
An international scientific team has redefined our understanding of archaea, a microbial ancestor to humans from two billion years ago, by showing how they use hydrogen gas.
Geoscientists show that rocks from the Isua Supracrustal Belt in West Greenland have experienced three thermal events throughout their geological history.
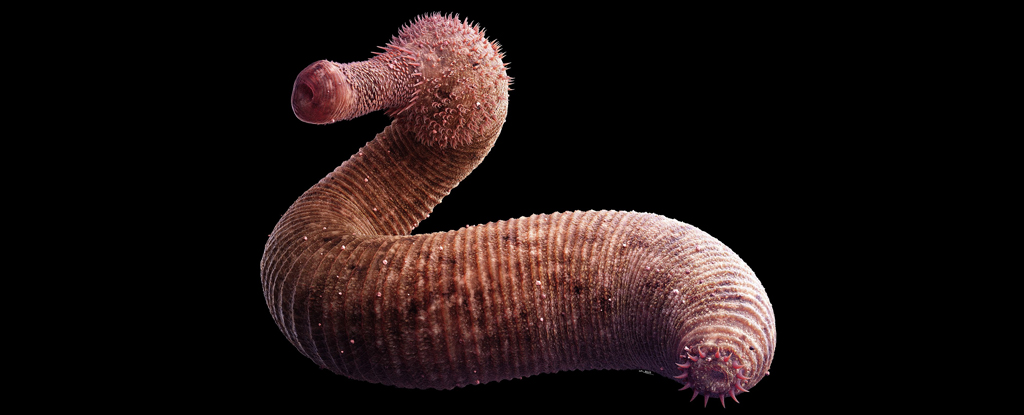
Prehistoric marine worms may have made an outsized contribution to the Great Ordovician Biodiversification Event.
New research finds Earth's surface was first sprinkled with fresh water some 4 billion years ago, a whole 500 million years earlier than previously thought.
