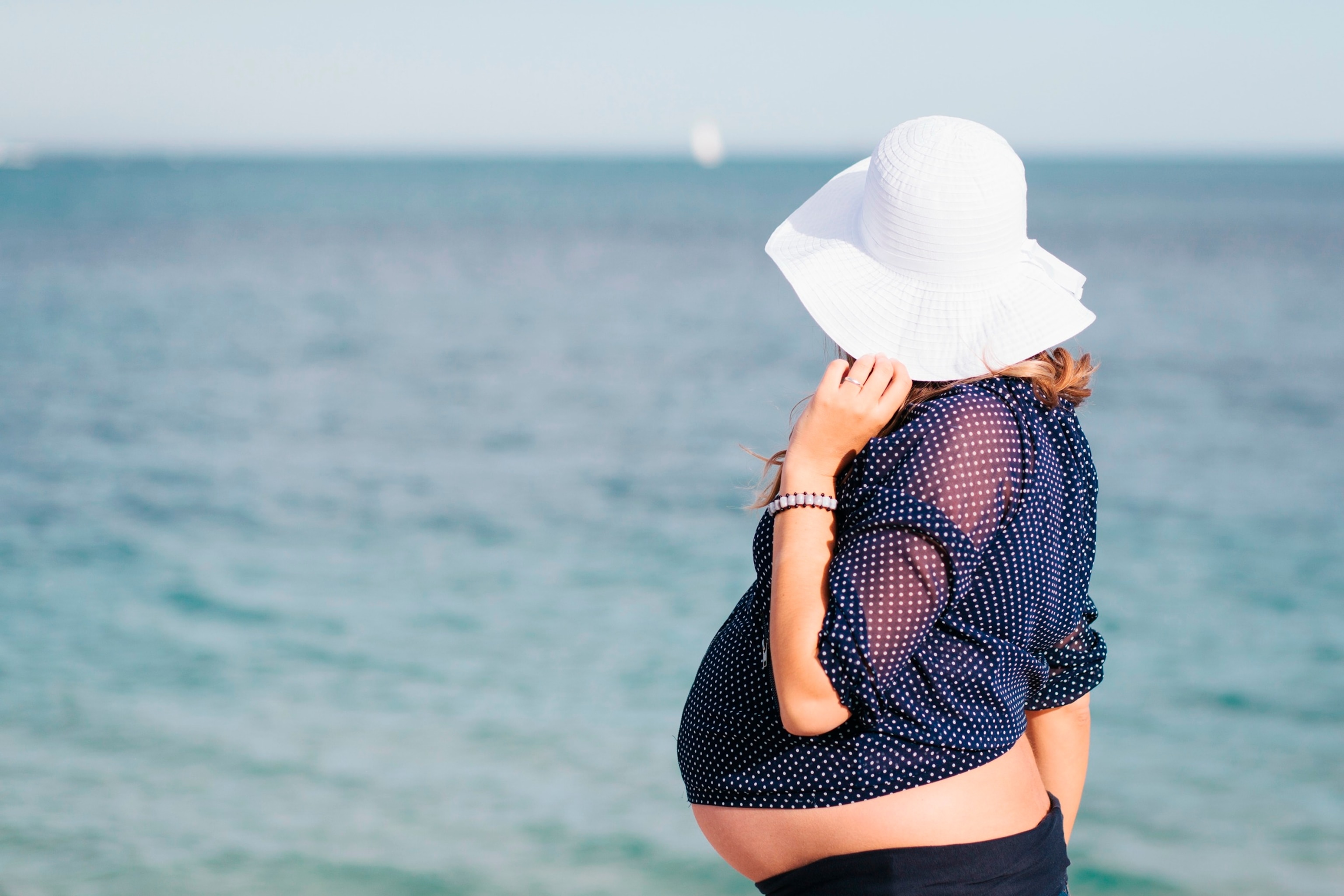

As the world braces for another summer of extreme heat, following the record-setting 2023 season, a recent study has acutely linked heat waves to the rate of early births among pregnant women.
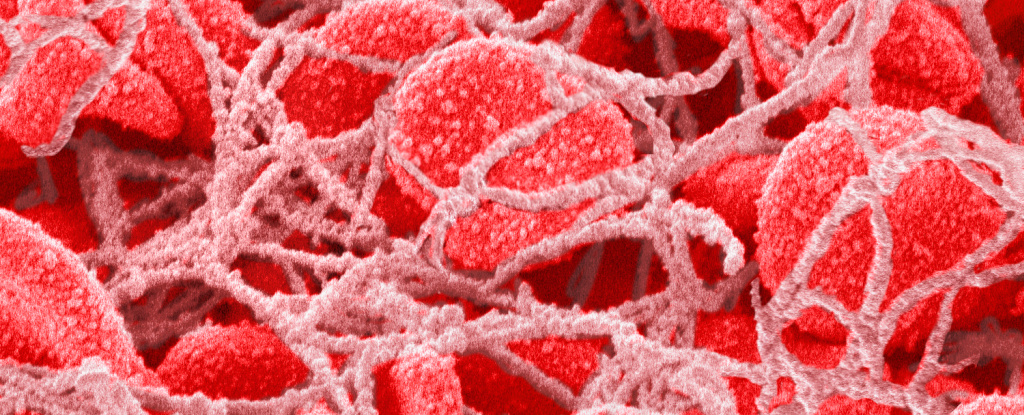
Now, a new study from researchers in China reports finding microplastics in blood clots surgically removed from arteries in the heart and brain, and deep veins in the lower legs.

Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) concentrations in cannabis products have increased over the years, from around 2%-4% to 15%-24% now. The impact of high-potency products must be taken seriously.

Research shows inhaled plastic particles deposit in the respiratory system, affecting health based on size, shape, and breathing rate.
The findings reveal that carbon dioxide (CO2) levels play a critical role in the lifespan and transmission of airborne viruses.
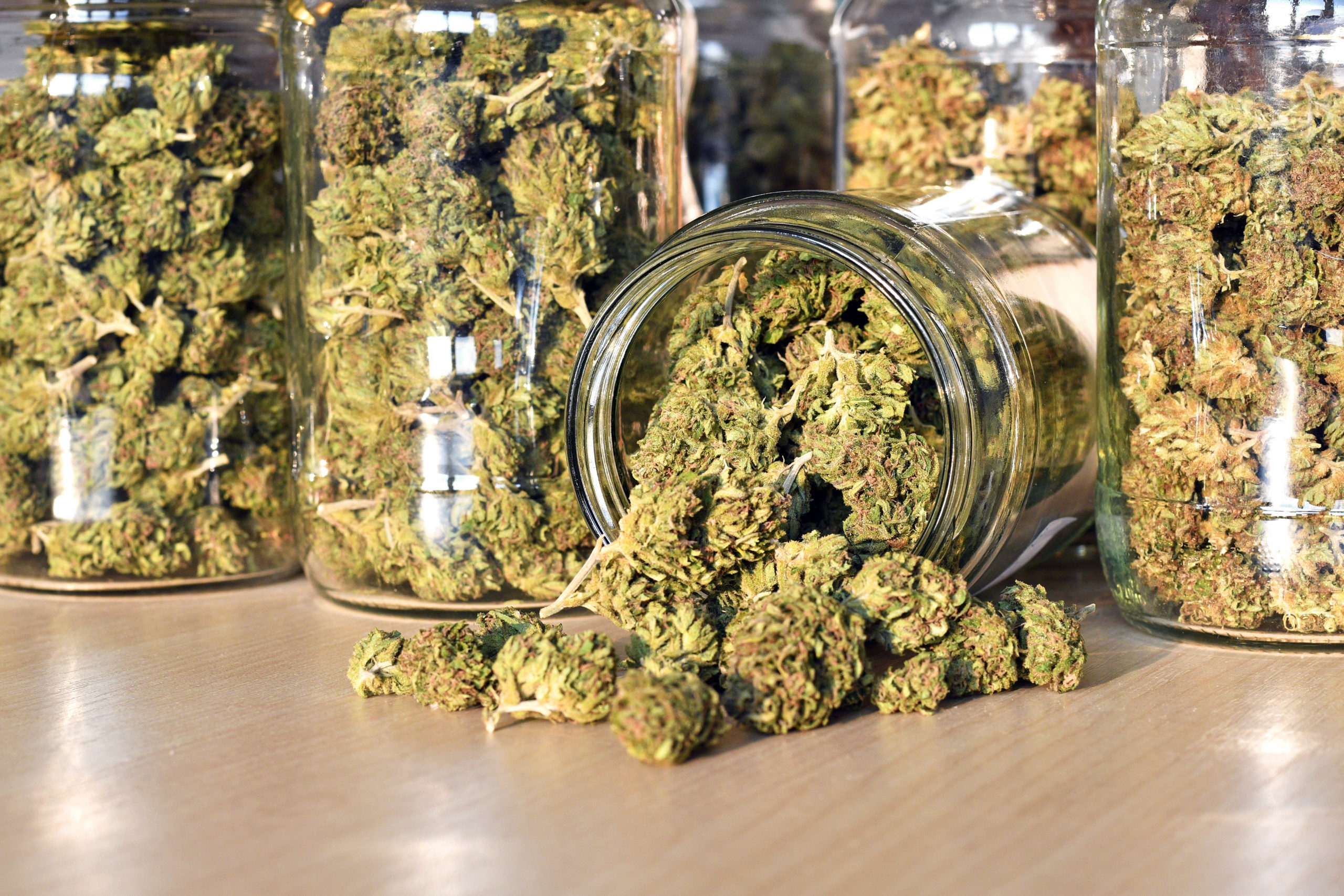

Recent and long-term marijuana use is linked to changes in the human genome, a new study has found.

Chemicals found in common household disinfectants, glues, and furniture textiles could damage supporting cells in the brain during critical stages of their development, a new study based on human cell cultures and mice has found.