
Killer cosmic rays from nearby supernovae could be the culprit behind at least one mass extinction event, researchers said, and finding certain radioactive isotopes in Earth.

Astronomers have found two objects that, added to a strange object discovered in 2018, constitute a new class of cosmic explosions. They share some characteristics with supernova explosions and gamma-ray bursts.

Astronomers have spotted the brightest and most energetic supernova ever recorded. The event, known as SN2016aps, may have been the result of two stars merging and then exploding.

Follow the story of golden atoms from their birth in stellar explosions via incorporation into formation of our planet to their coming together in a golden nugget and appearance in the Earth's crust.

The star will go supernova at the end of its life, but that’s not projected to happen for tens of thousands of years or so. However, the great dimming of Betelgeuse continues.

Betelgeuse in constellation of Orion is looking markedly faint, the faintest it has been for the 21st century. Betelgeuse is a nearby supernova candidate. Its transformation into Type II supernova could occur 100,000 years from now… or tonight.

Data obtained by VLT showed evidence of massive stars bursts billions of years ago in the galaxy’s center. The more recent burst was so intense that resulted in 100,000 supernova explosions. These findings are inconsistent with our notions that stars formed continuously in our galaxy.

Japanese astronomers have captured images of an astonishing 1800 supernovae. 58 of these supernovae are the scientifically-important Type 1a supernovae located 8 billion light years away and are known as ‘standard candles’ in astronomy.

Many supernovae show a gradual increase in the light they put out. But for ASASSN-18bt, you could clearly see there's something unusual and exciting happening in the early times - an unexpected additional emission.

Supernovae happen all the time, but this one was different. "Cow," as astronomers are calling it, was a massively bright explosion 200 million light years away.

A mysterious cataclysm in a neighboring galaxy was spotted in the sky above Hawaii last week, sending astronomers around the world scrambling to understand the source of the staggeringly brilliant flash.
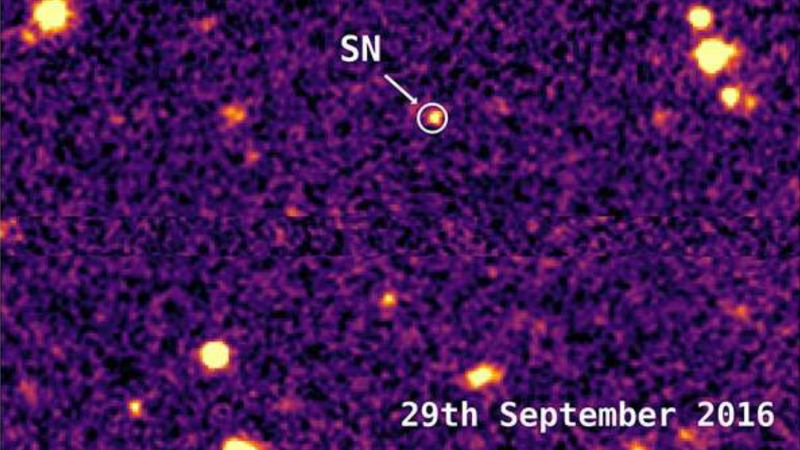
On August 22, 2016, astronomers spotted a superluminous supernova whose light traveled over 10 billion years to reach us.

Contrary to what was expected, a team of astronomers has discovered that kilonova event has been brightening ever since it first appeared.

Astronomers have made a bizarre discovery; a star that refuses to stop shining.

Scientists appear to have found the first X-rays coming from type Ia supernovae.