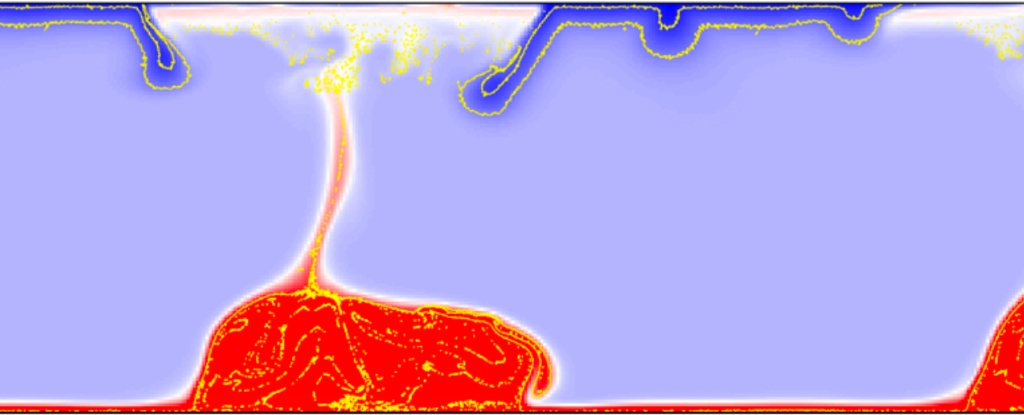
On the scale of cataclysmic events, the whomping impact of a Mars-sized object that crashed into Earth some 4.5 billion years ago ranks pretty highly: thought to have set in motion the movement of our planet's fractured, rocky crust.
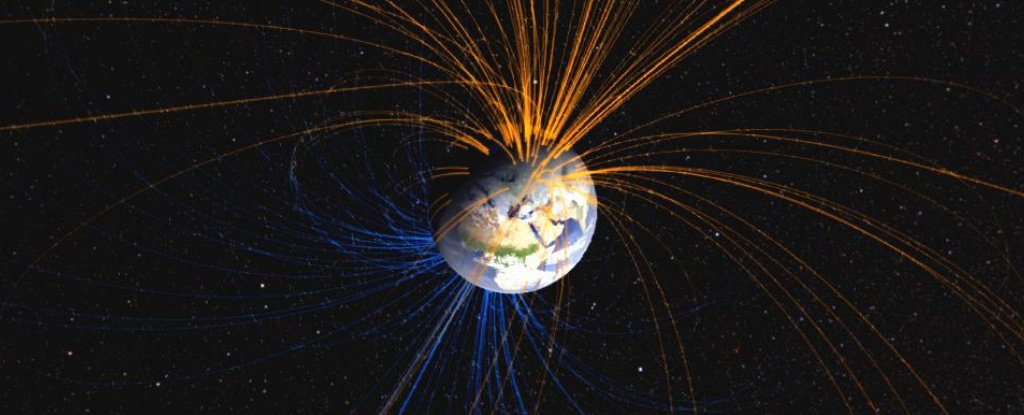
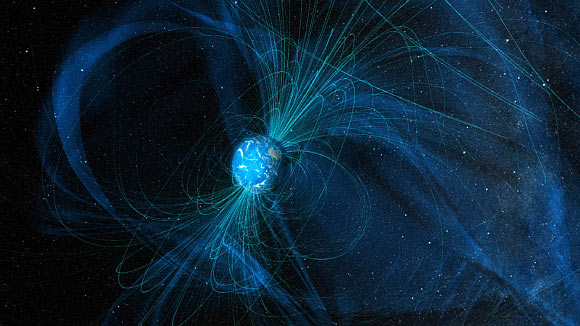
Earth's magnetic field nearly collapsed some 590 million years ago, presumably putting life on the planet's surface at risk of a rise in cosmic radiation.
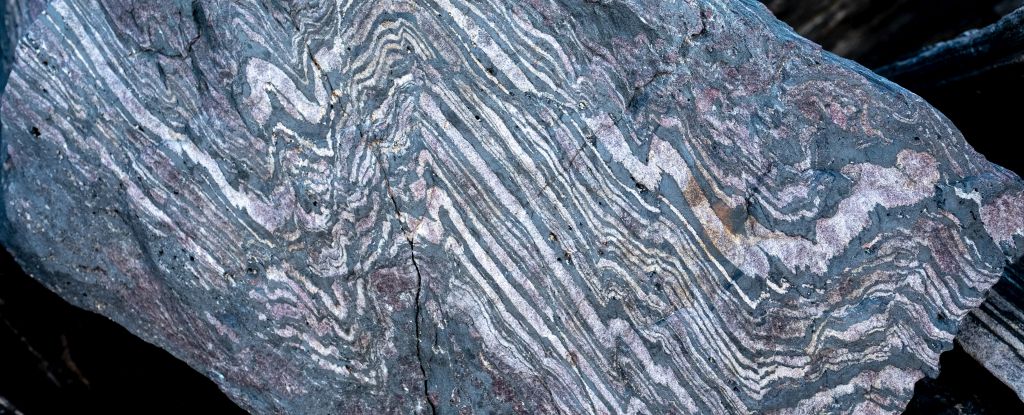

