
Researchers have developed a new platform that makes CRISPR less like a cutting tool and more like a word processor with a search-and-replace function.

Affordable, rapid DNA sequencing is causing a revolution in medicine and healthcare globally, and it's happening now.

Scientists have revealed how a population of 'bad' antibodies in the immune system can provide crucial protection against invading microbes.

US Scientists managed to identify the gene that caused Alzheimer’s disease. Not only that, but they also managed to neutralize the gene so that it did not lead to Alzheimer’s development.

In a review article a prominent scientist calls for more integration between two fields of DNA-based research: genetics and epigenetics.

This month, the Estonian government kicks off a program that aims to collect the DNA of 100,000 of its 1.3 million residents. In return, it will offer them lifestyle and health advice based on their genetics.

Researchers have fused living and non-living cells for the first time in a way that allows them to work together, paving the way for new applications.

Researchers from UK have created the world's first synthetic vaccine.The non-biologic influenza vaccine, which can be delivered orally, could herald a revolution in vaccine delivery.

Inspired by the human eye, researchers have developed an adaptive metalens that is essentially a flat, electronically controlled artificial eye.

Researchers have identified fifteen genes that determine our facial features.

Scientists have successfully produced human kidney tissue within a living organism which is able to produce urine, a first for medical science.

Each scaffold was made by 3D printing a replica of each patient’s ear using a Z Corporation Spectrum Z510 3D printer. The scaffolds were then populated with living cells from each patient.
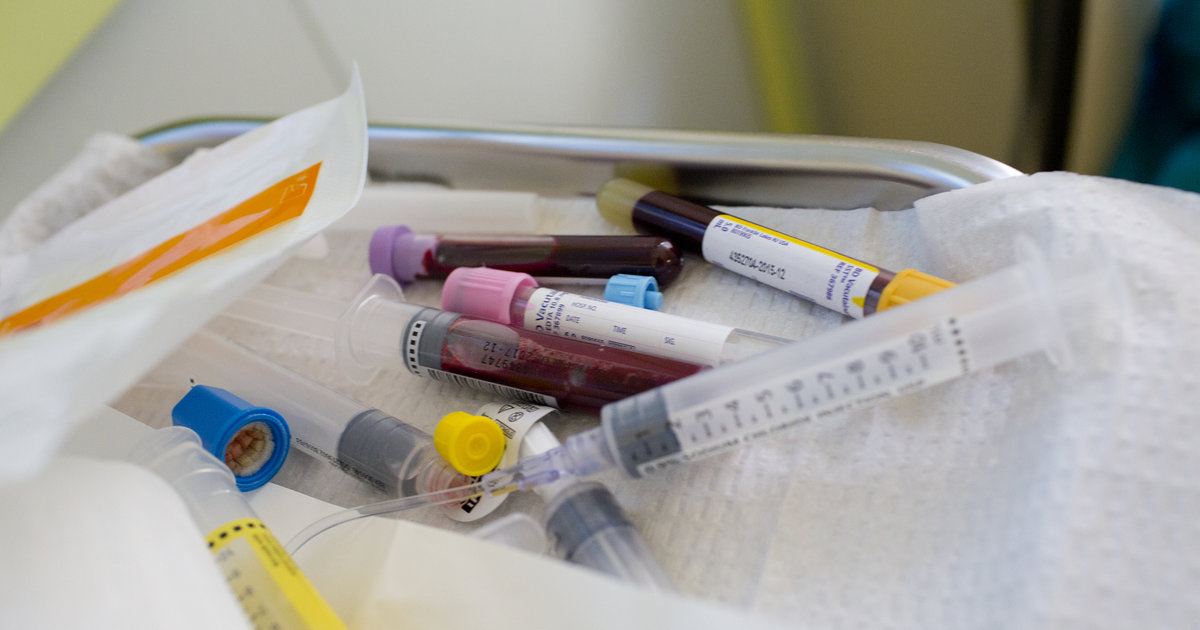
CancerSEEK, which was 70 percent accurate in a human trial, could be major breakthrough in early identification of cancers and where in the body they are located.

A team at Duke University, US has overcome significant hurdles to create the first functioning human muscle from these stem cells.

Researchers refine method of making bio-ink droplets stick to each other, enabling 3D printing of highly complex biological structures with a wide variety of cell types using inkjet printers.