Rocks that formed some 3.7 billion years ago in the early Archean have given us the earliest glimpse yet of Earth's magnetic field.

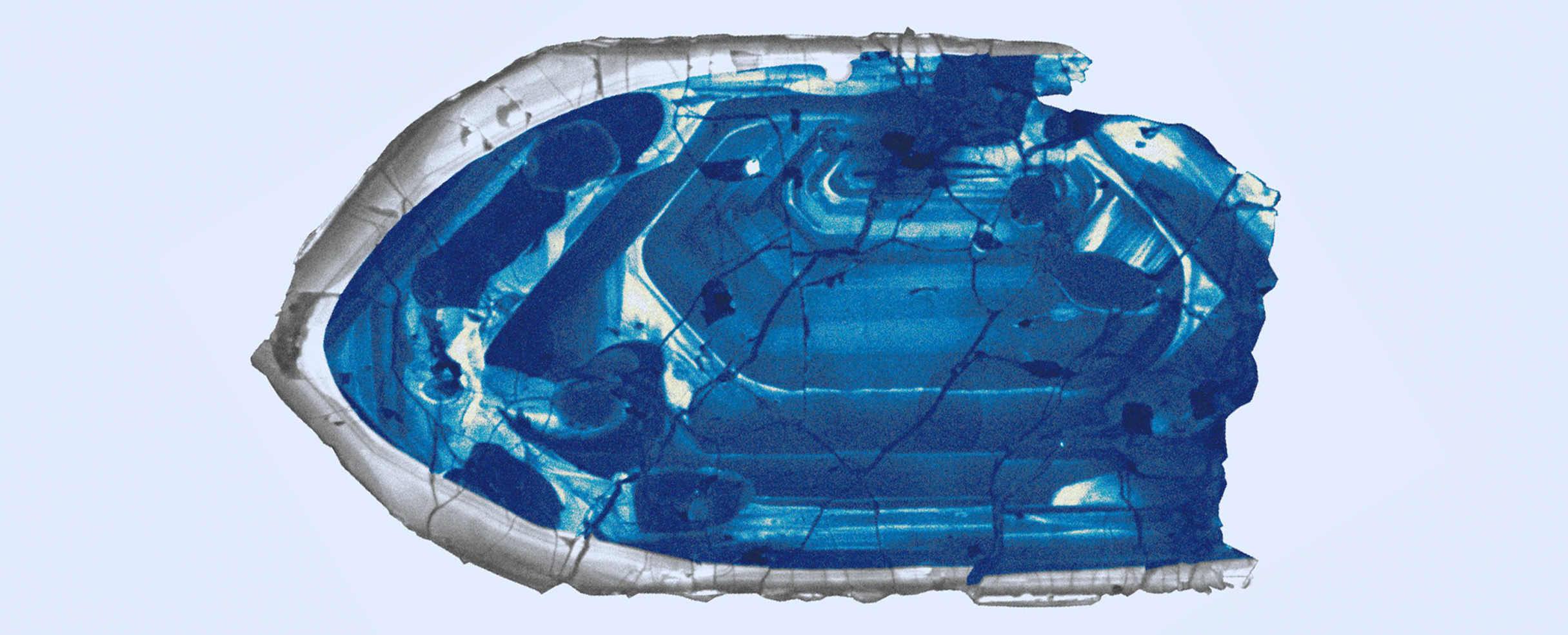
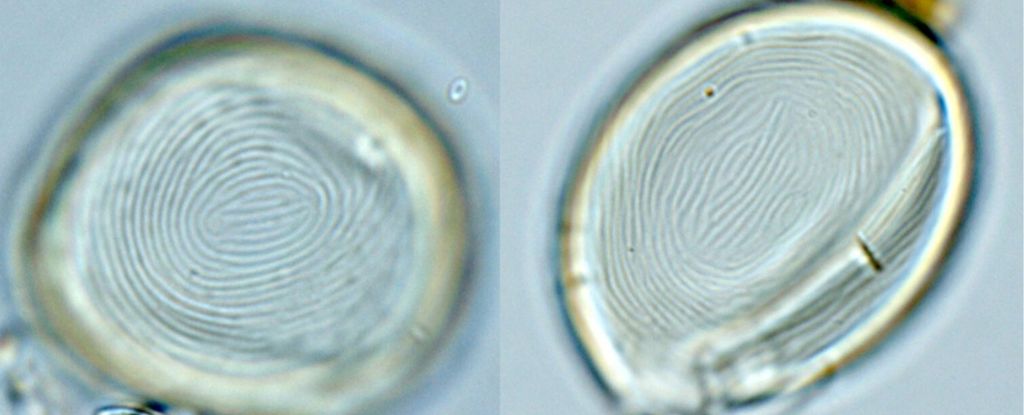
Encased inside some of the oldest rocks on Earth are previously overlooked nanocrystals that tell a story about how life might have emerged.

The research team investigated how the emergence of the first living systems from inert geological materials happened on Earth more than 3.5 billion years ago.

It is neither animal, vegetable, nor mineral. It's not even a bacterium or fungi. It's called a Euglenid – and it's a weird fusion of a bunch of different living things.

Long ago, an alien planet crashed into Earth – causing a collision so big the debris formed the Moon and left mysterious remnants lodged deep in the Earth’s mantle.

Scientists now find that the earliest leafy plants did not have Fibonacci spirals, contradicting our initial assumptions on plant evolution.

New findings suggest the water originates from the space between solar systems, billions of years before the birth of our sun.

Microscopic fragments of environmental DNA were found in Ice Age sediment in northern Greenland. Researchers discovered the fragments that are one million years older than the previous record for DNA.

Australian researchers have discovered evidence of an approximately four billion-year-old piece of the Earth’s crust that exists beneath the South-West of Western Australia